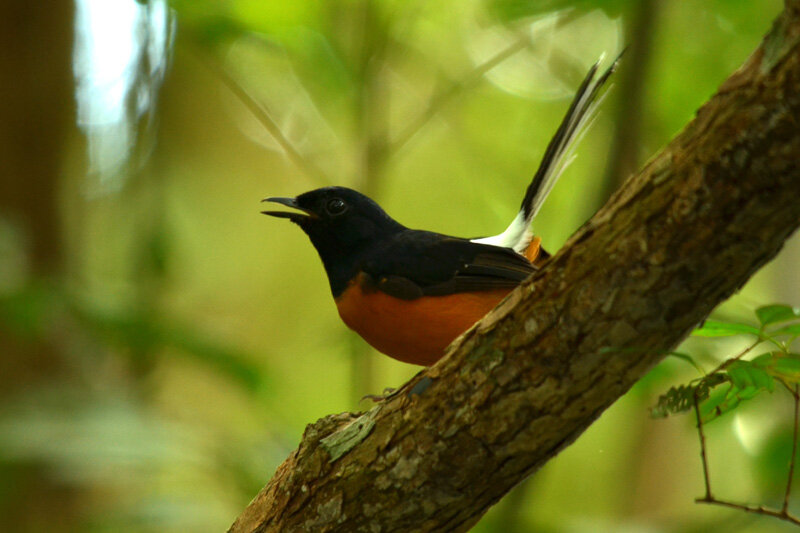
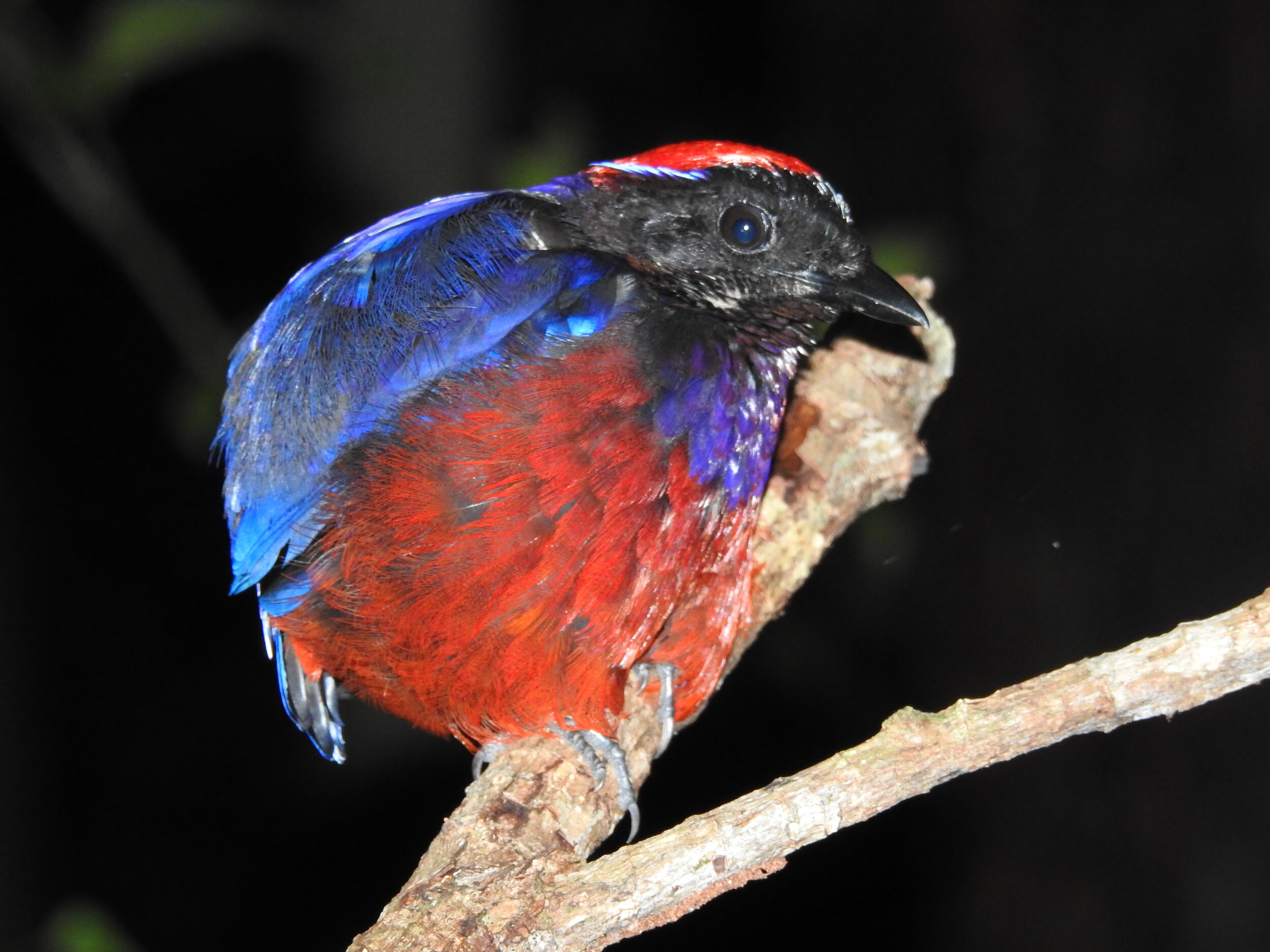
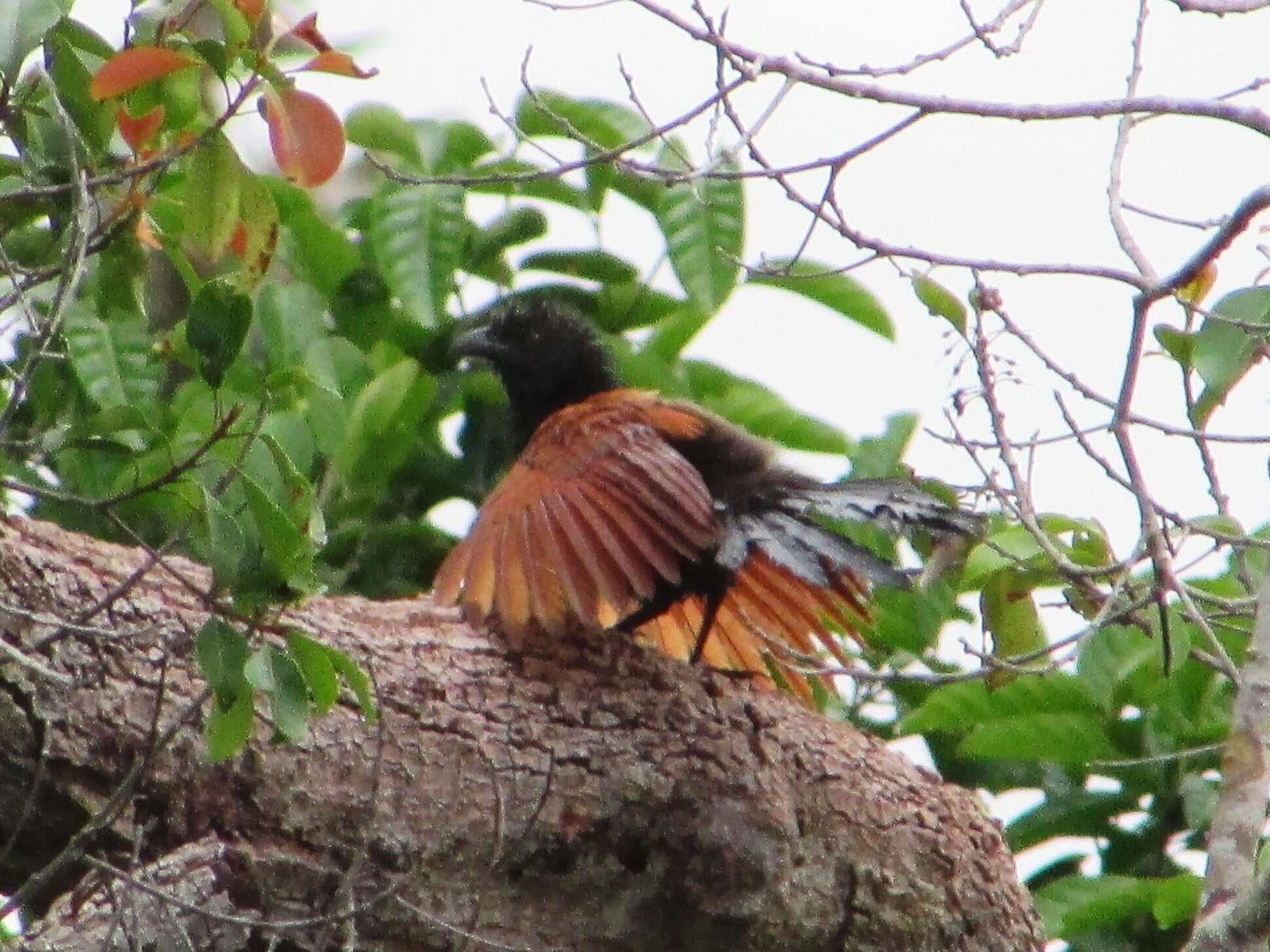
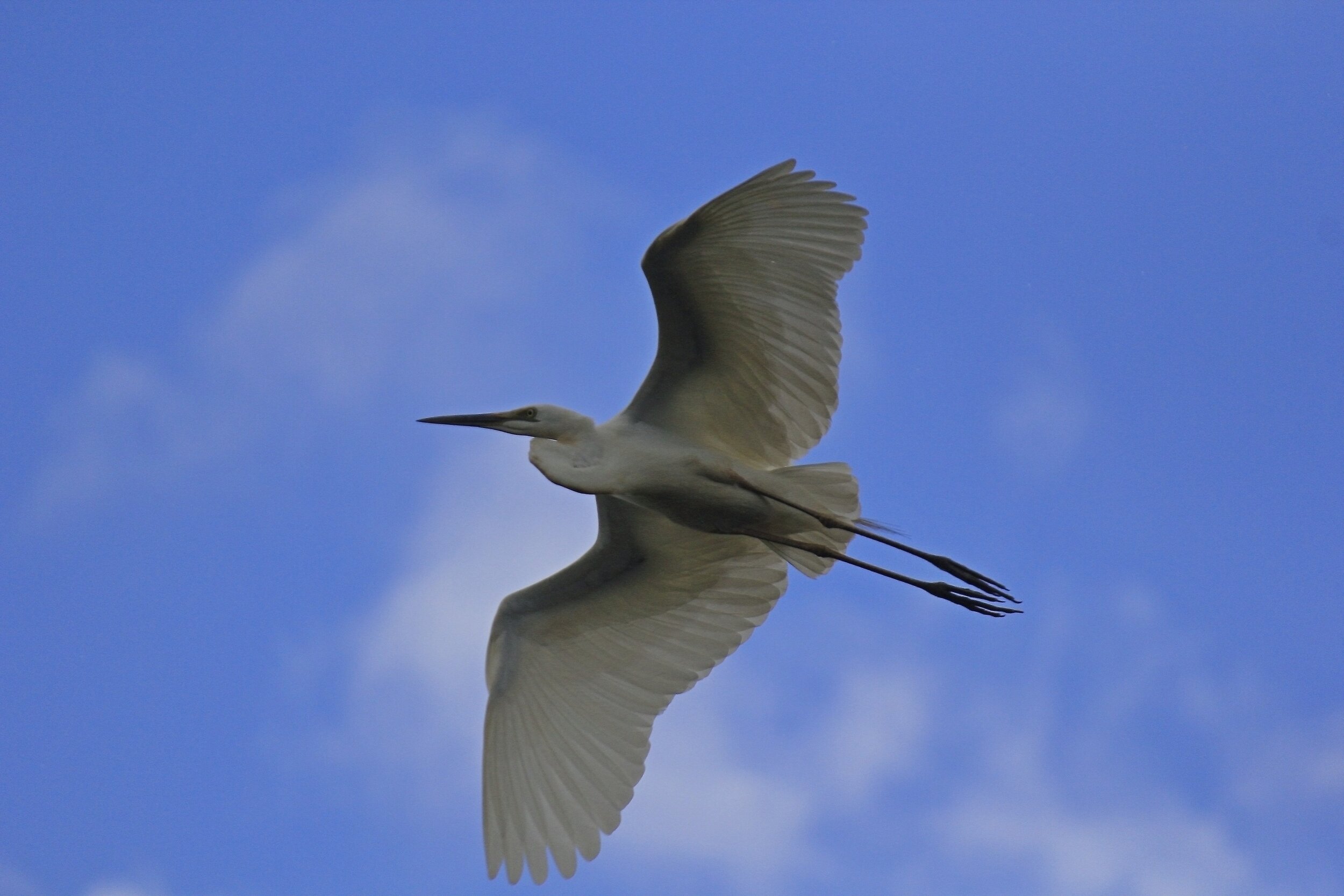
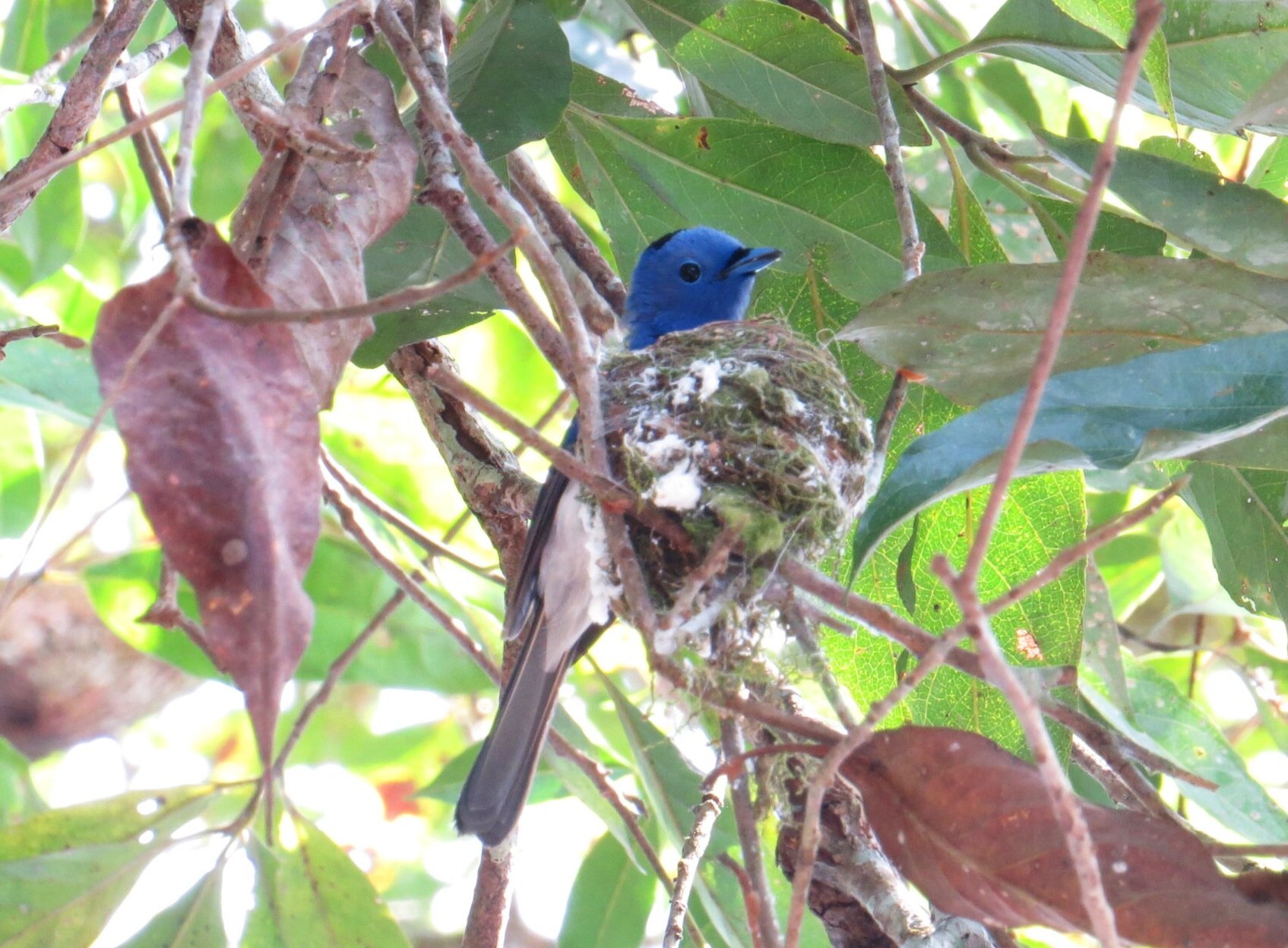
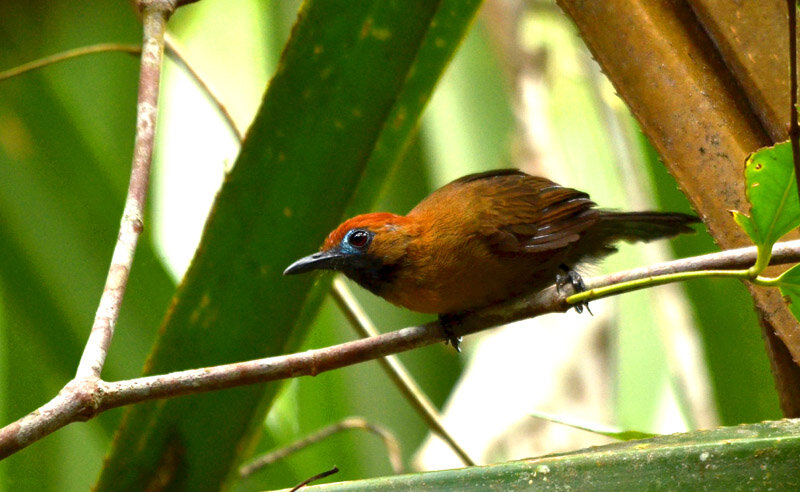
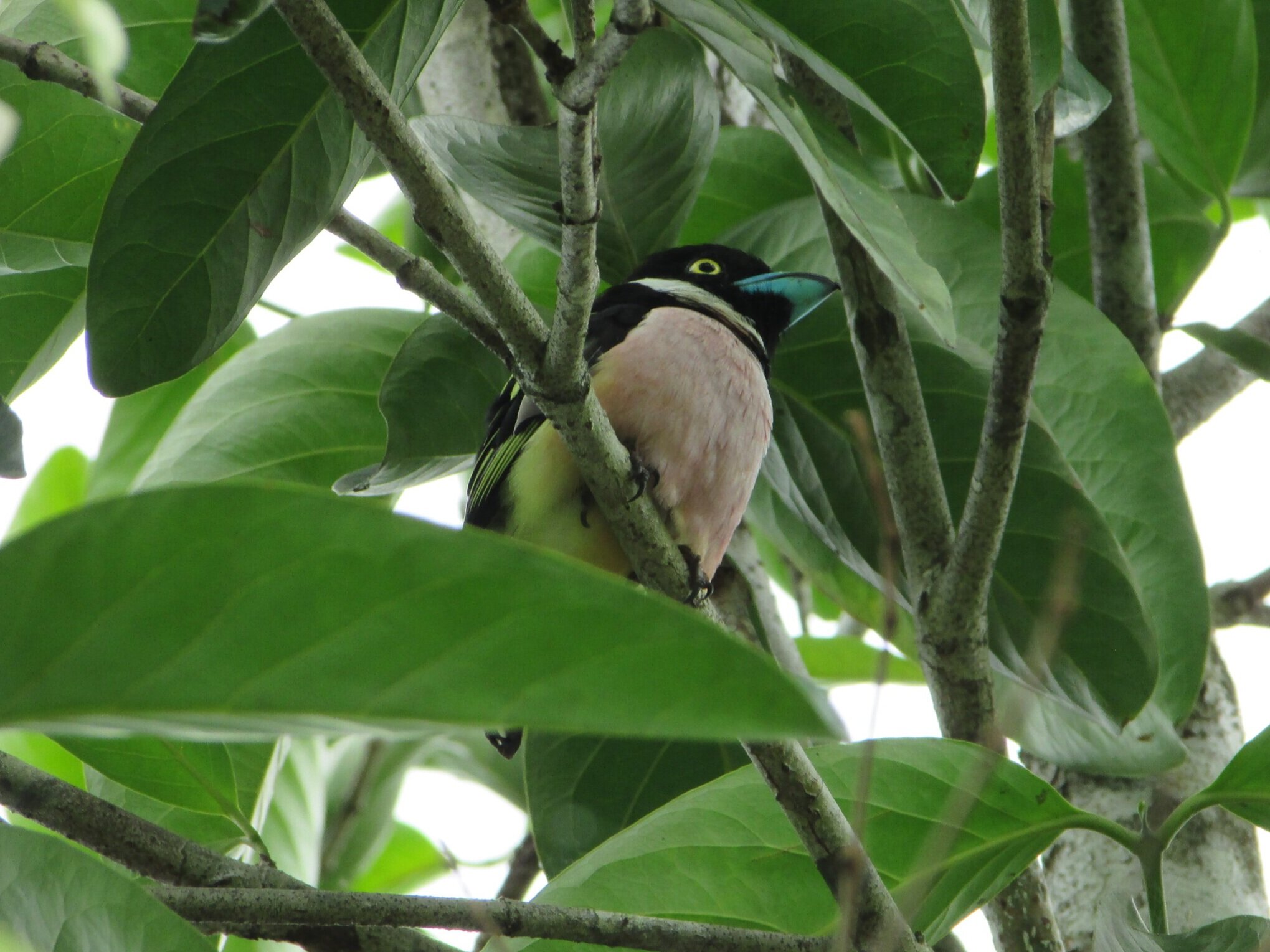
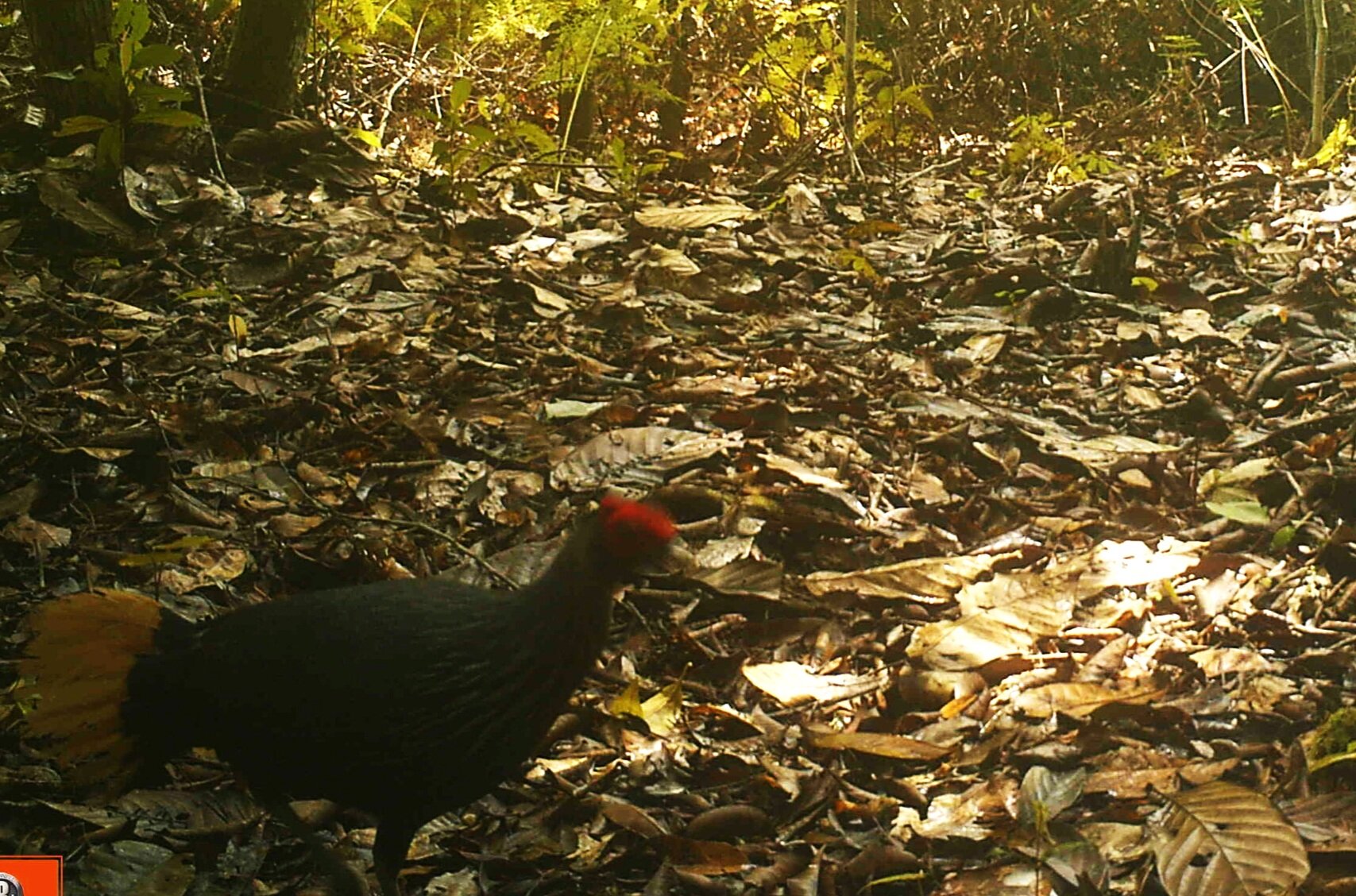
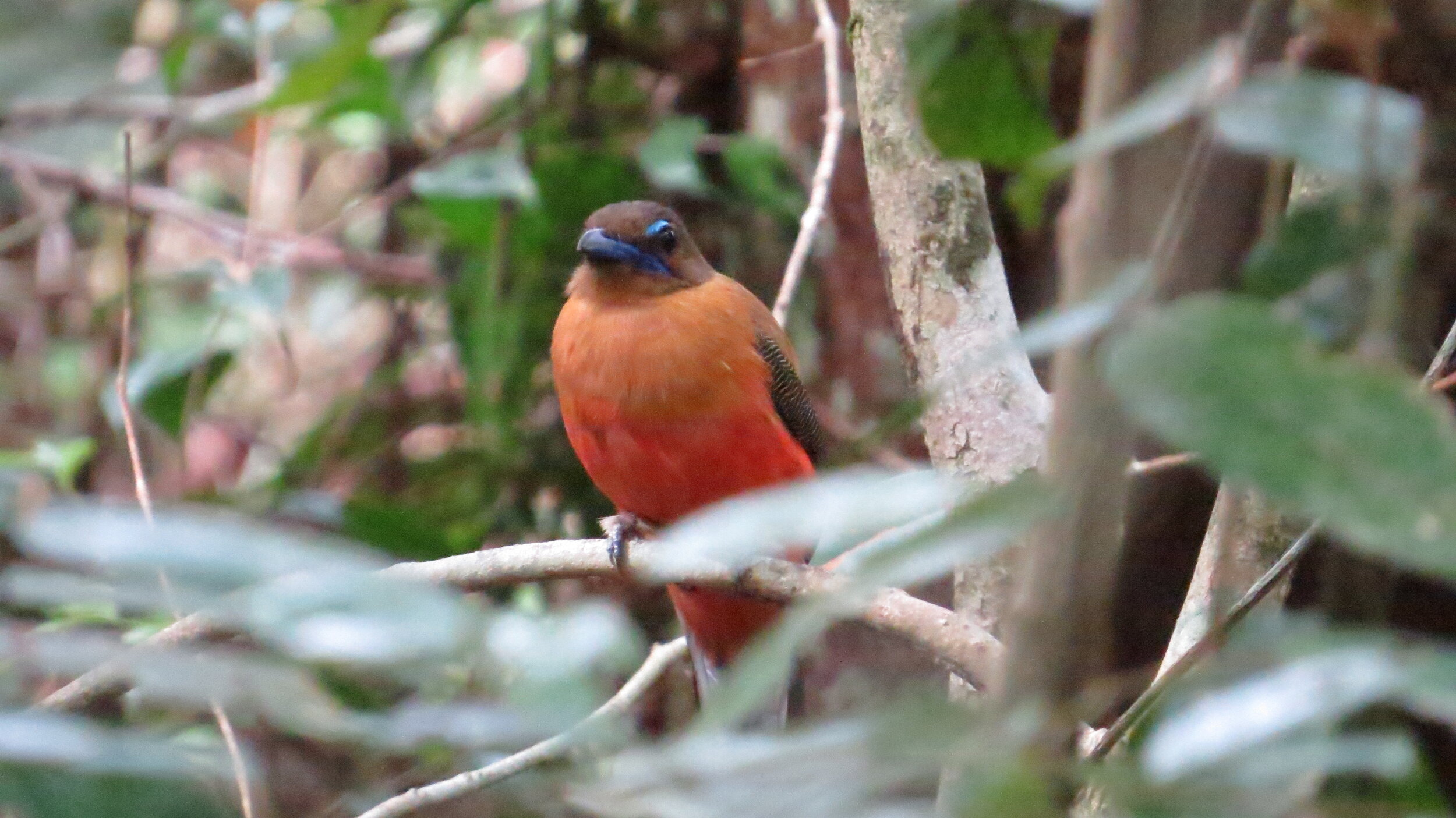
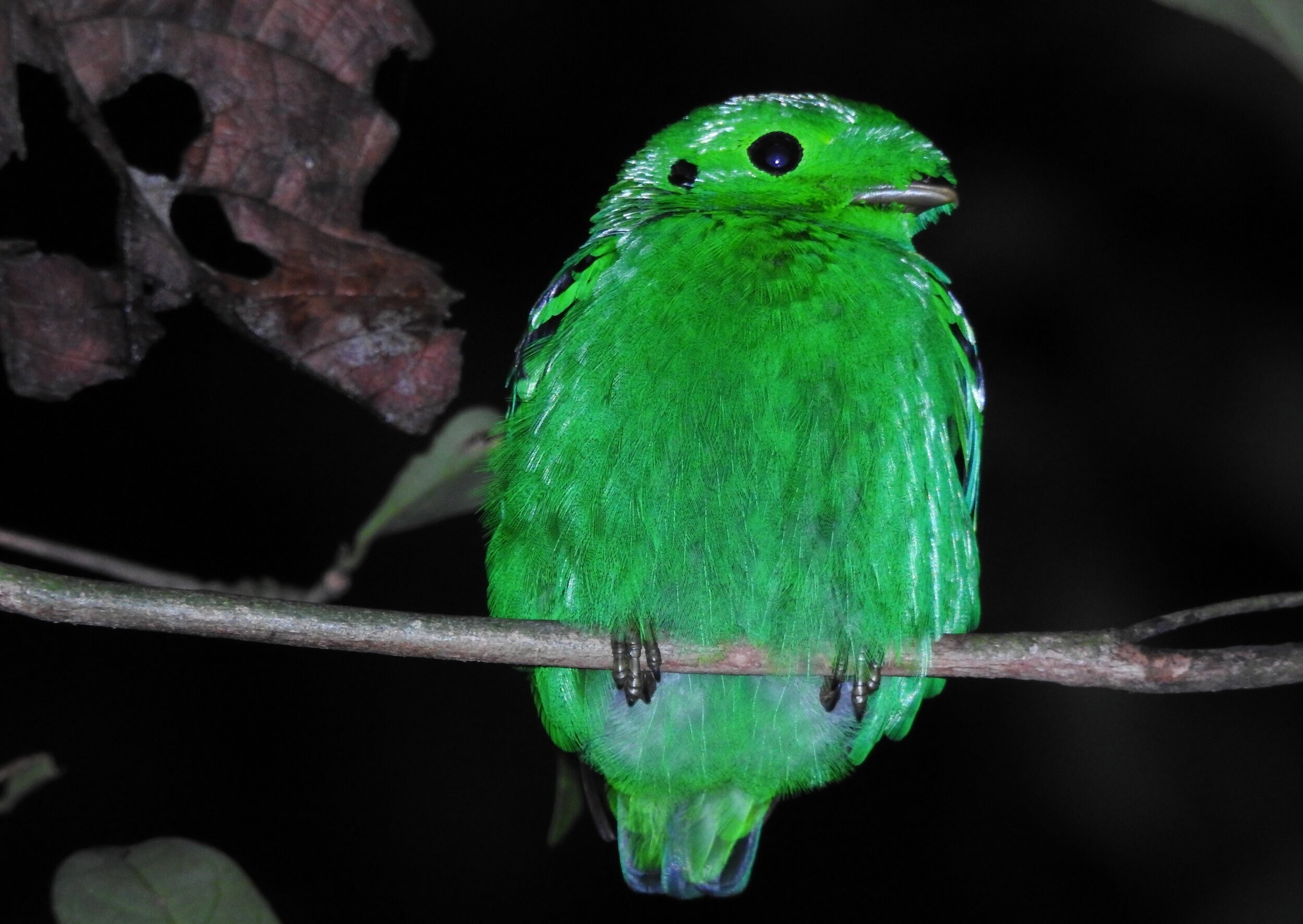
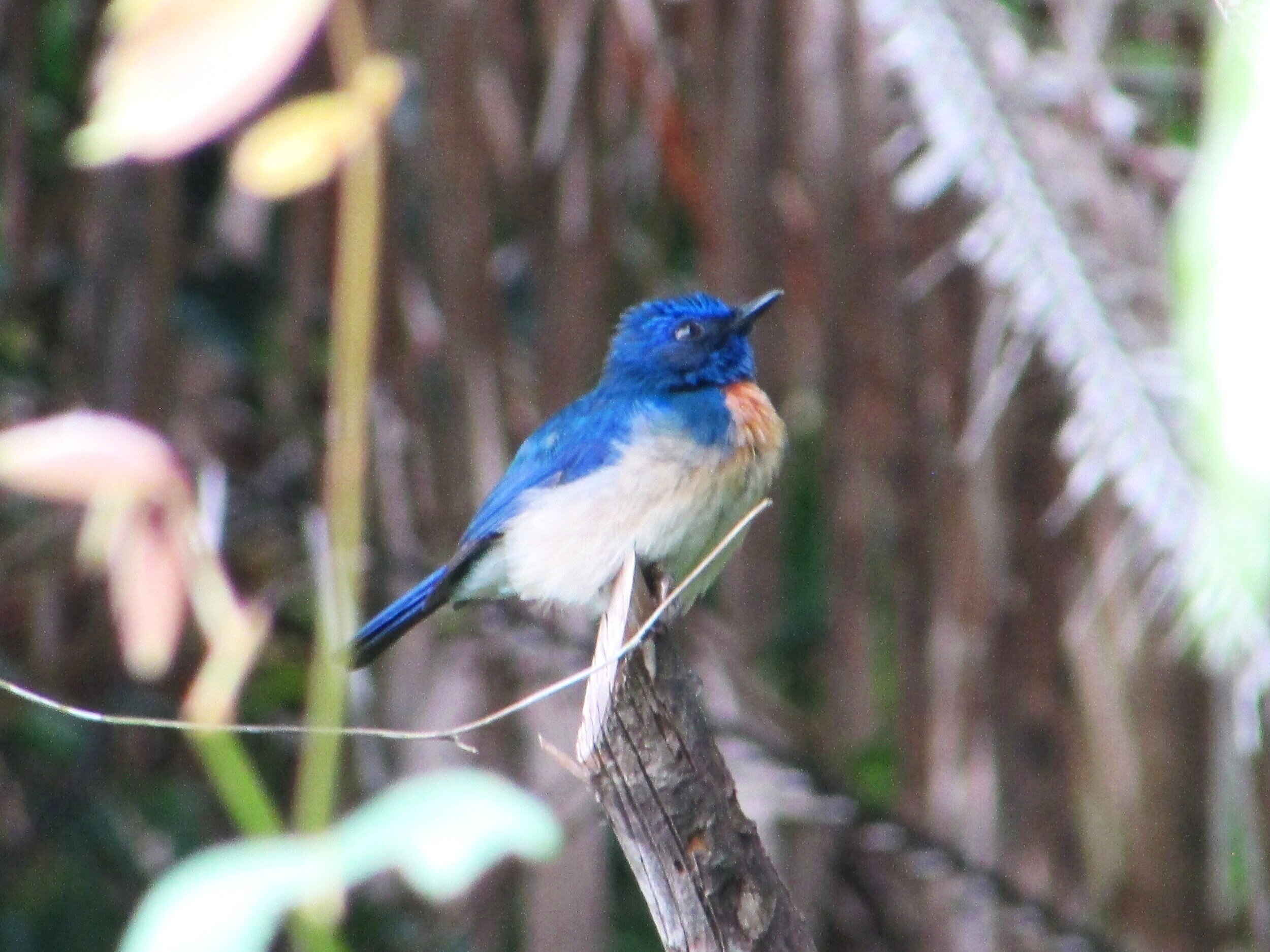
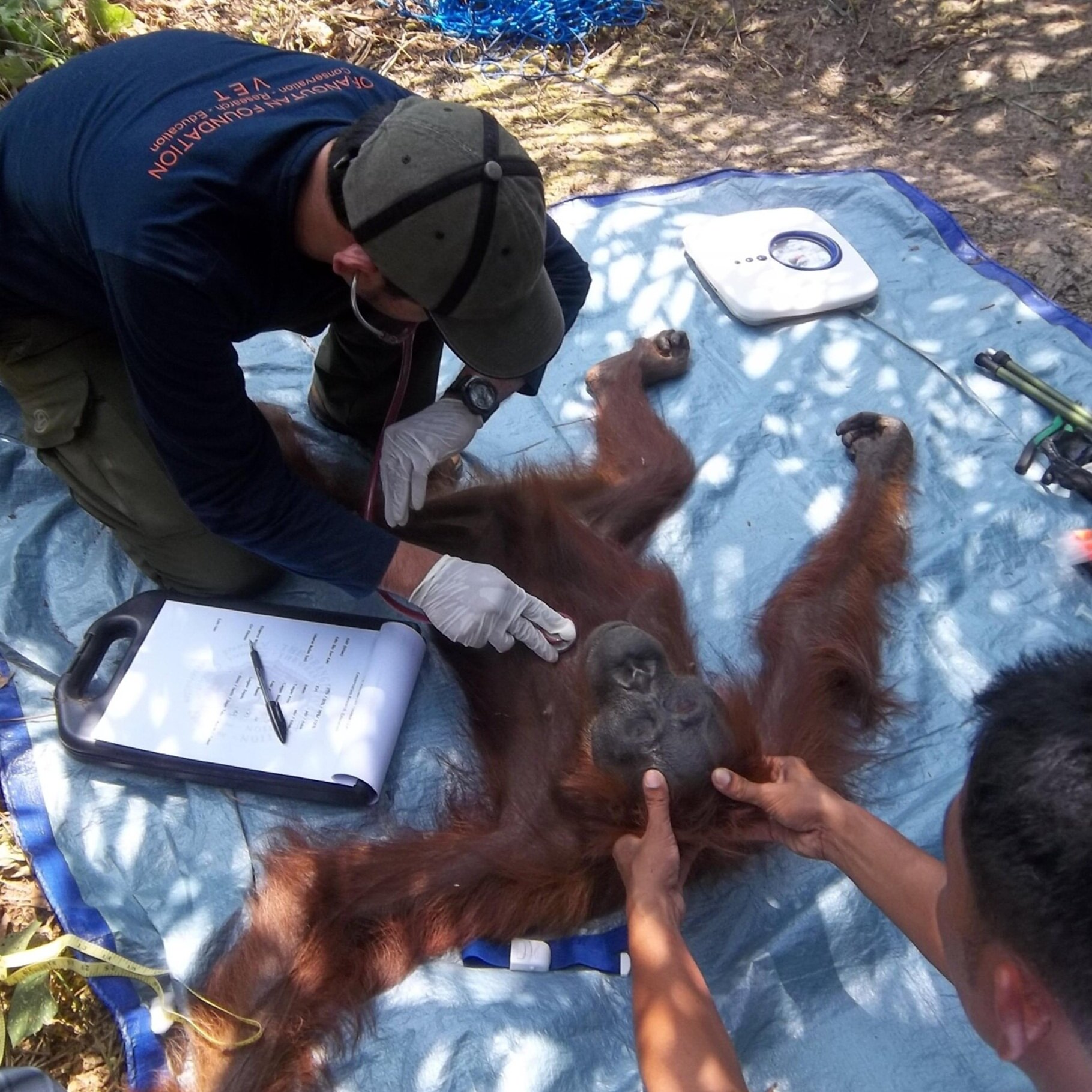
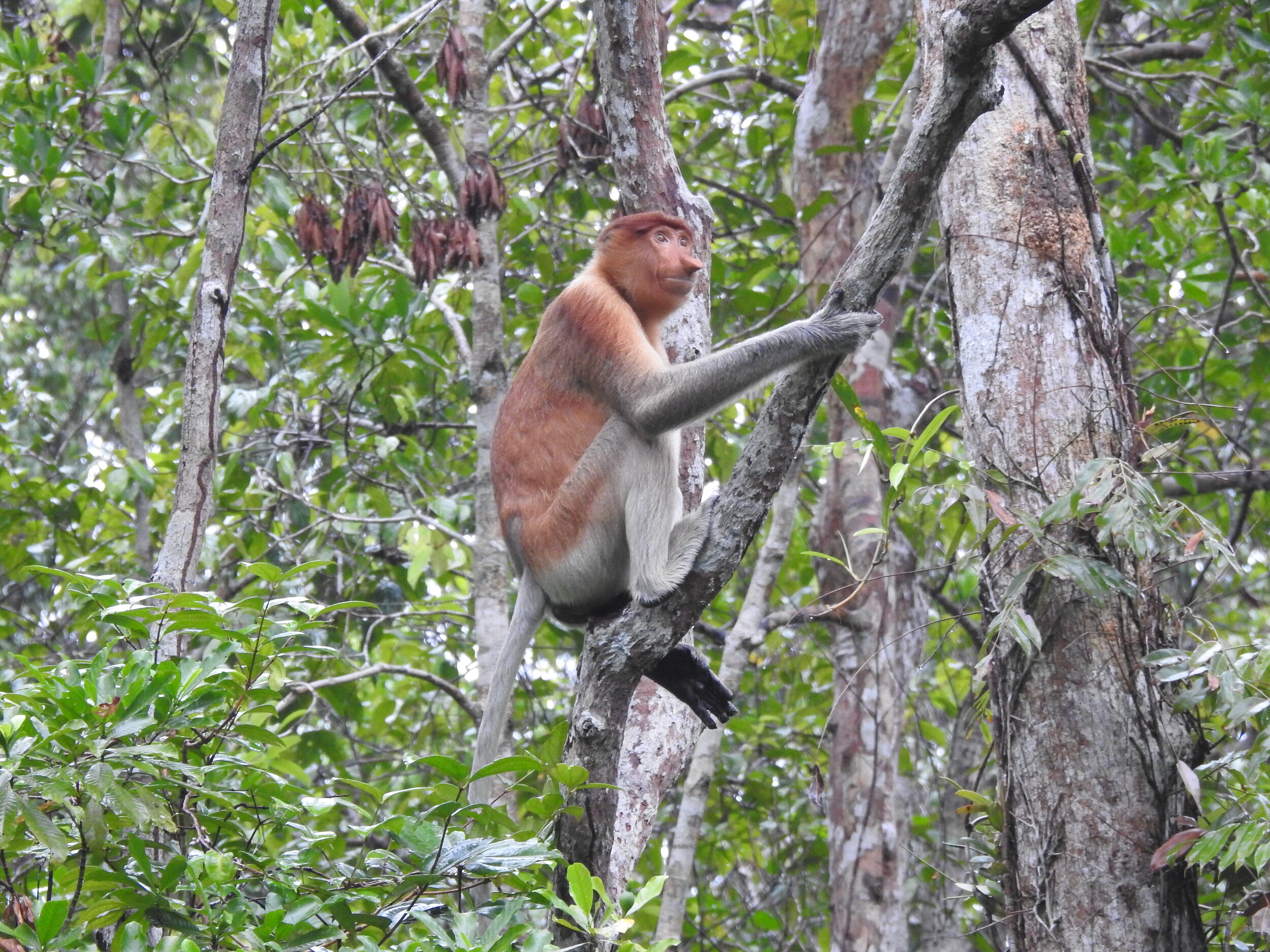
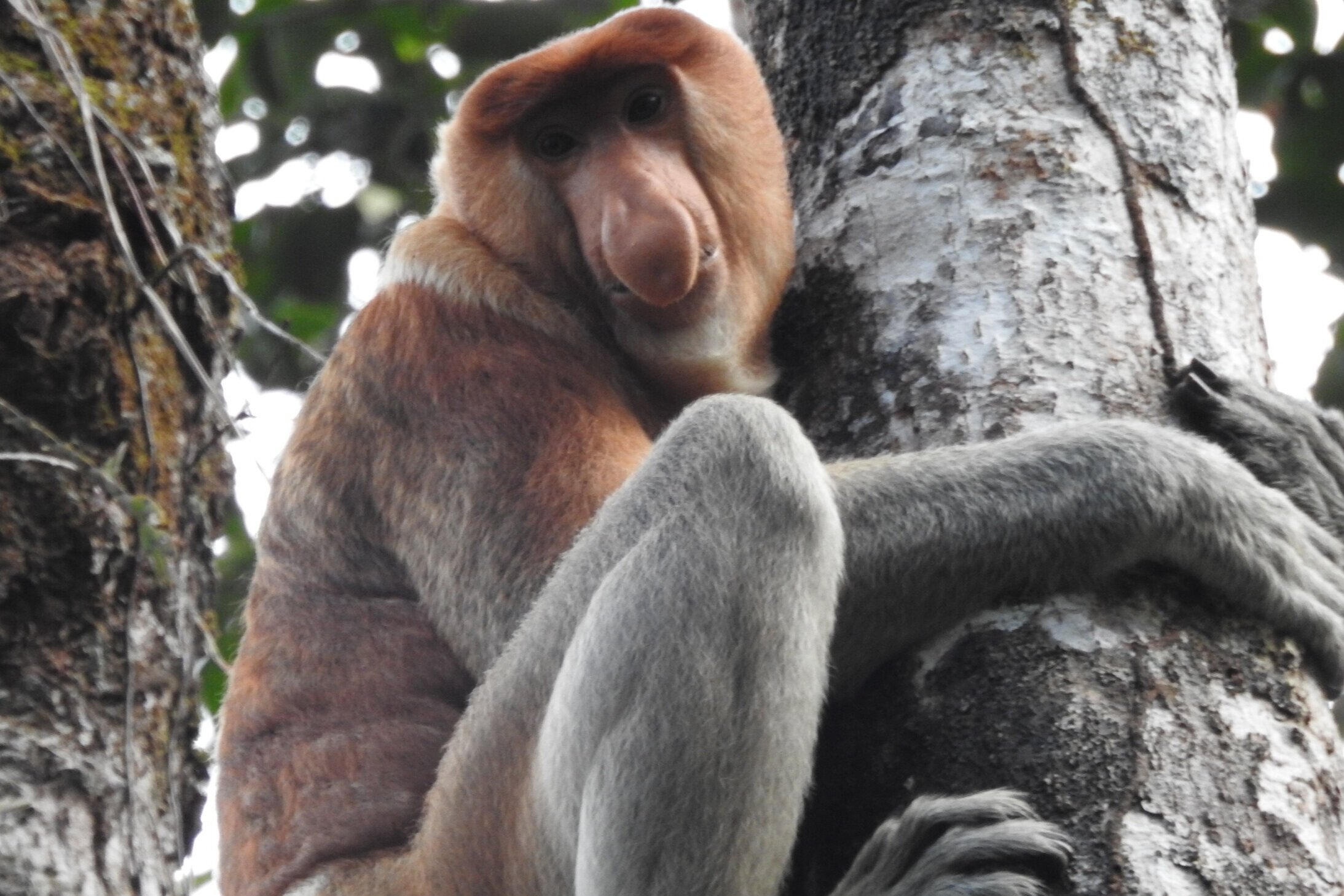
