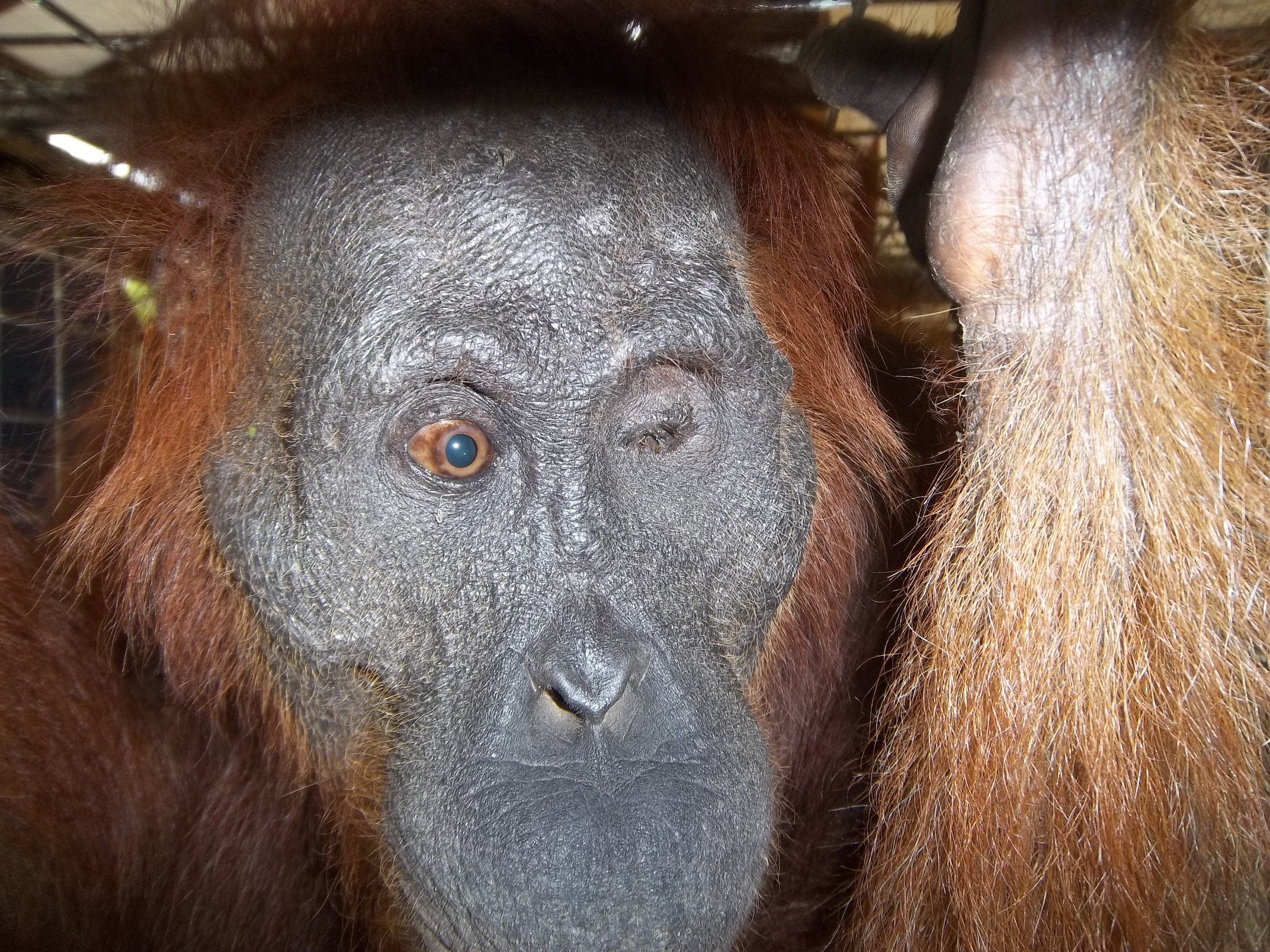
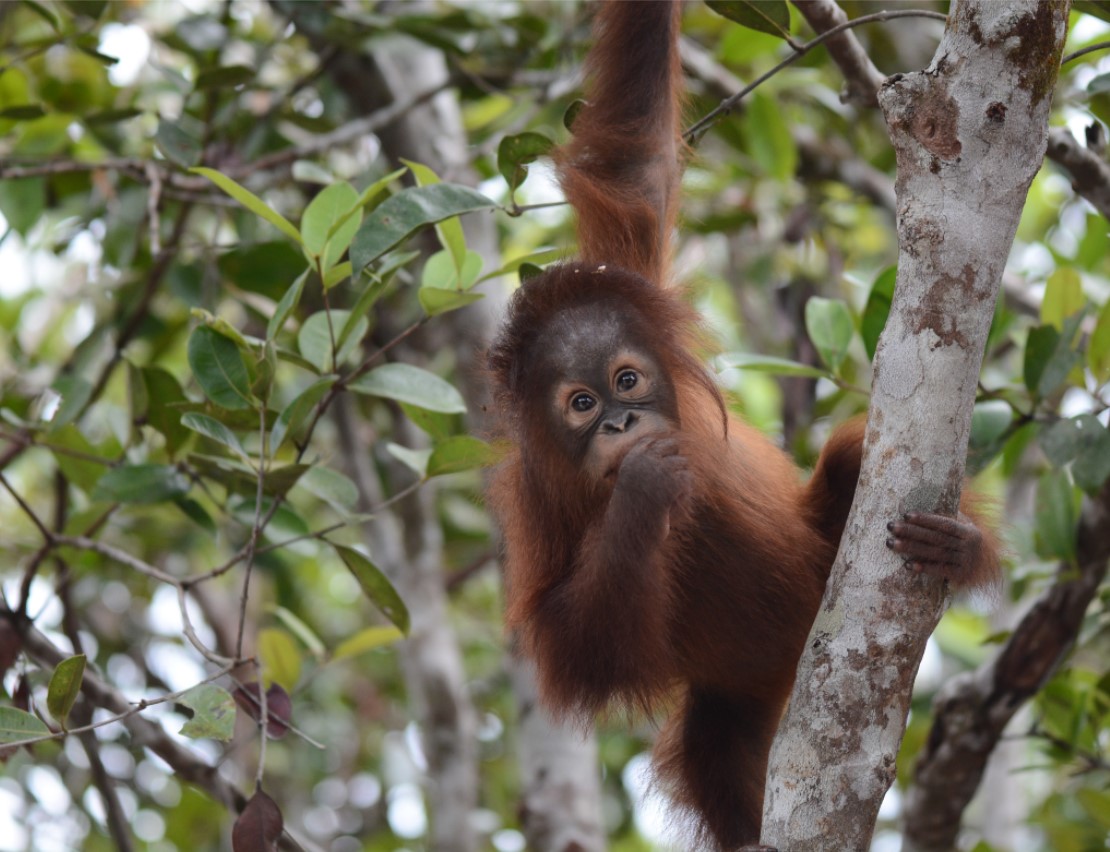