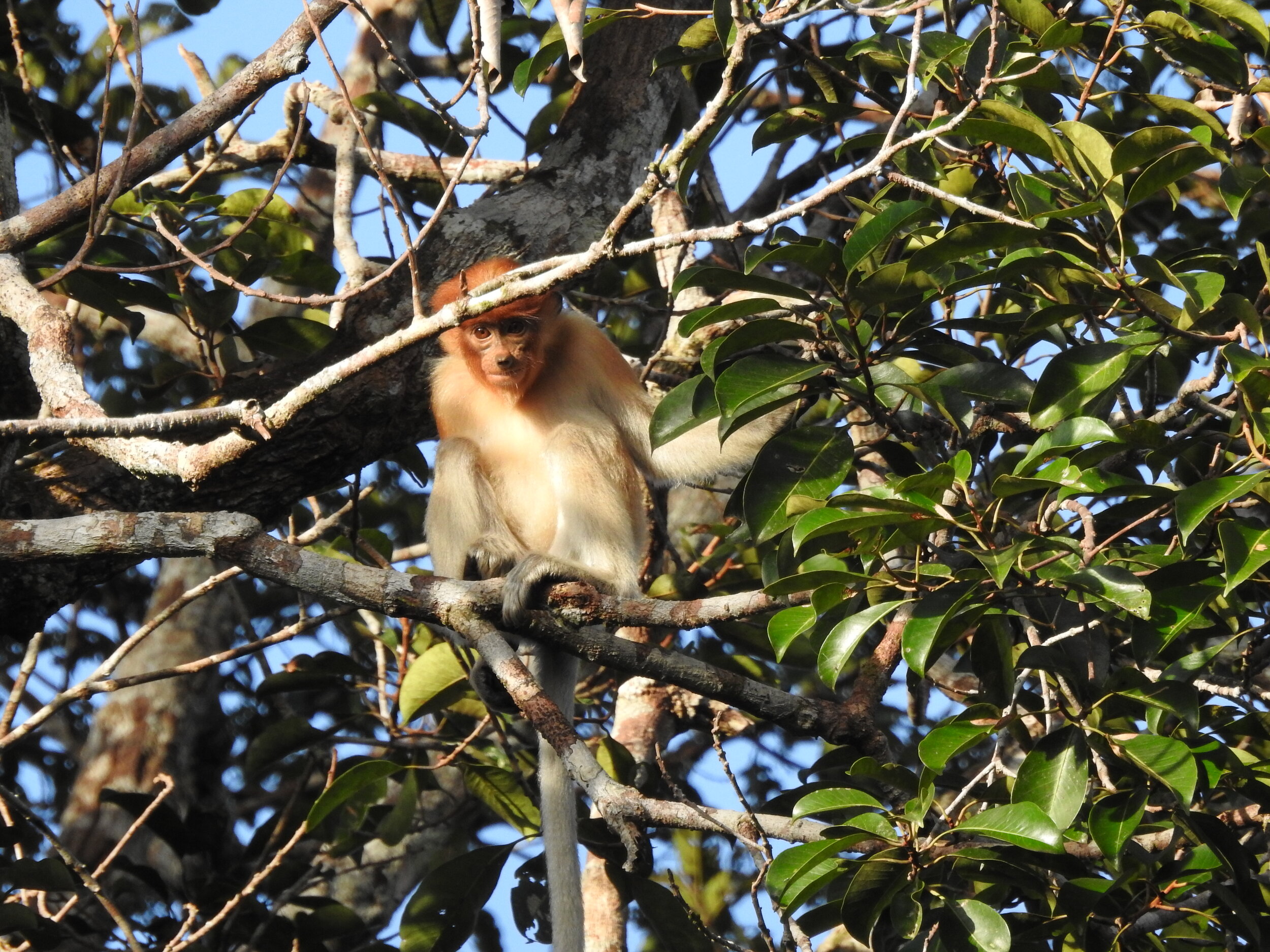
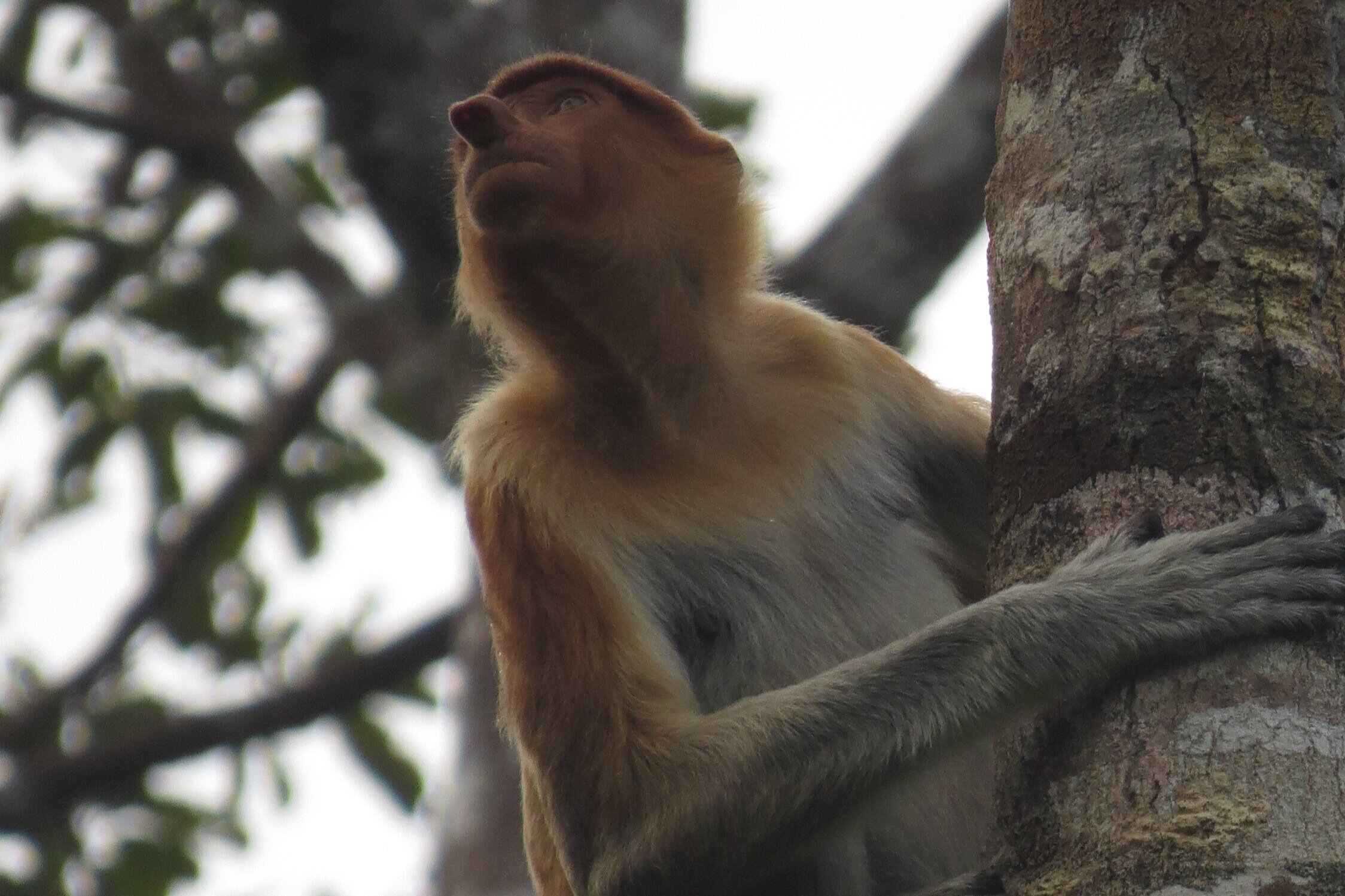
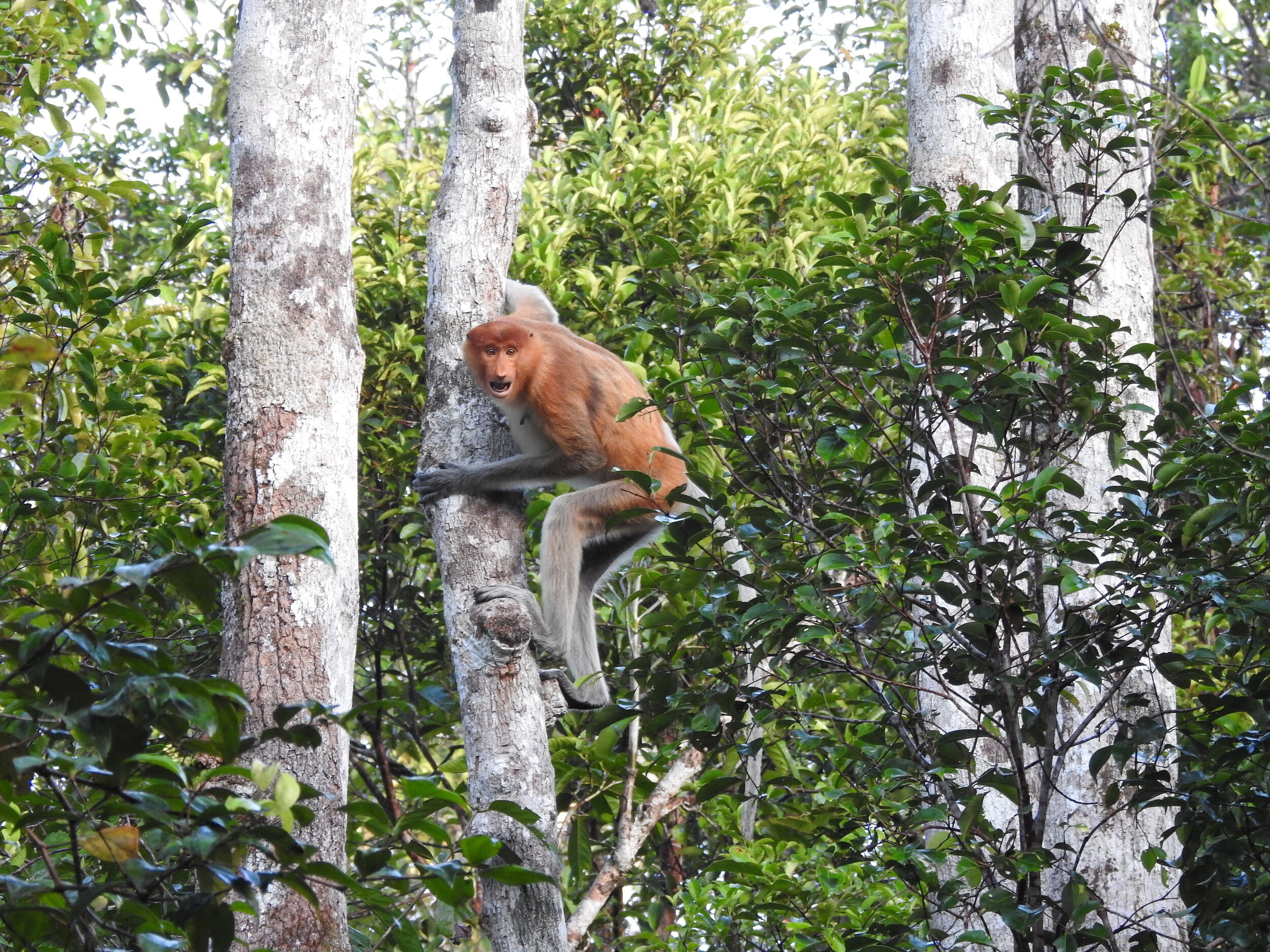
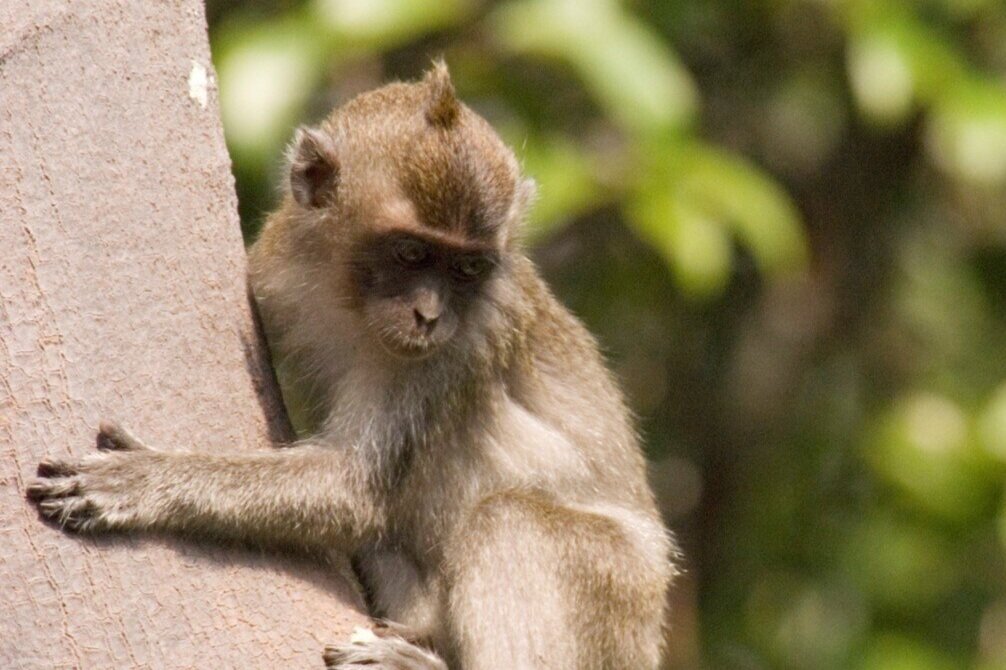
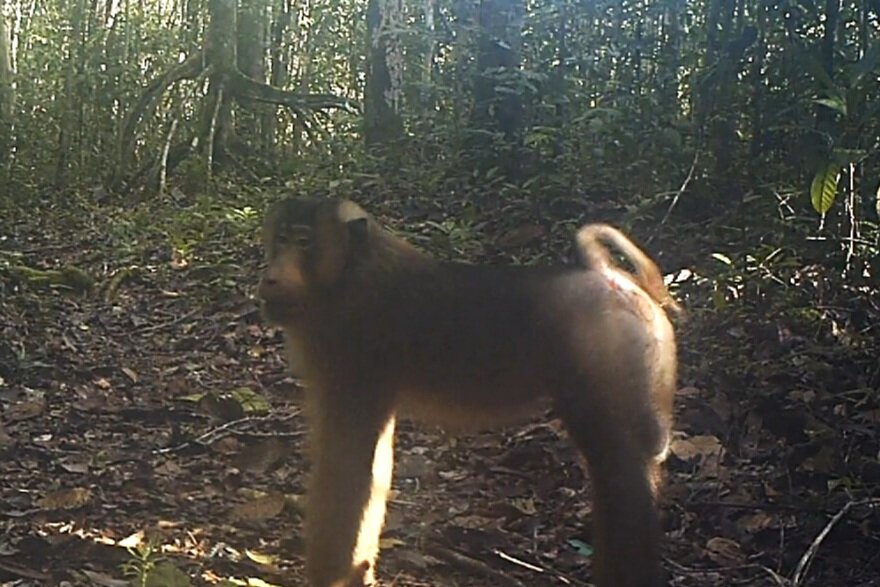
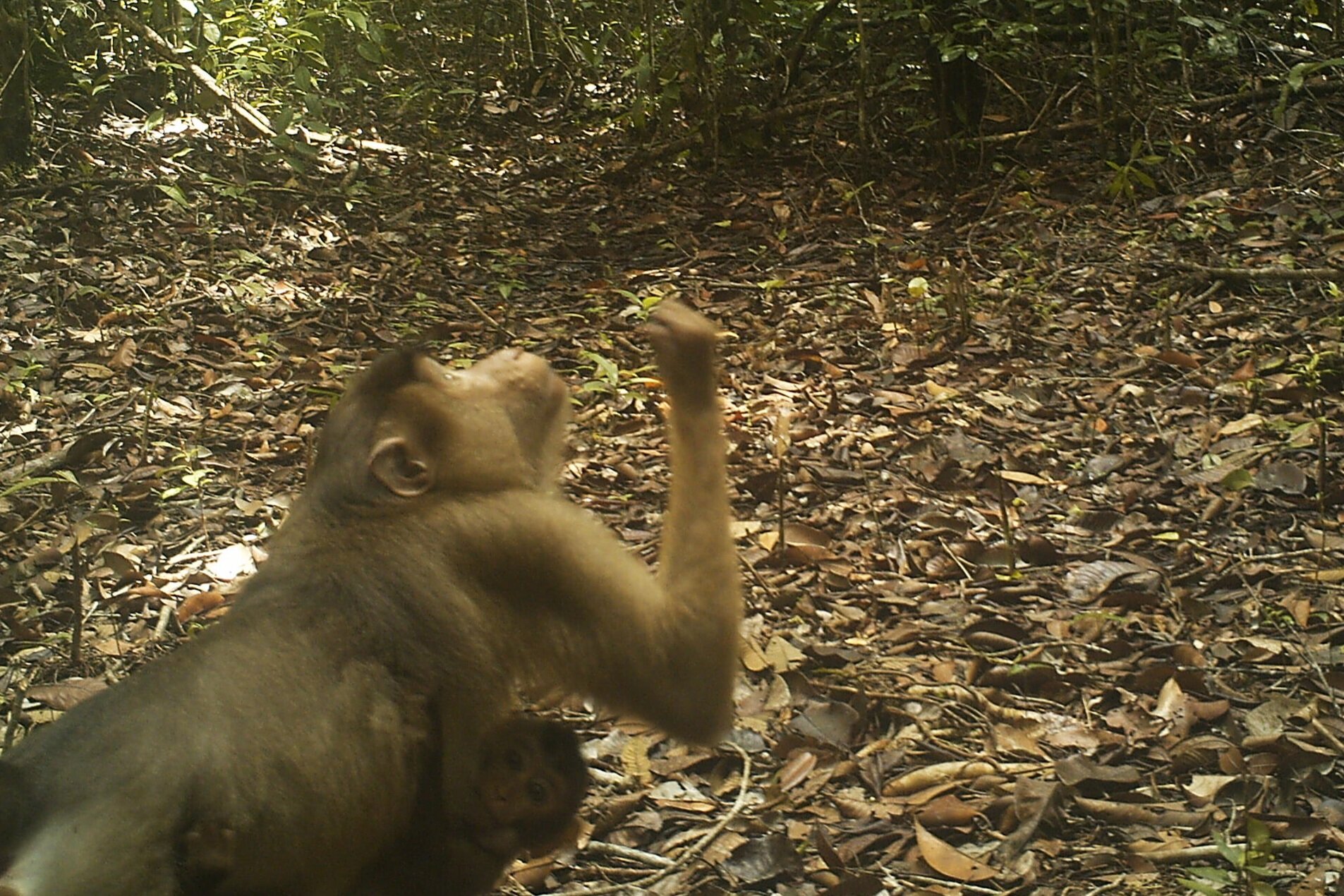
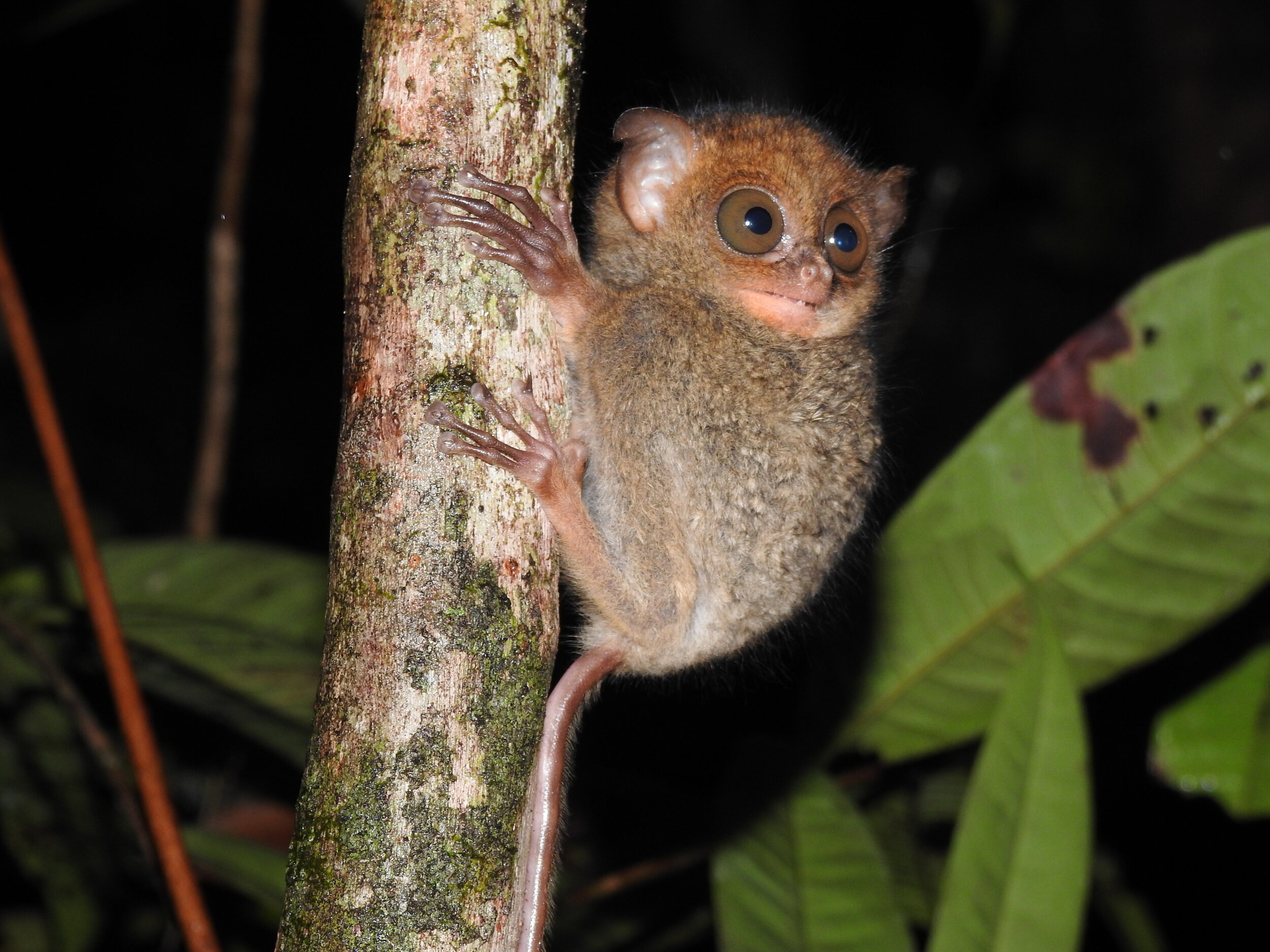
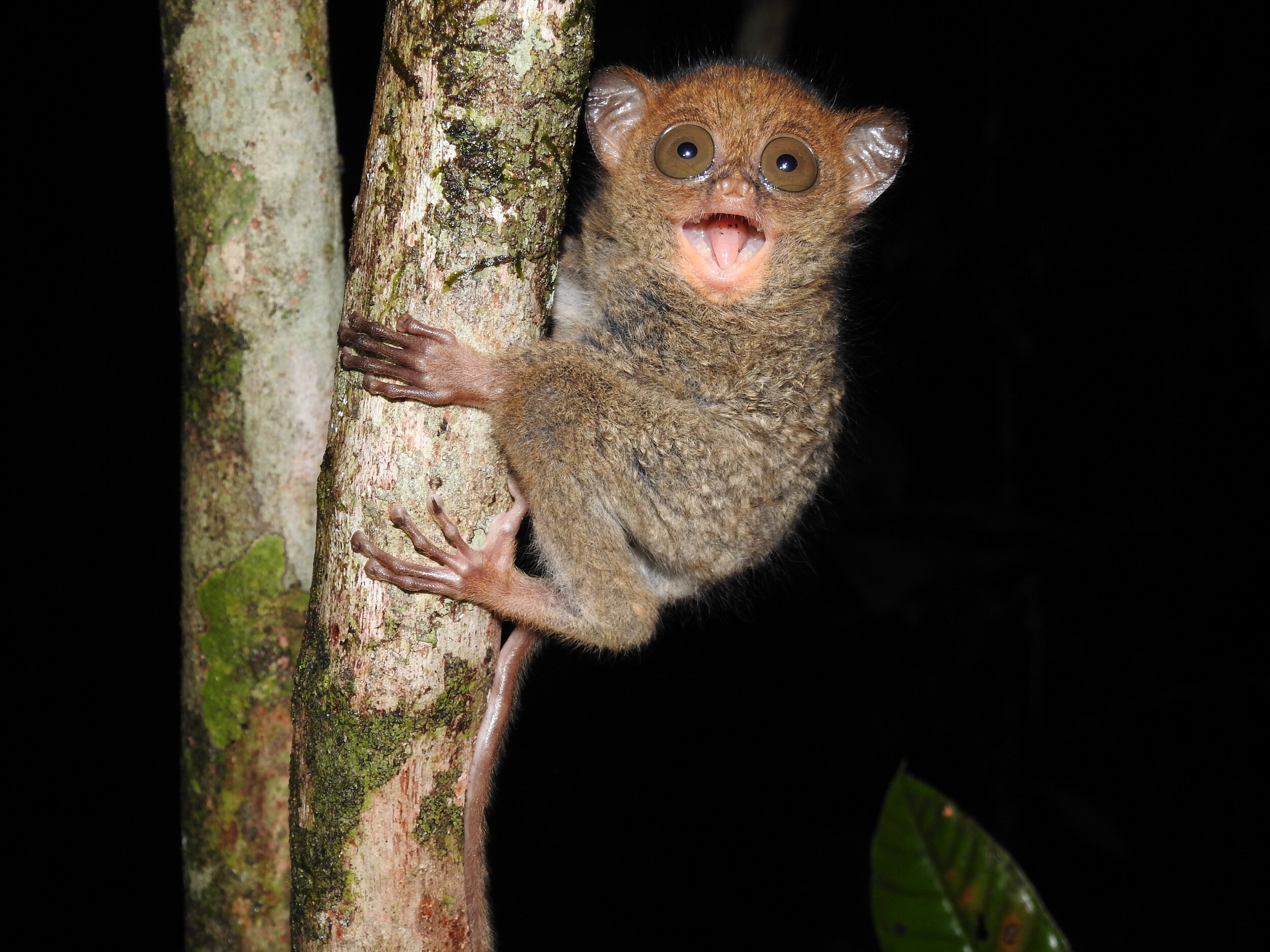
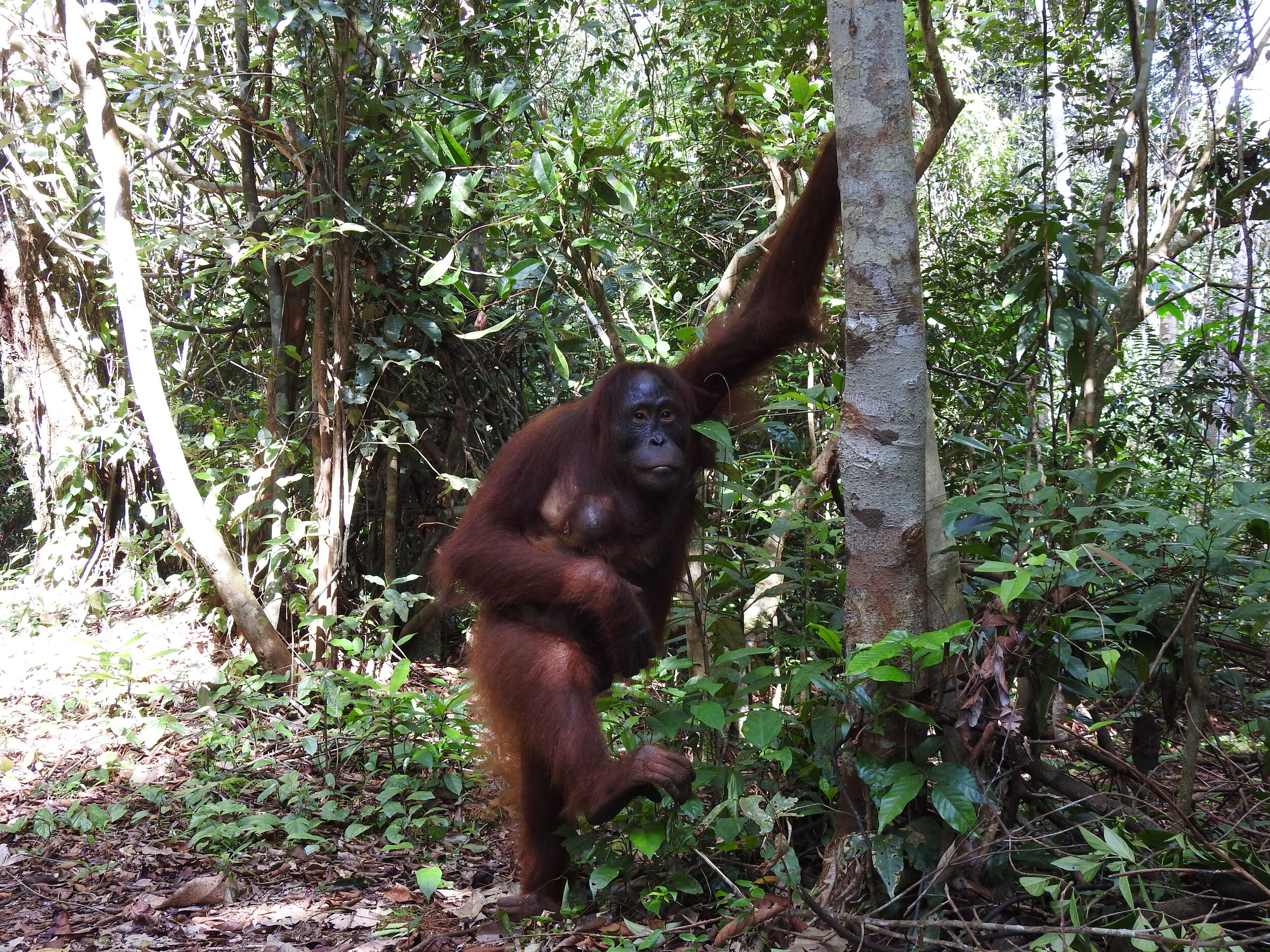
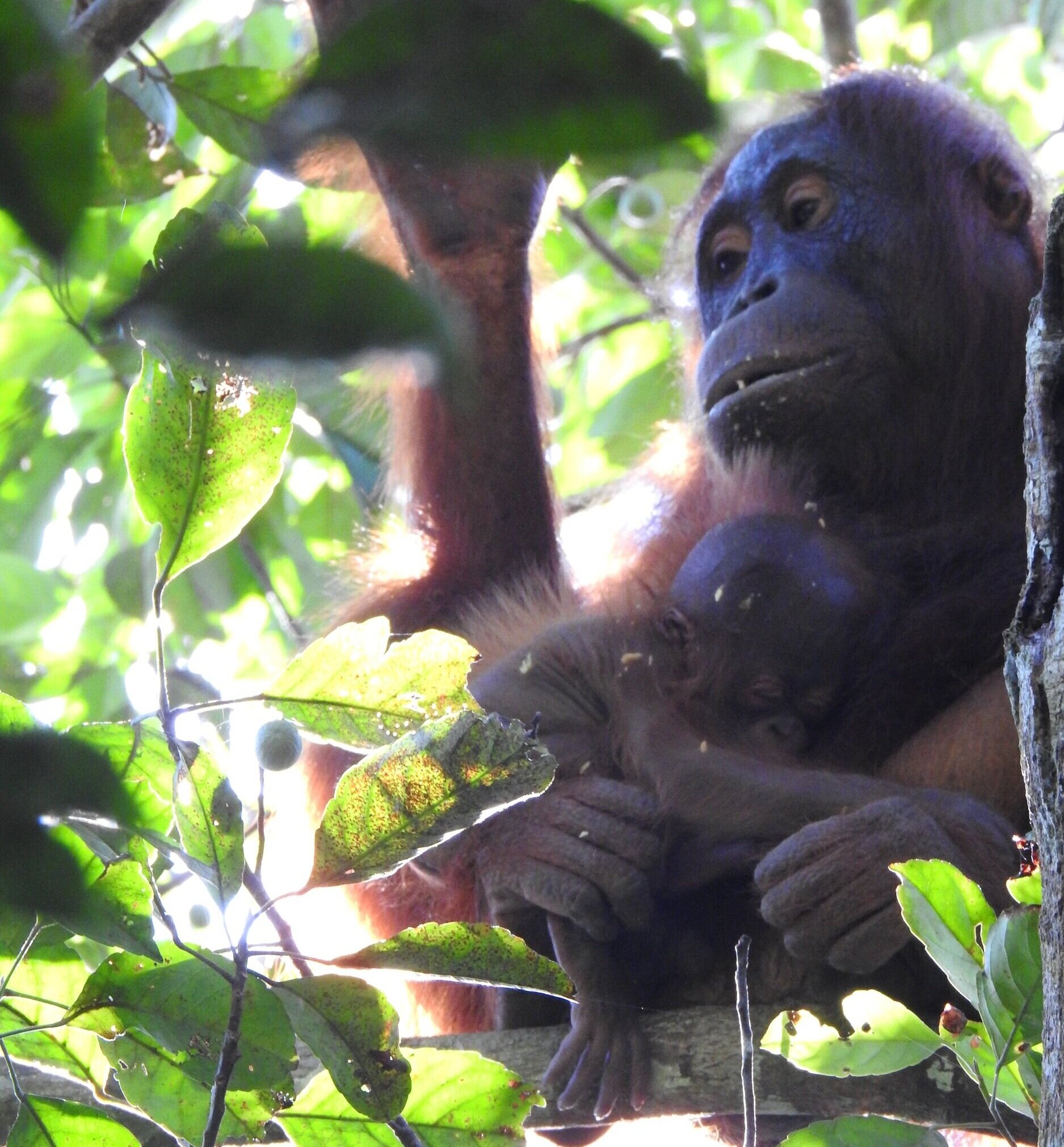
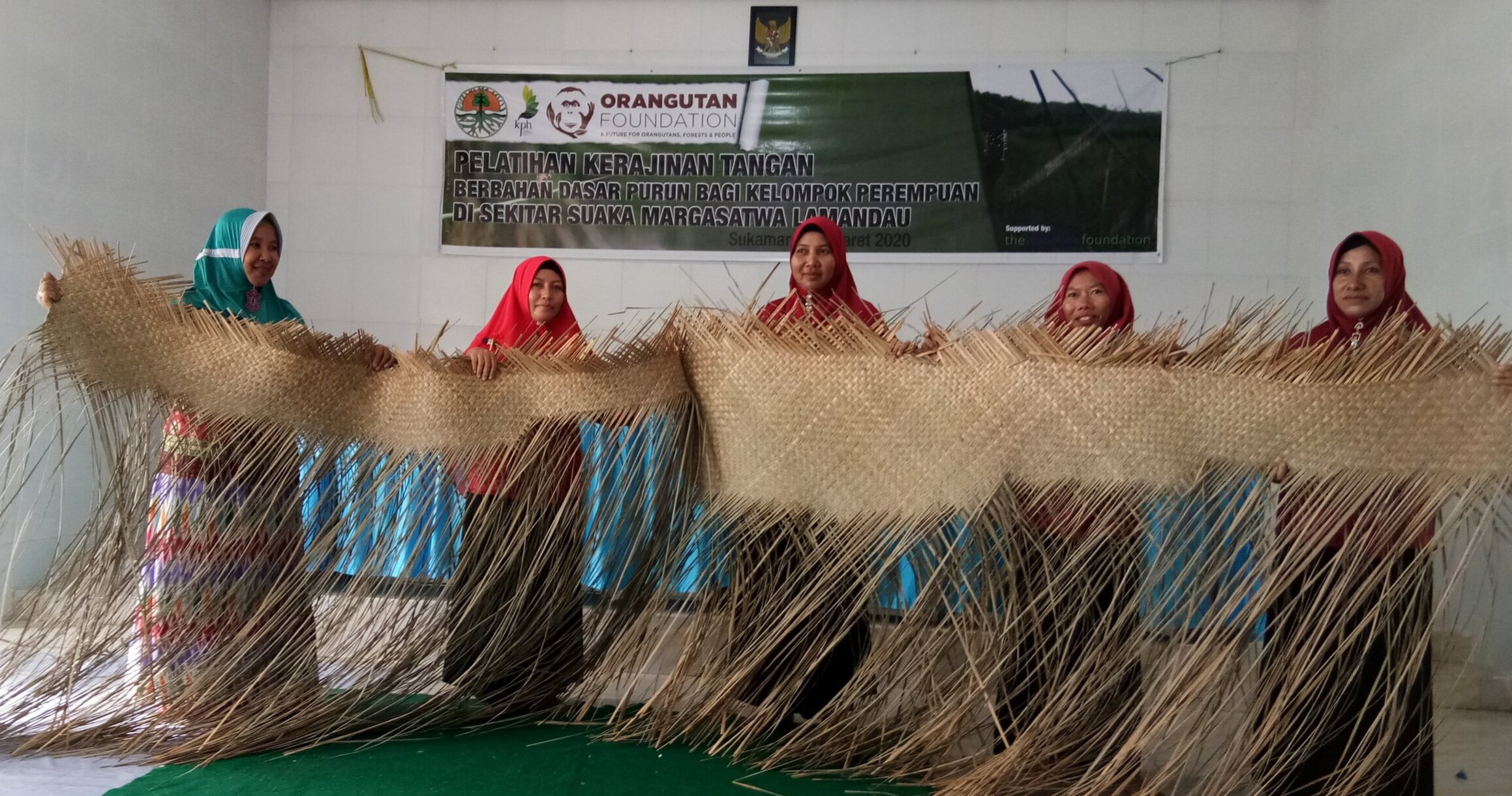
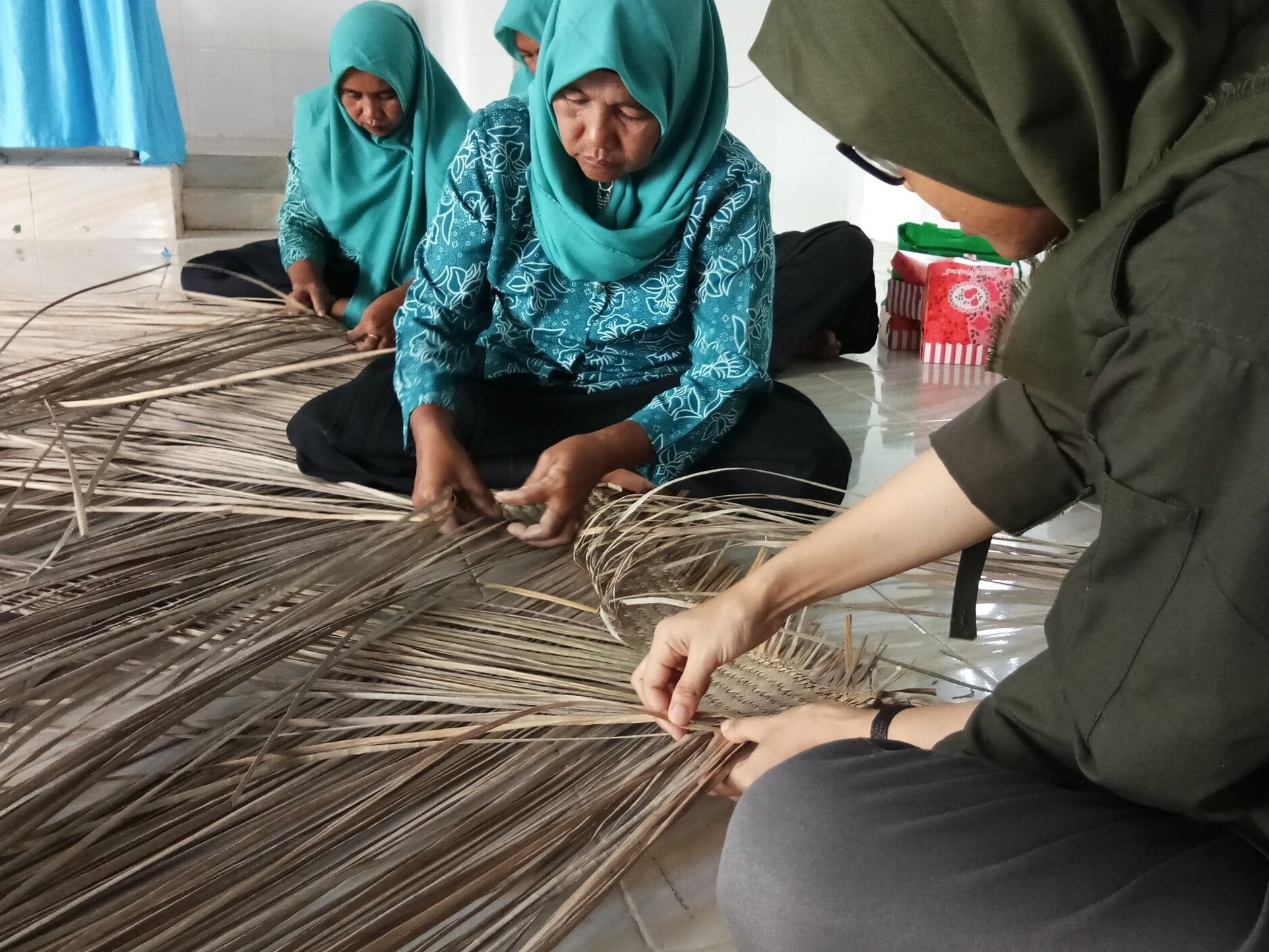
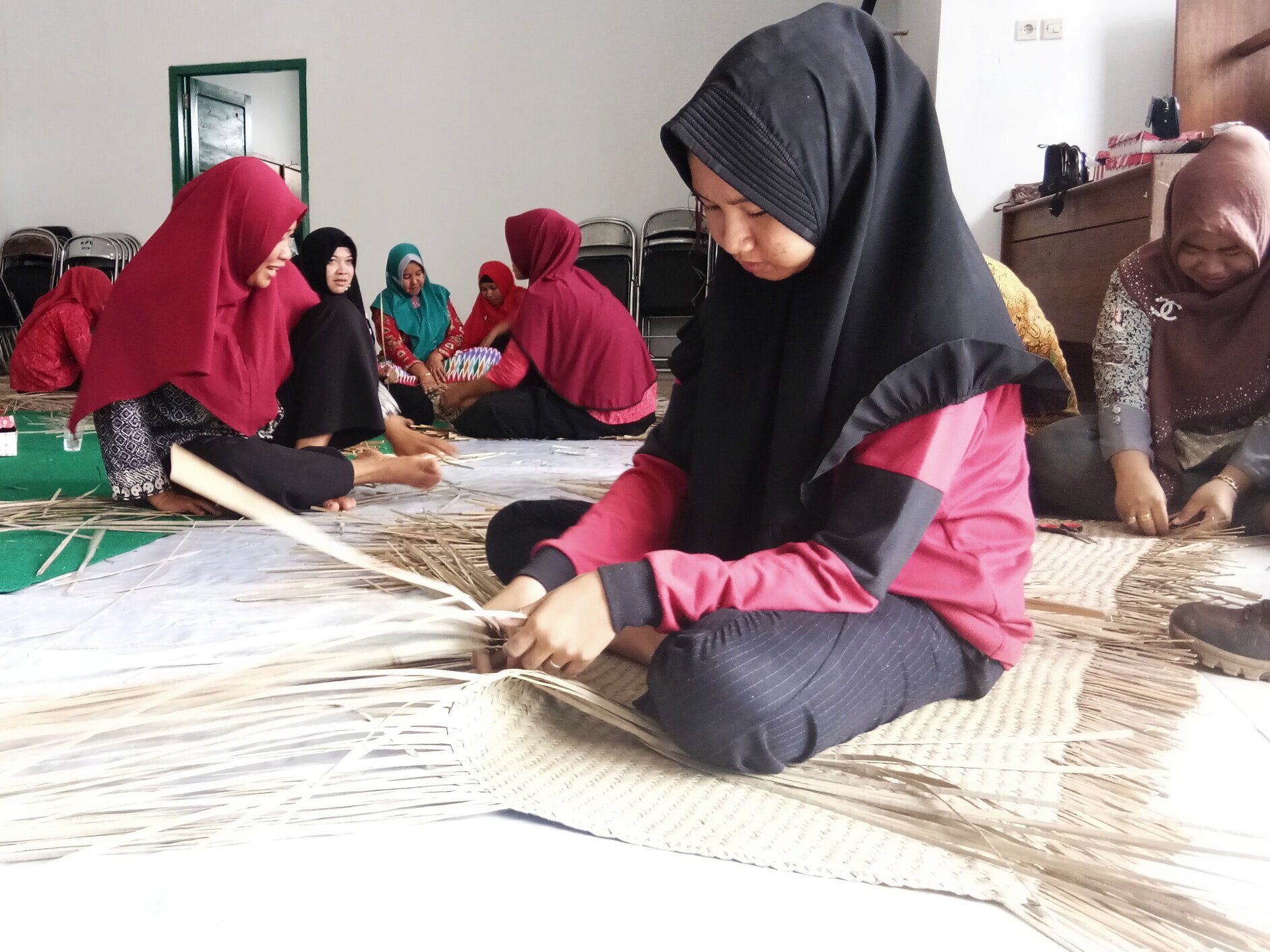
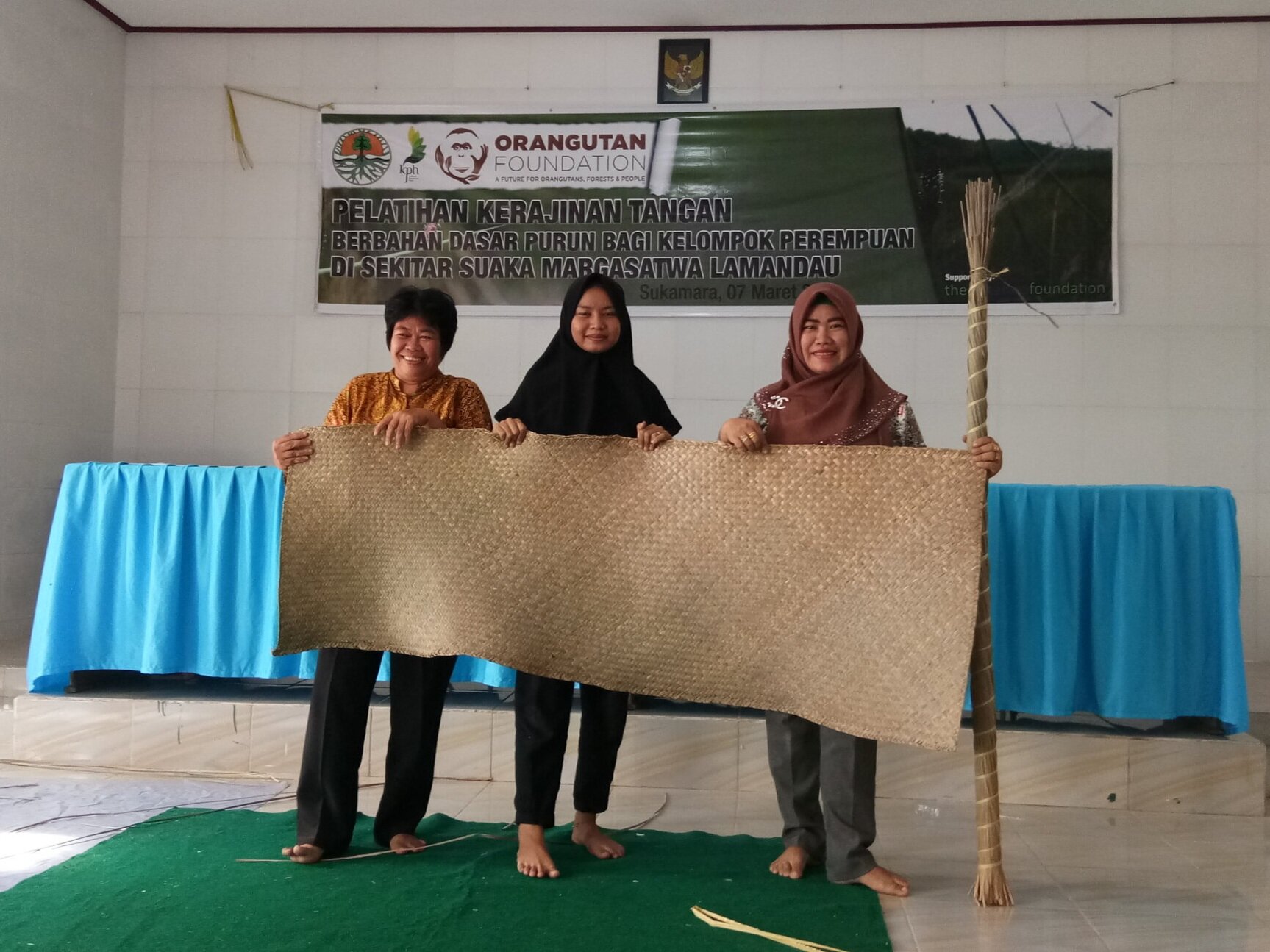
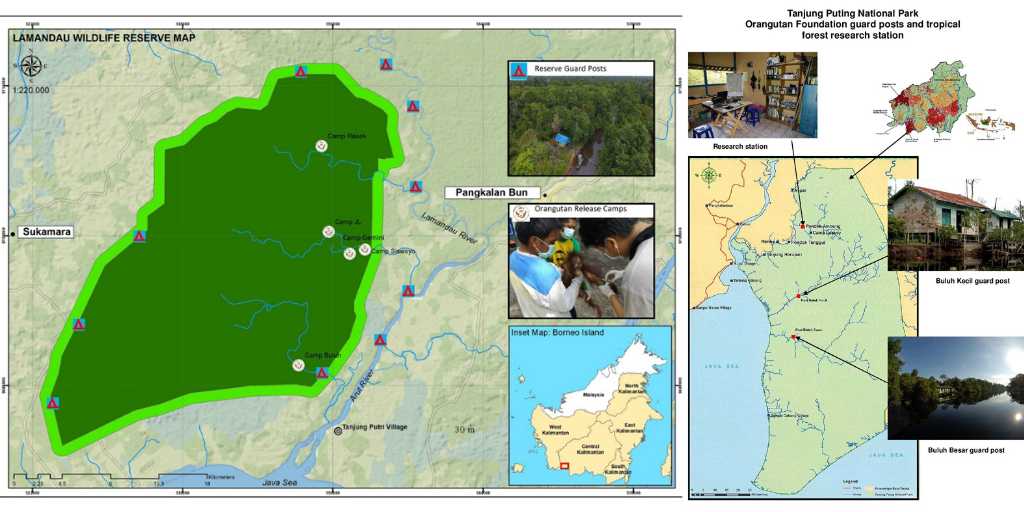
The diverse ecosystems within Tanjung Puting National Park and the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve in Indonesian Borneo are truly bursting with life. Our staff are fortunate to come across a variety of interesting species as they monitor orangutans in the field, conduct research, and safeguard the forest. Some of the most eye-catching species we come across are Birds, including:
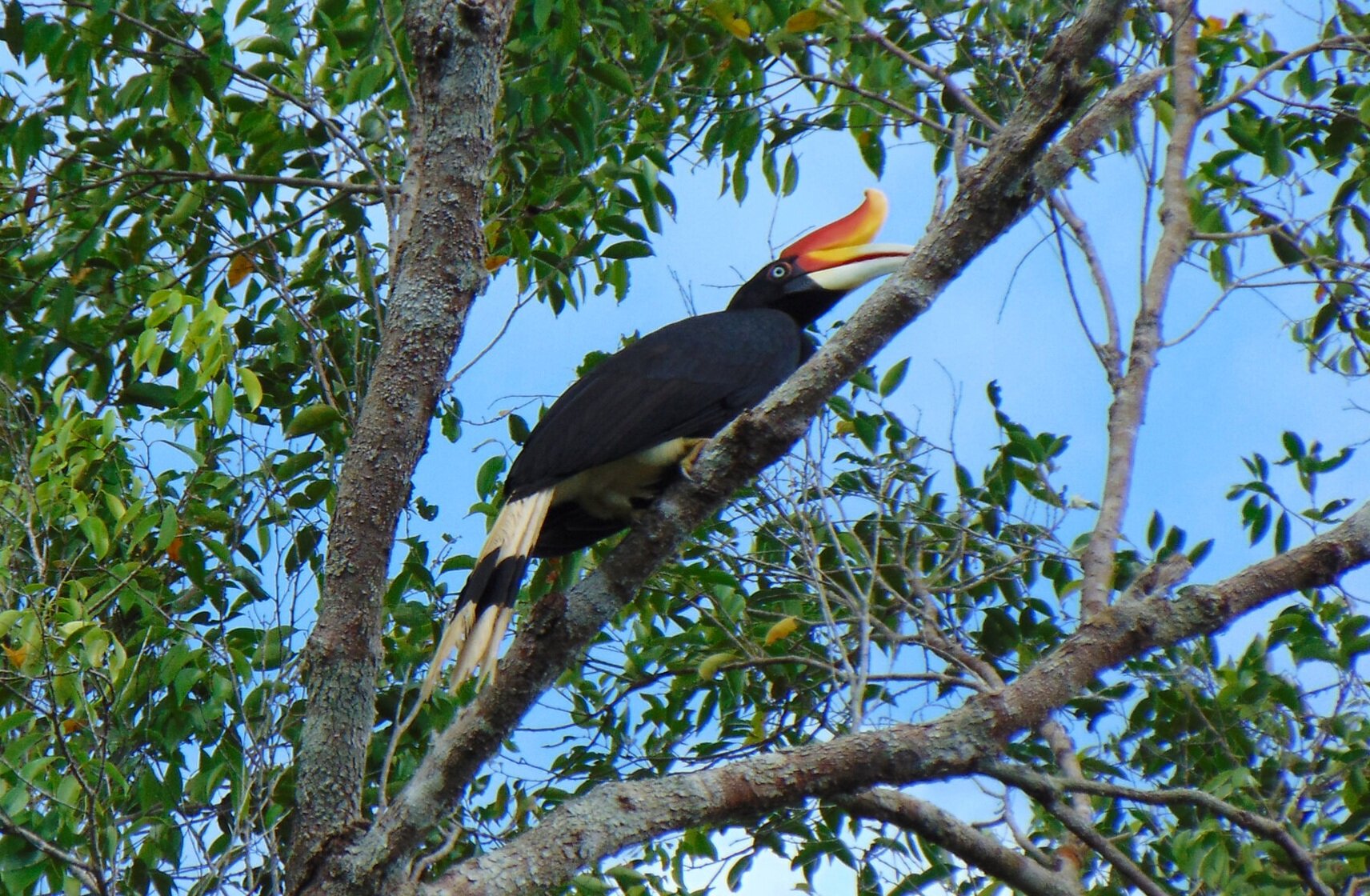
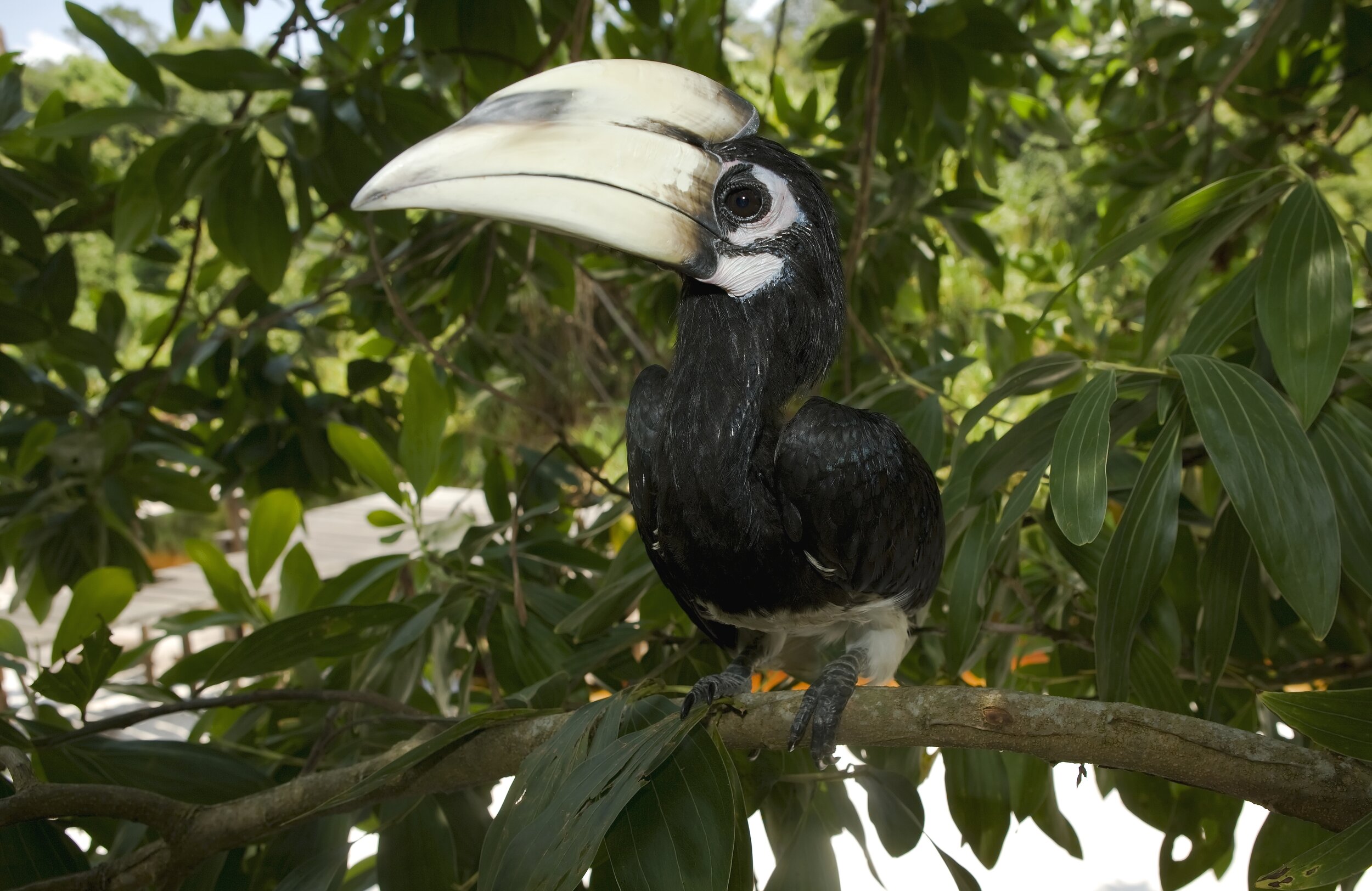
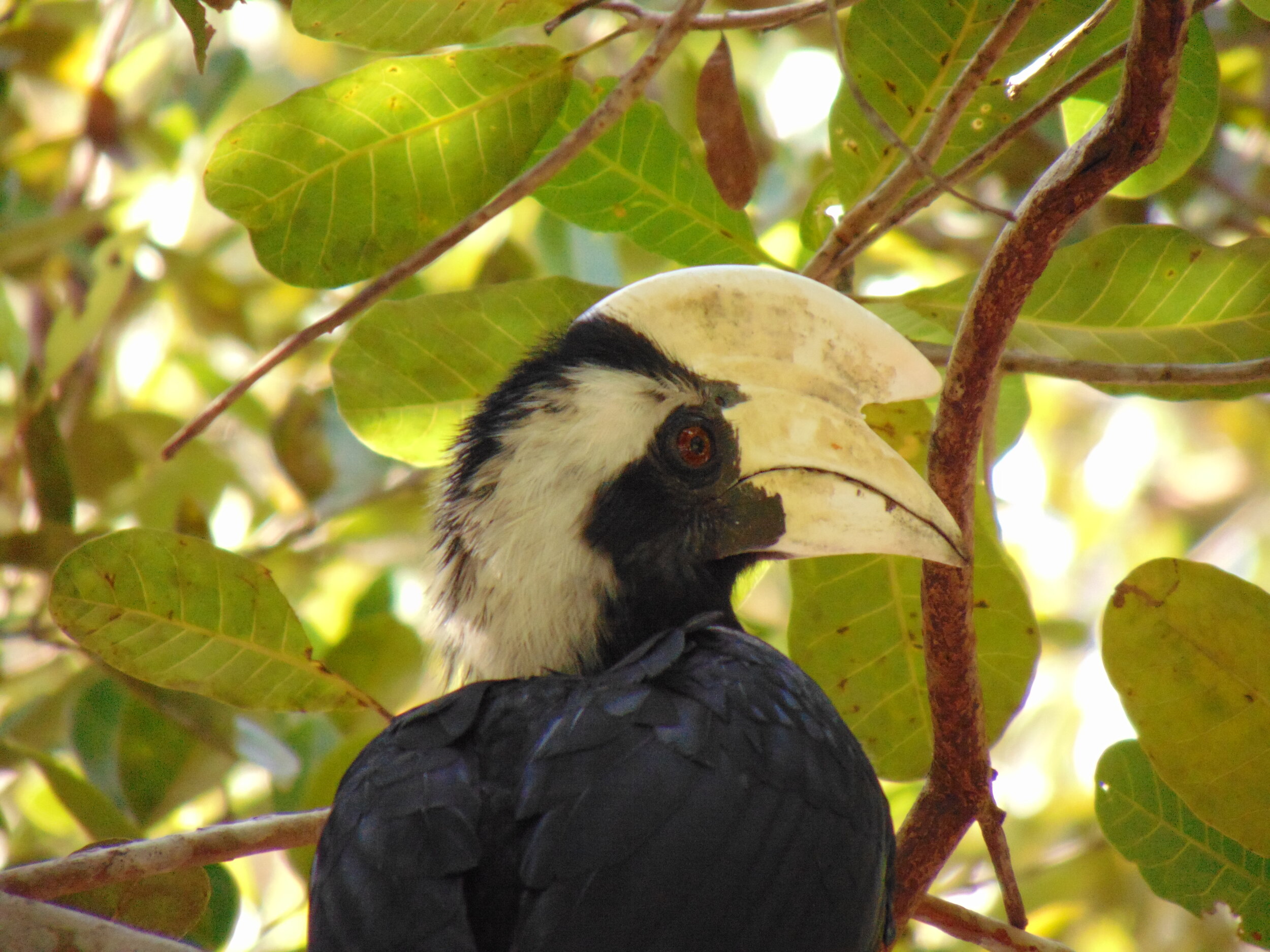