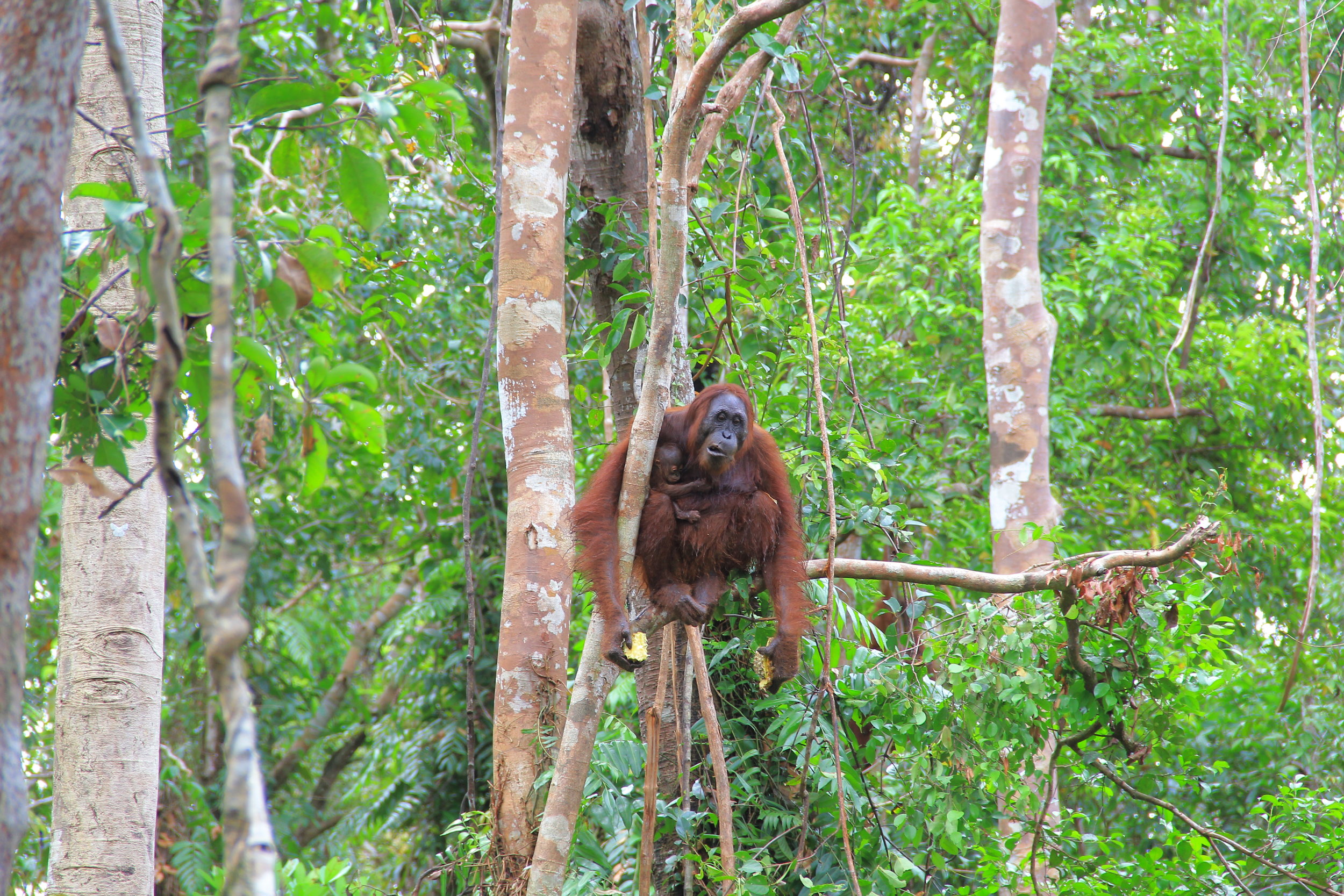
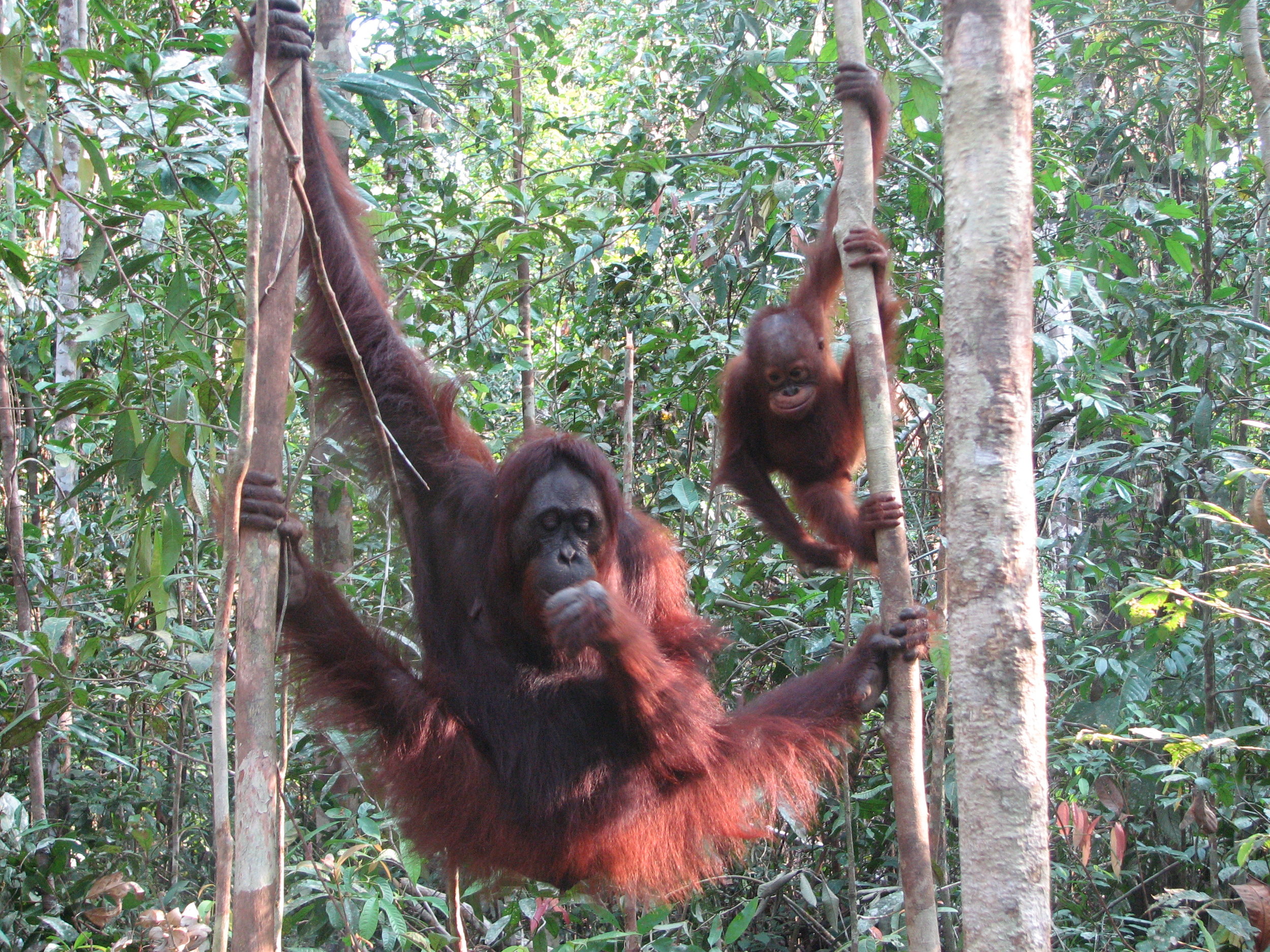
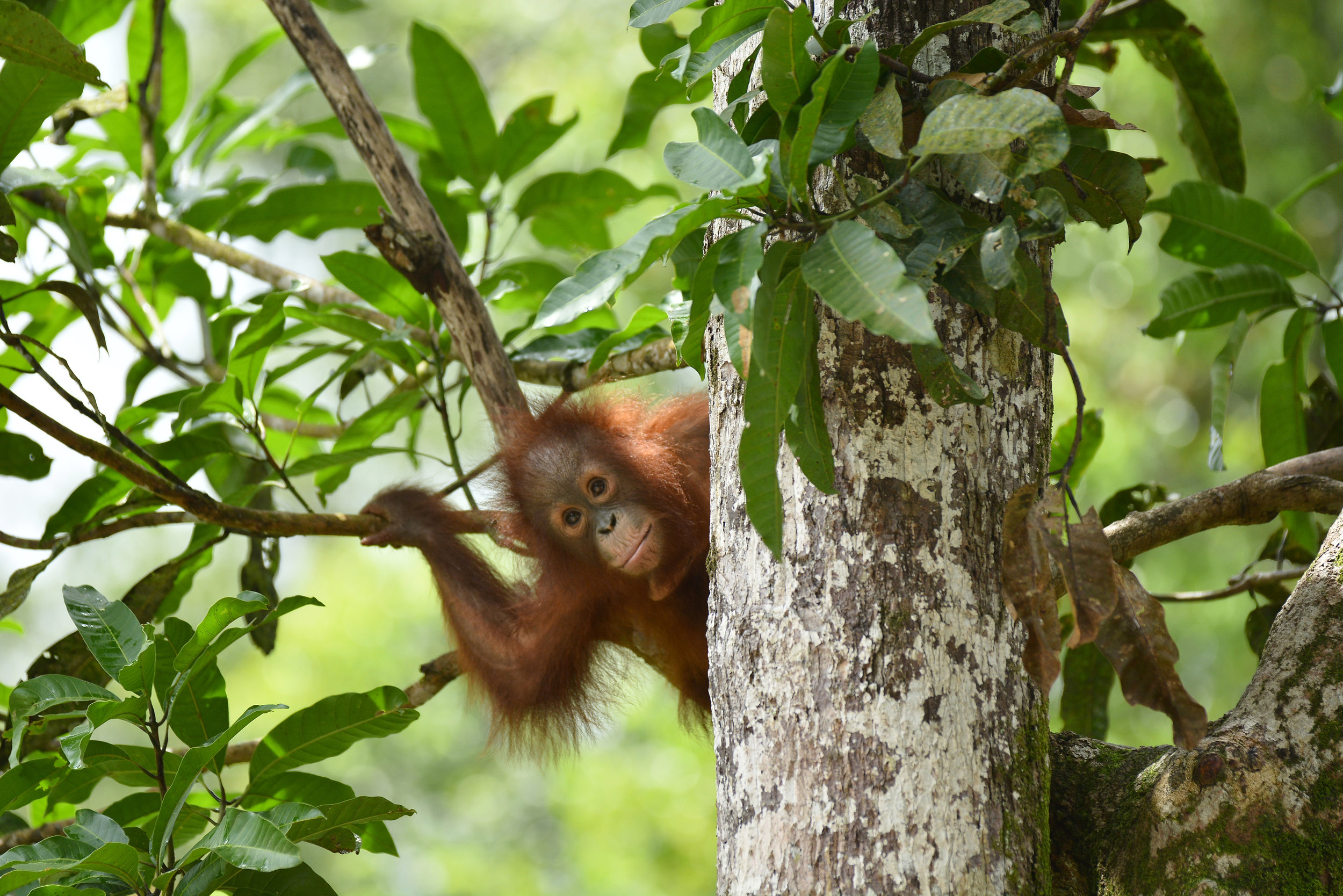
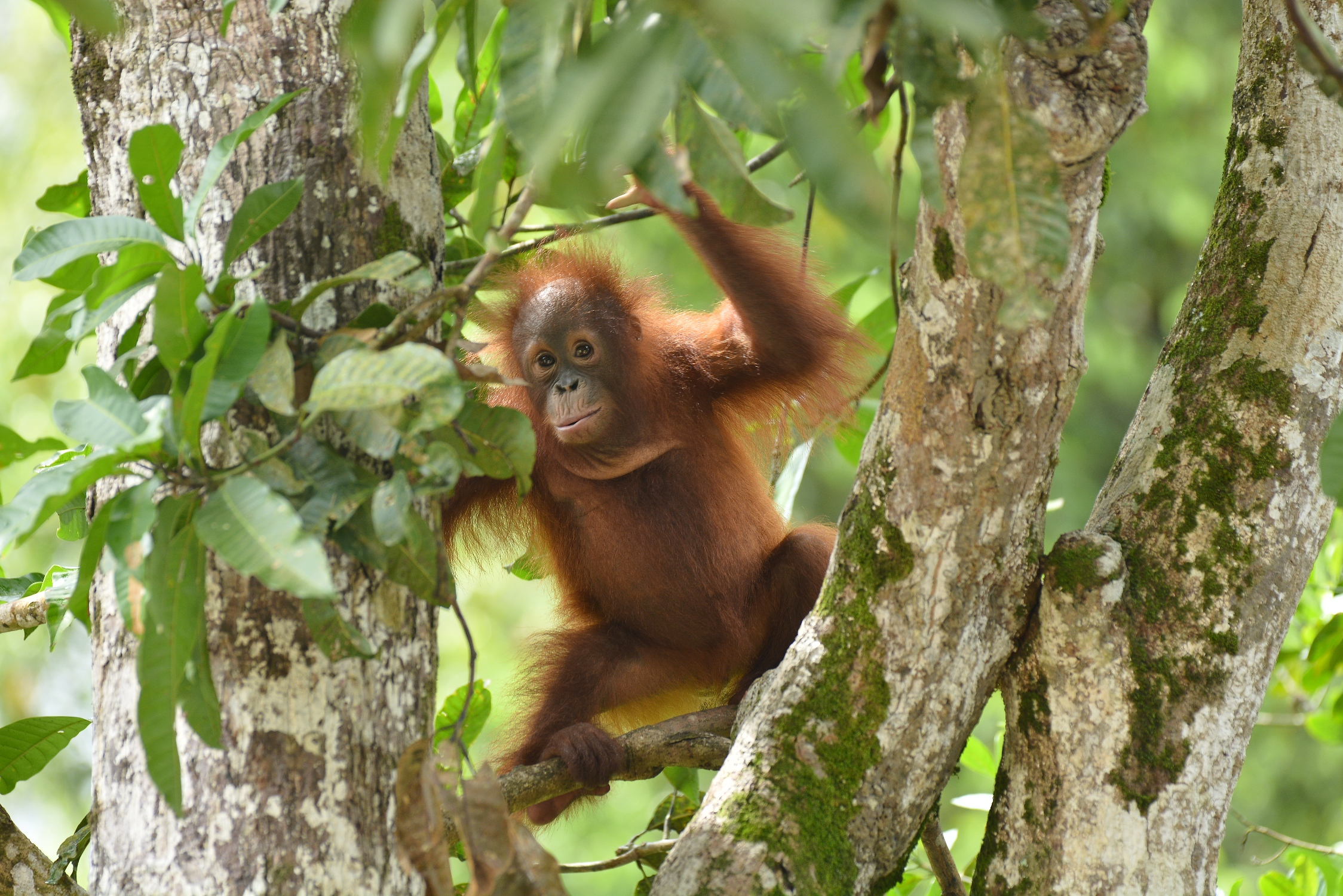