Hornbills - There are 8 species of hornbill found in Borneo, and they are perhaps the most iconic birds found in the forests of this tropical island. Hornbills are infamous for the large casques on their beaks, the most eye-catching of which is the Rhinoceros Hornbill, Buceros rhinoceros. These impressive birds have brightly coloured beaks, can have a 50-inch wingspan, and typically mate for life.
Crested Serpent Eagle - Spilornis cheela - These raptors are found in various forest types and can survive in areas of disturbed habitat where other birds may not. In fact it could be said that these eagles prefer forest edges, where they can hunt for a variety of prey from snakes and lizards to small mammals and fish. This adaptability helps make them such a successful raptor species and they can also be found as far as India and the Philippines.
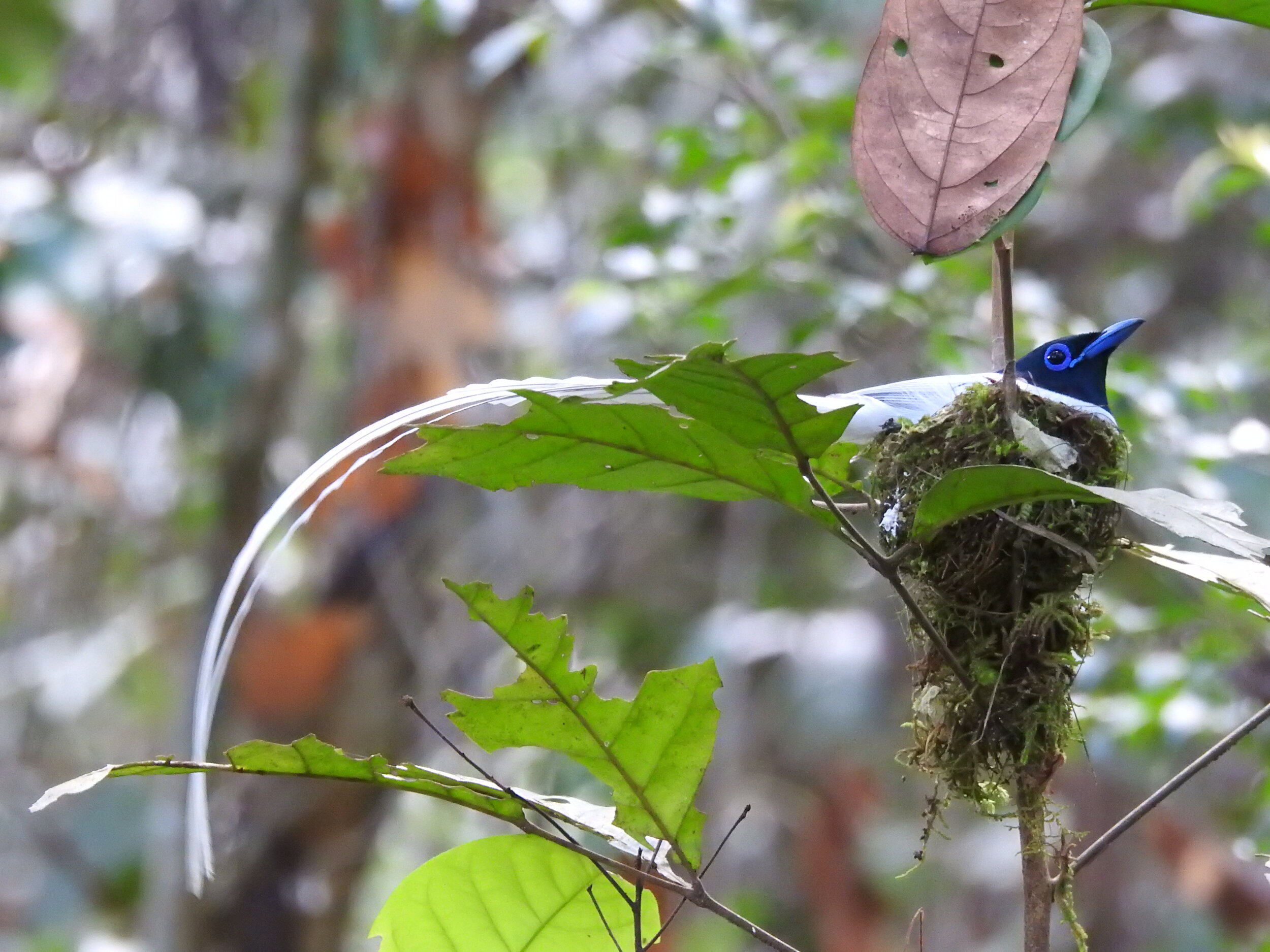
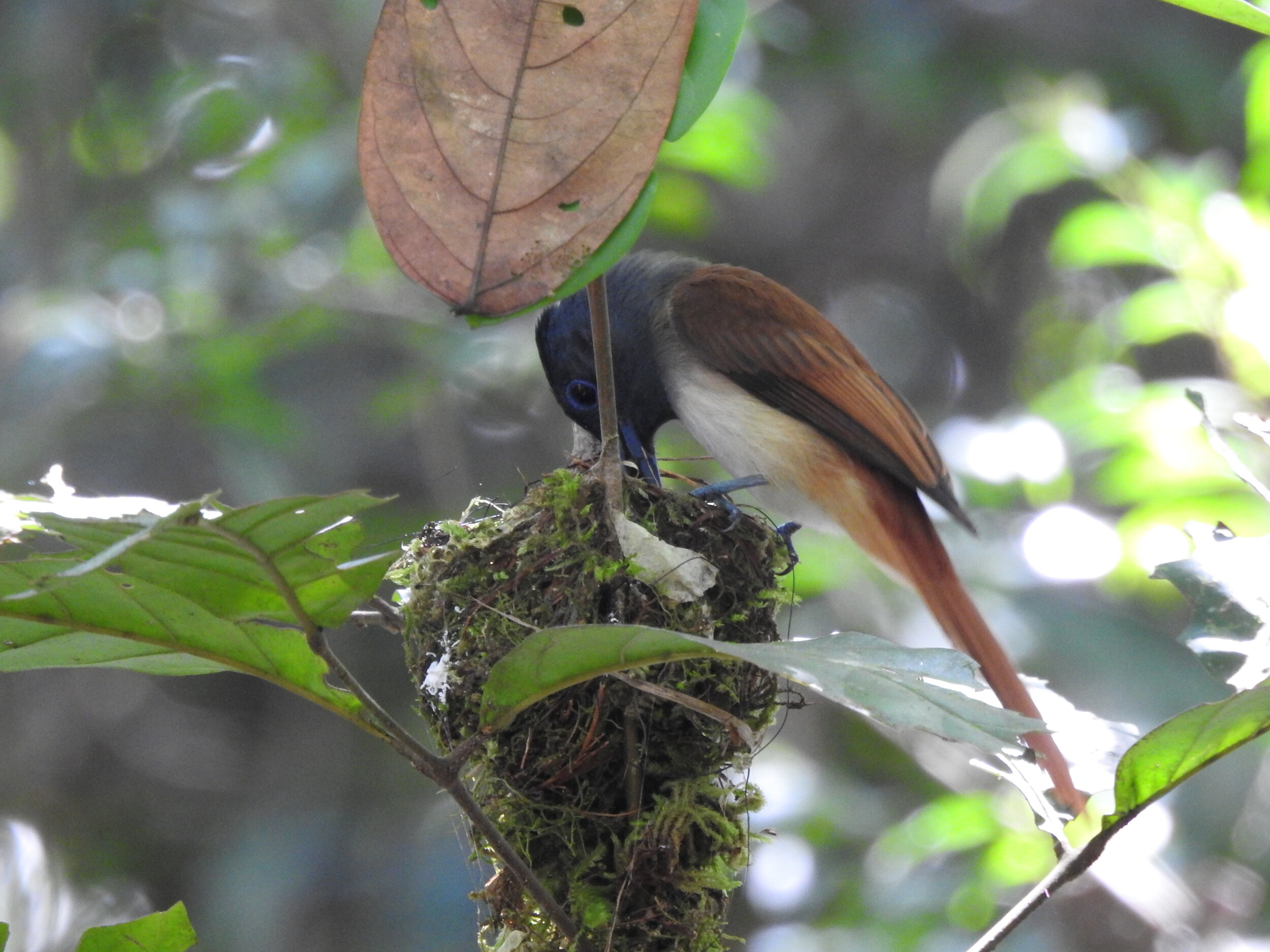
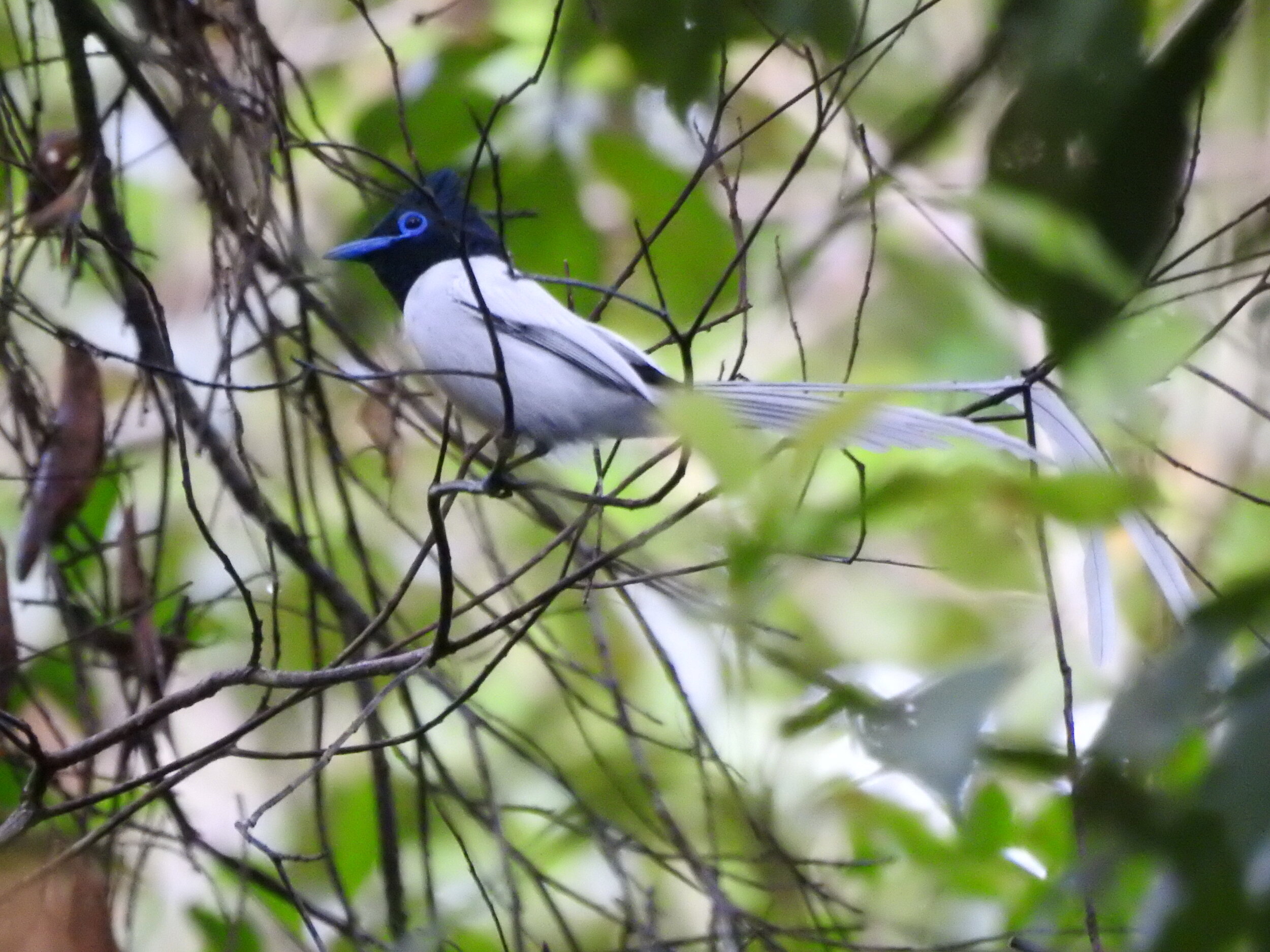
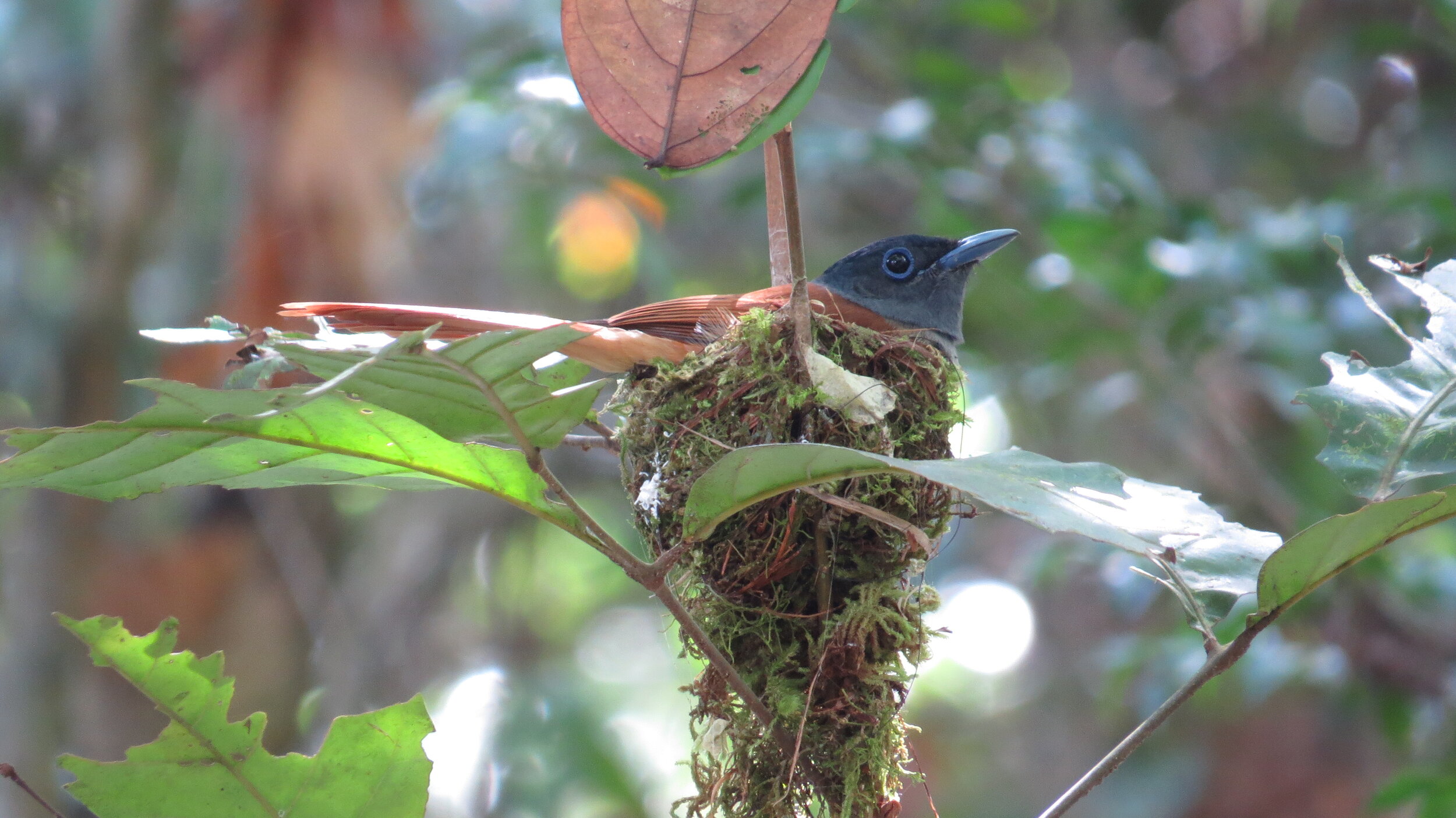
Asian Paradise Flycatcher - Terpsiphone paradisi - By looking at them, you could be forgiven for thinking