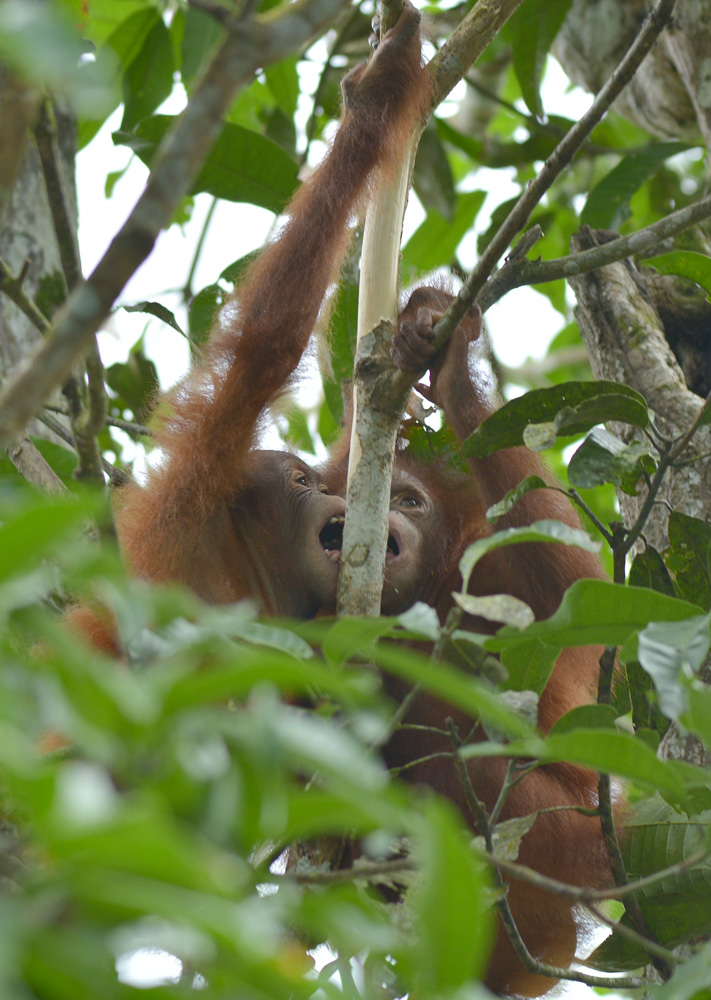
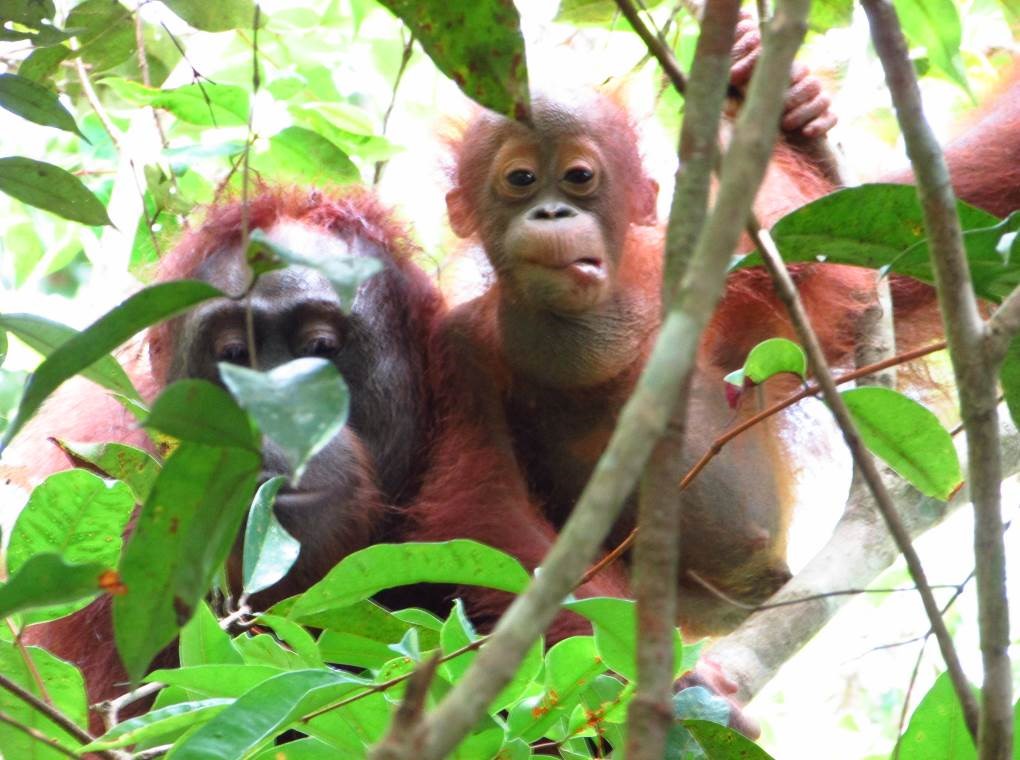
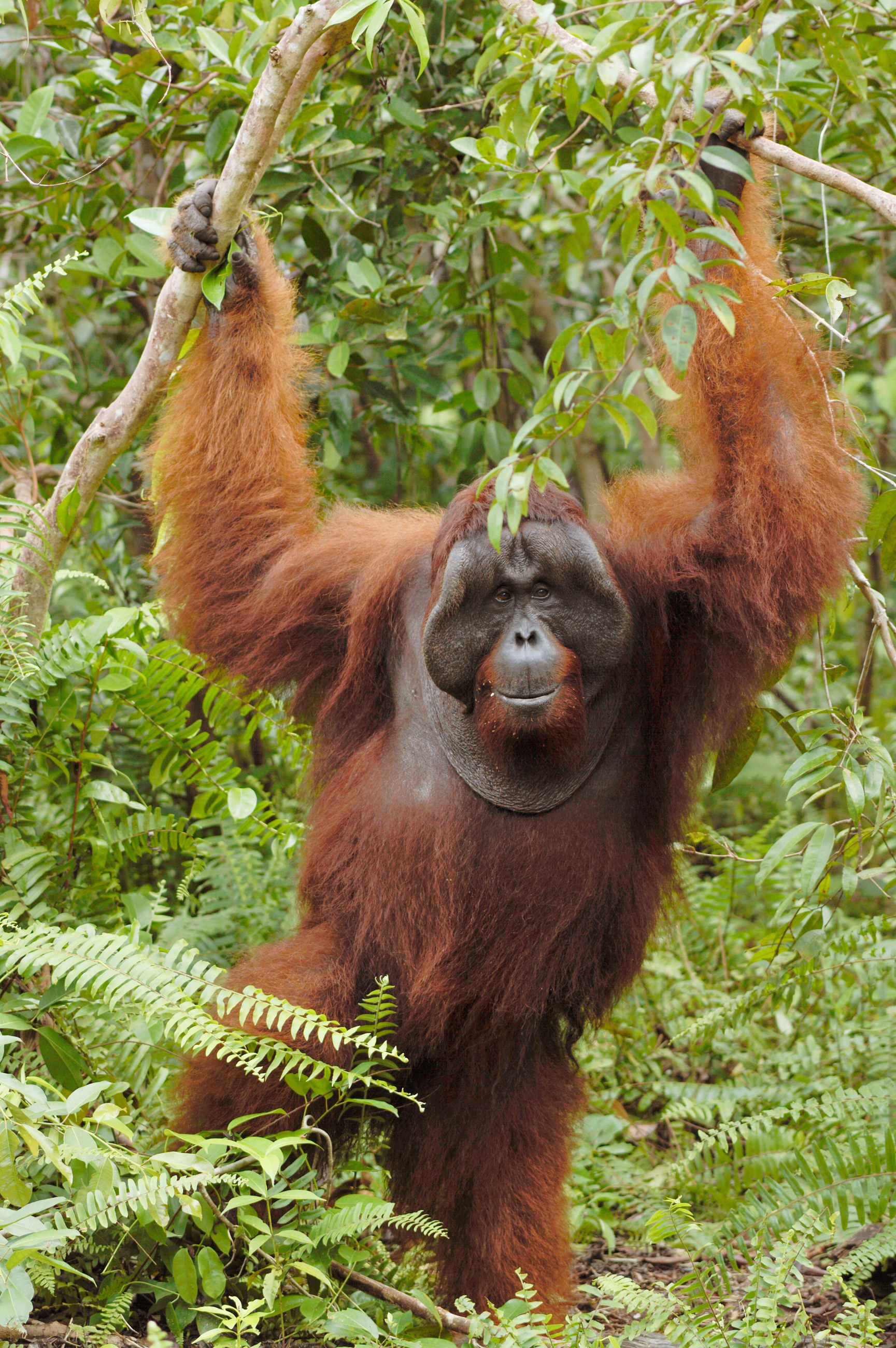
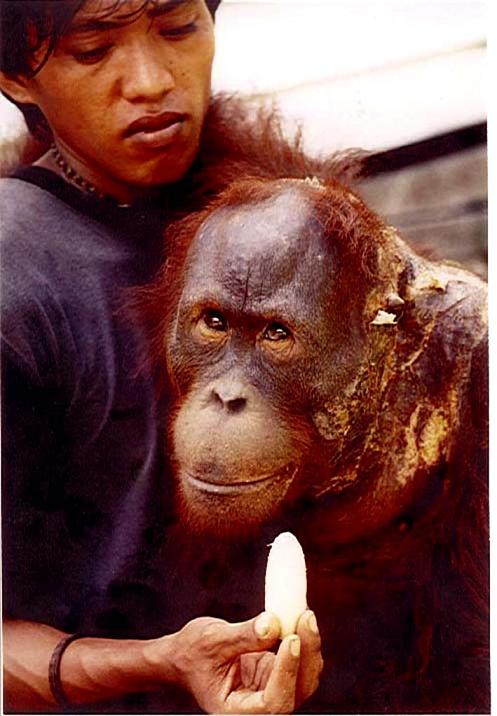