that the male and female Asian Paradise Flycatcher are birds of completely different species, such is the contrast in their appearance. Females are modest-looking with black feathers on their heads and brown bodies, whereas adult males have bright white plumage and two enormous tail streamers. It’s thought these feathers are elongated to attract a mate and can grow up to 12 inches- longer than their entire body!
Storm's Stork - Ciconia stormi - This is sadly a species in decline and thought to be the rarest of all storks. Due to the loss of habitat in this part of the world, Storm’s Storks are listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List with fewer than 500 individuals remaining in the wild. These forests in Indonesian Borneo are a real stronghold for this vulnerable species so sightings of breeding pairs are vitally important.
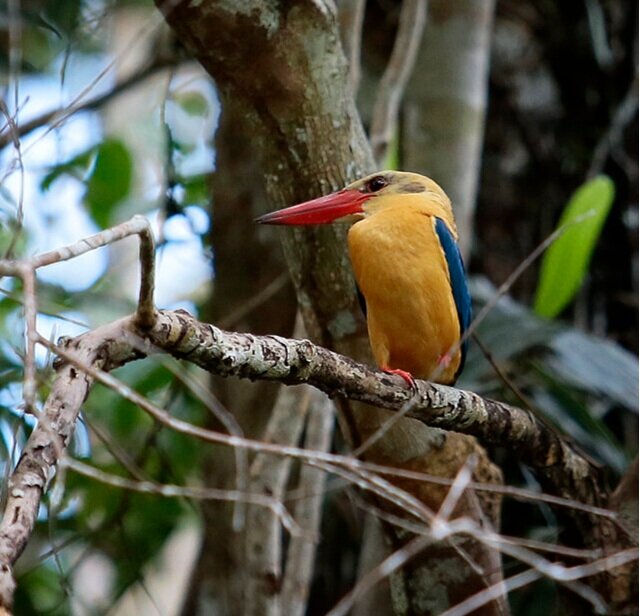
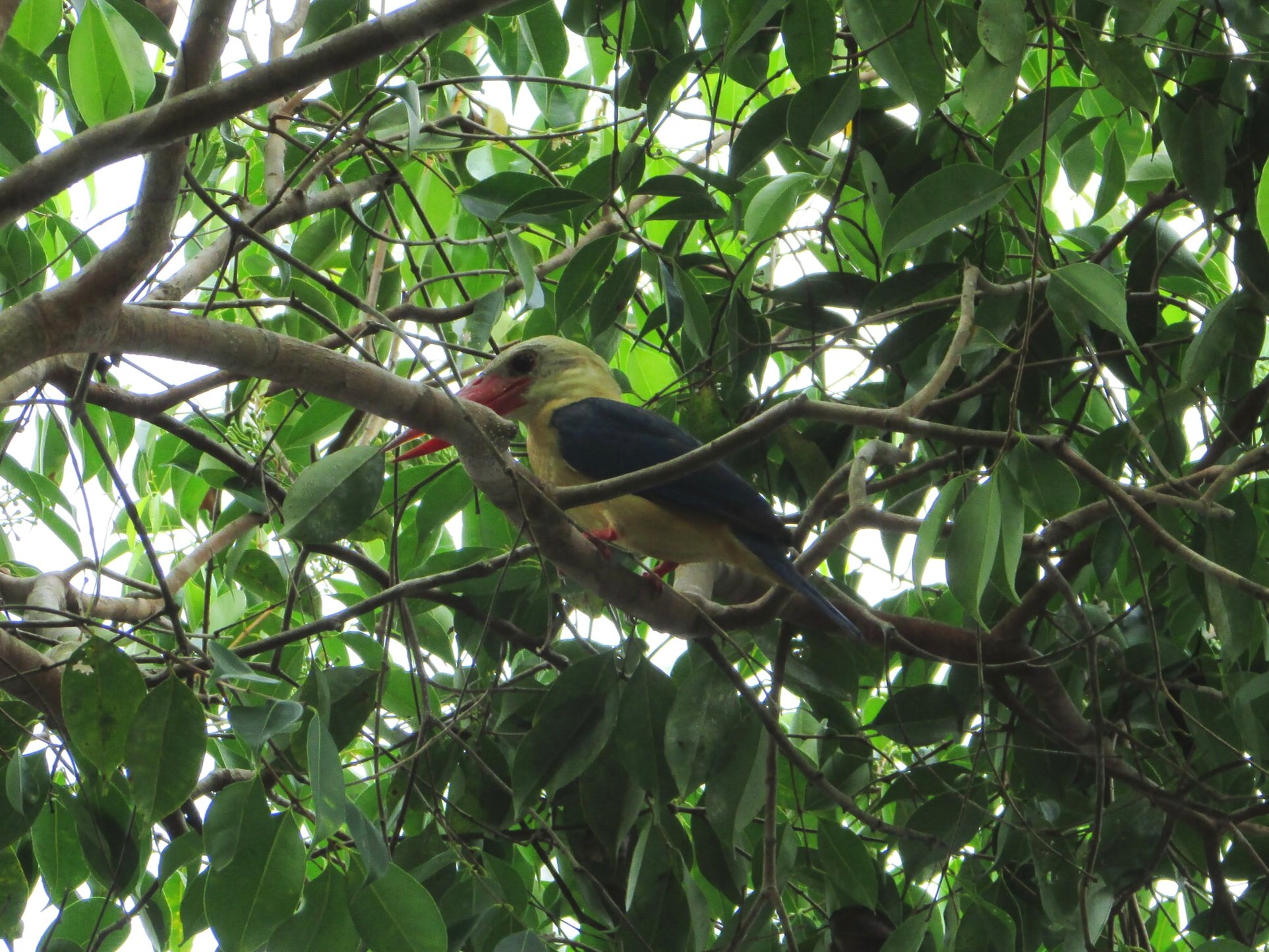
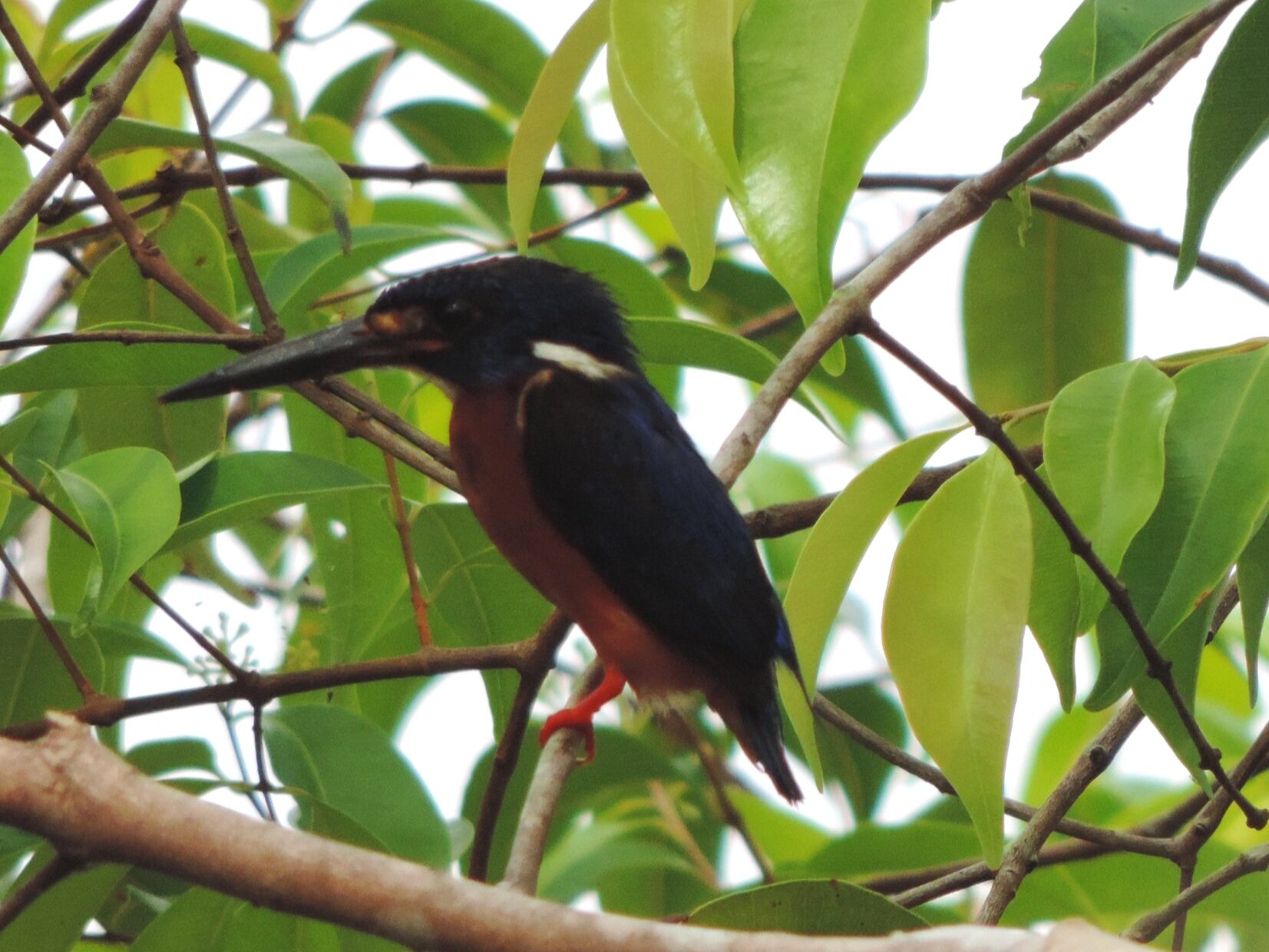
Kingfishers - The easiest way for our field teams to navigate through the forest is via the network of rivers, an ideal habitat for kingfishers. The Stork-billed and Blue-eared Kingfisher (Pelargopsis capensis & Alcedo meninting) are the most commonly seen species in these forests. Stork-billed are perhaps the most striking as they have large red bills and an explosive alarm call which is then followed by an unusual cack-cack-cack-cack laugh!
This is just a selection of the hundreds of bird species found in this diverse tropical forest environment. By supporting our guard posts and habitat restoration programme, your help is ensuring that these important species continue to live in a haven which is protected.