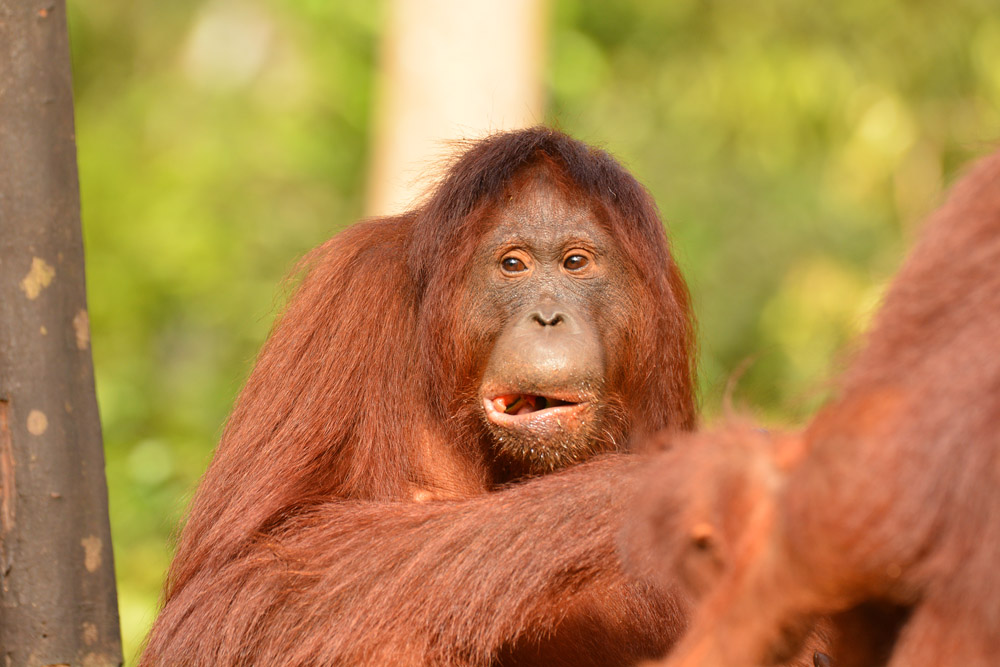
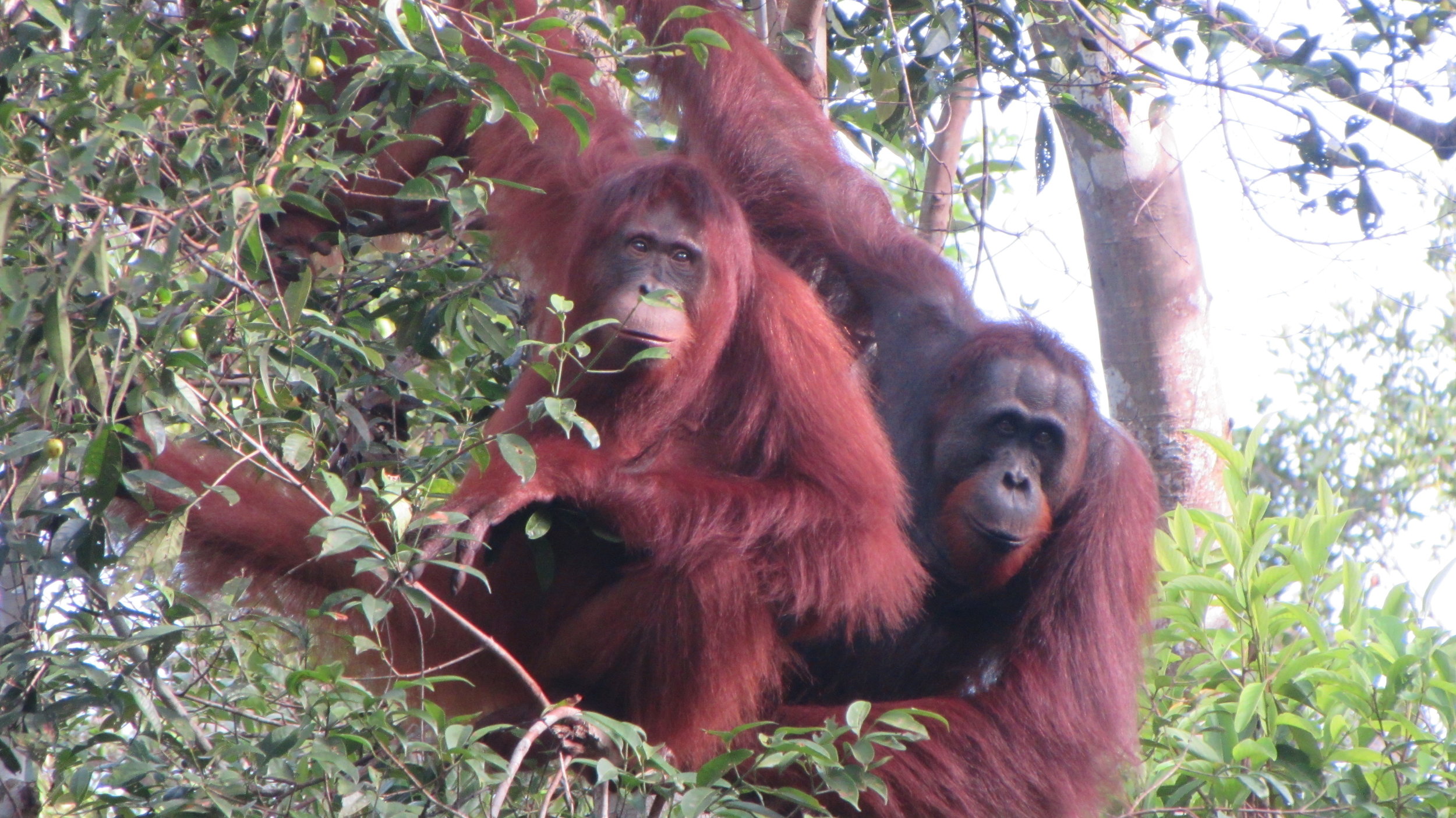
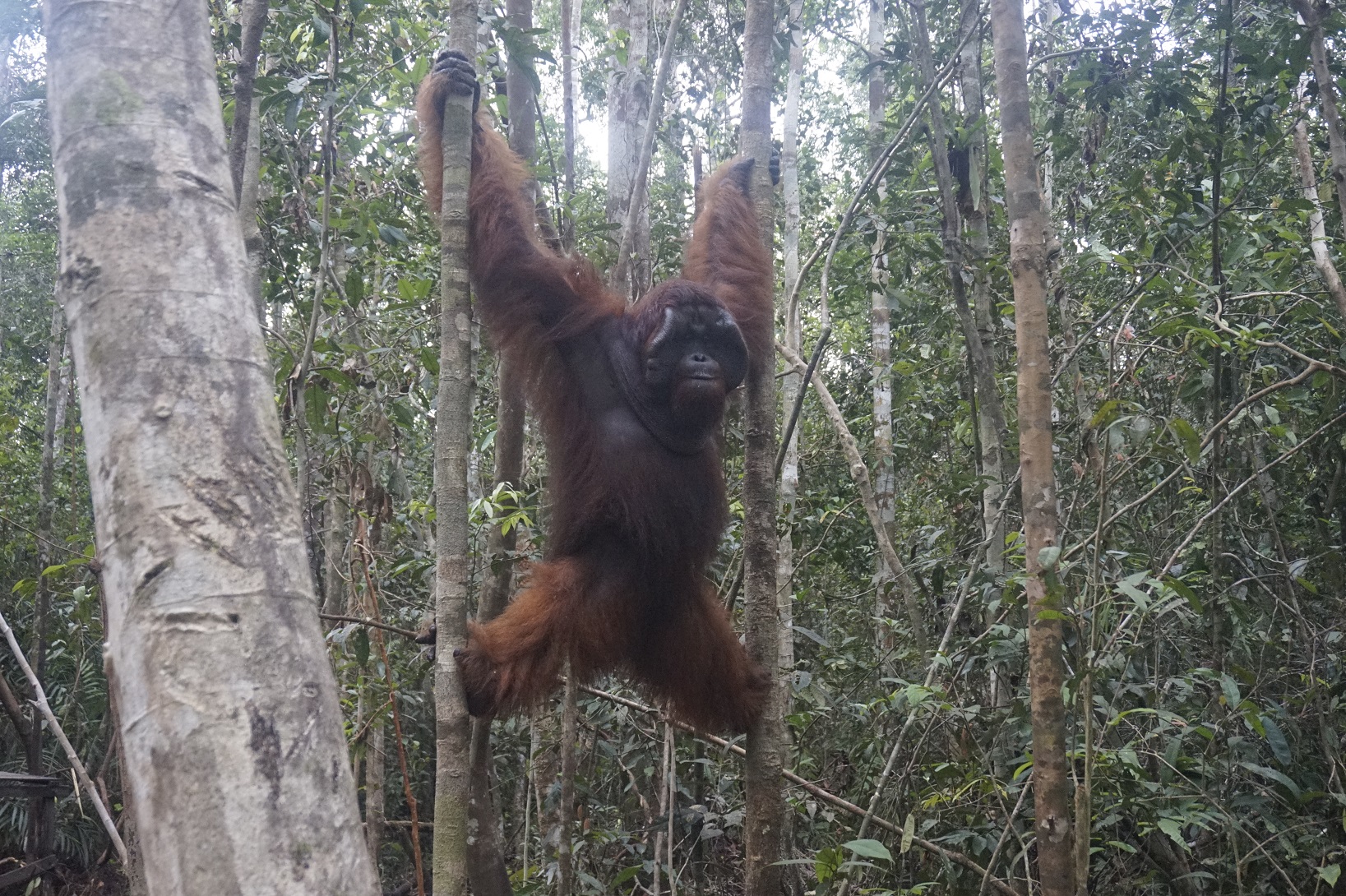
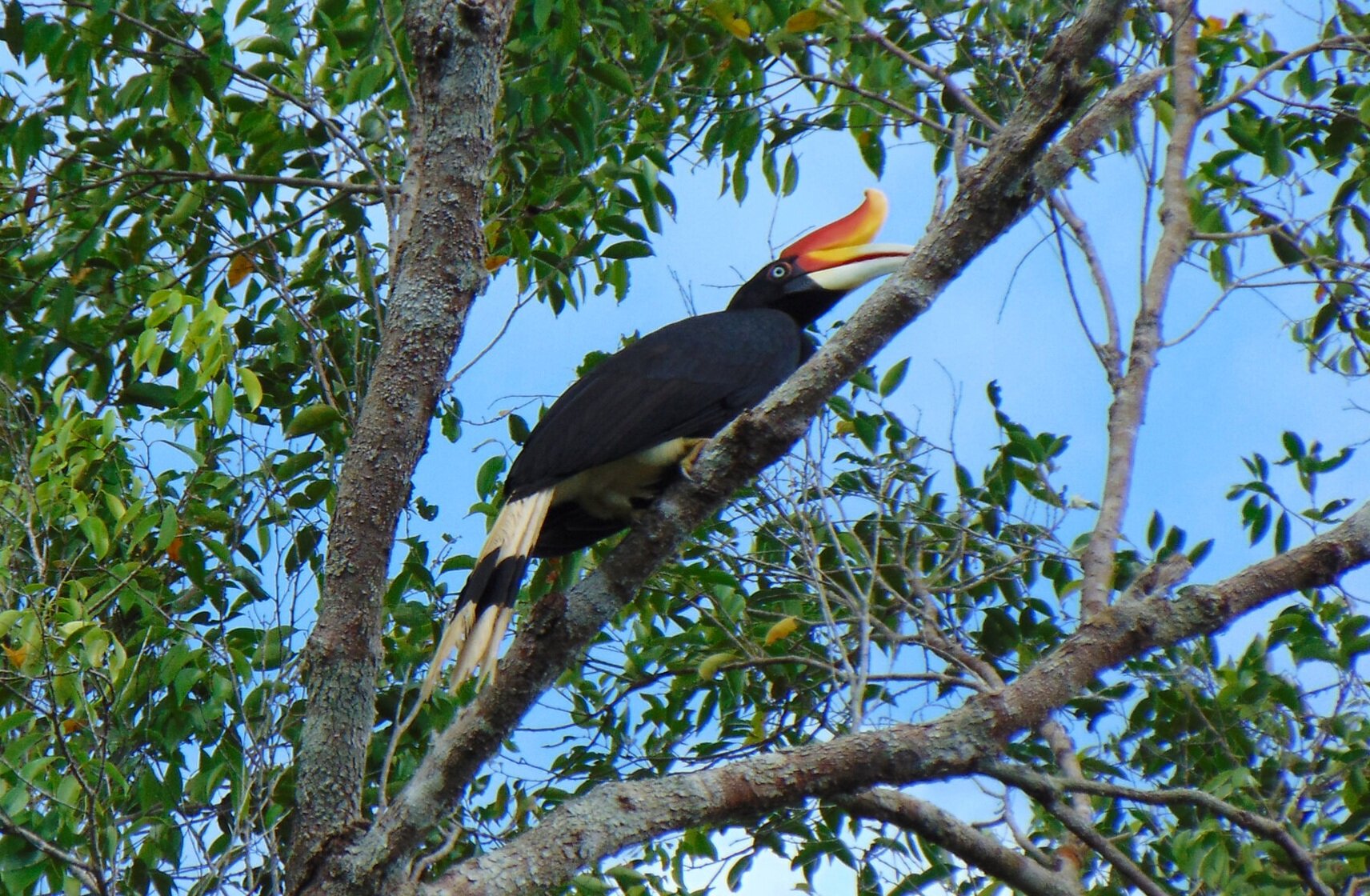
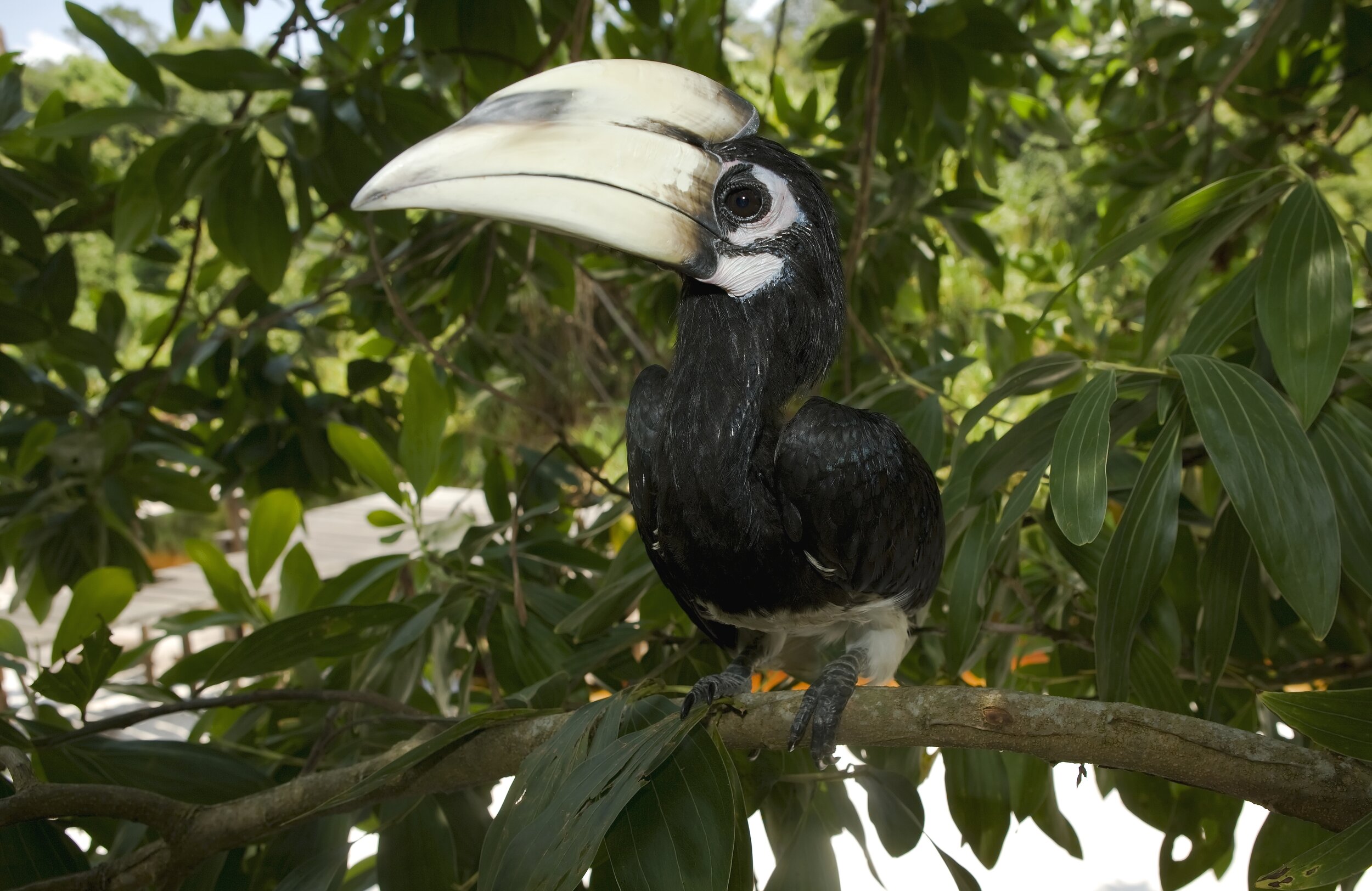
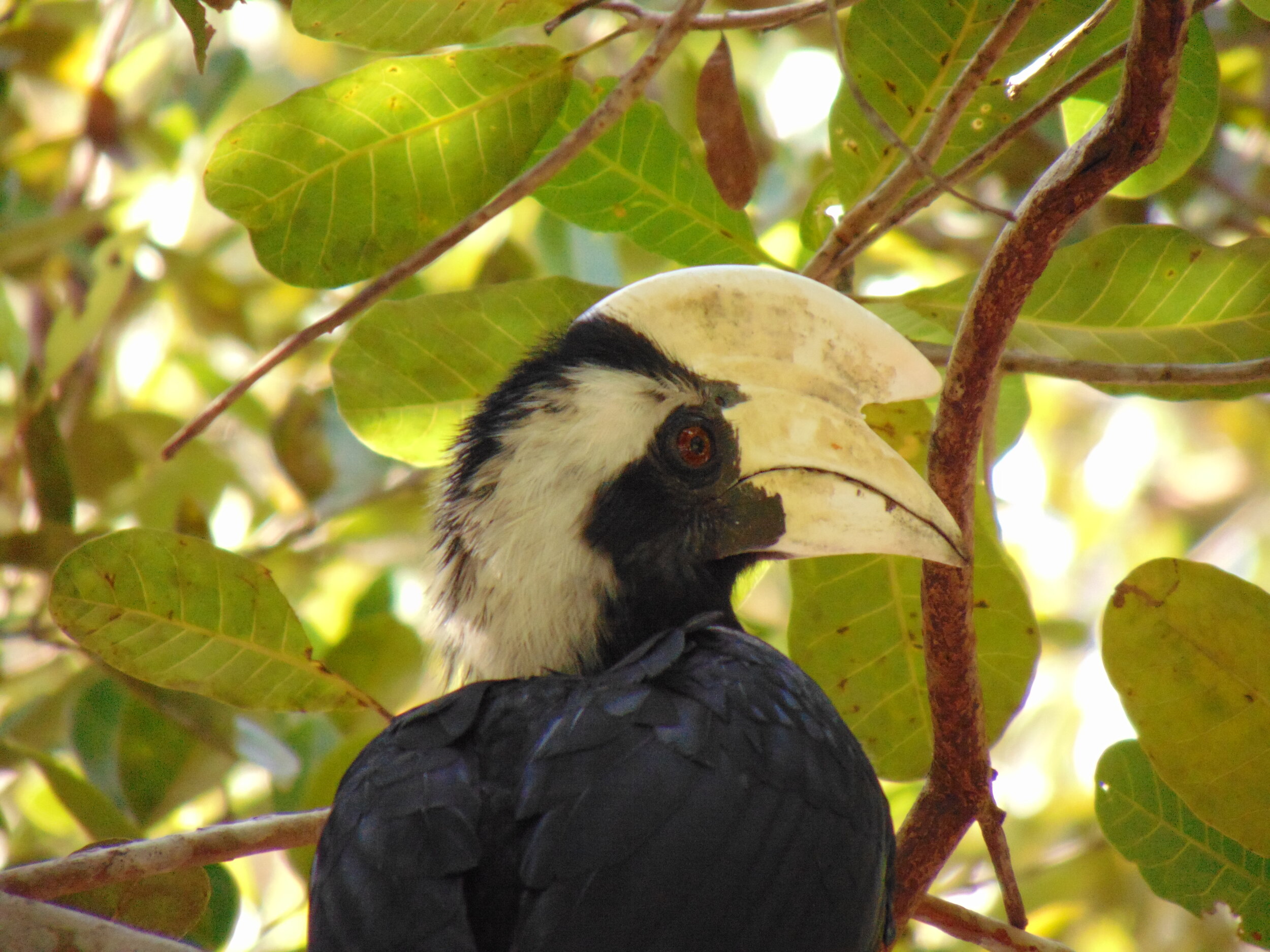
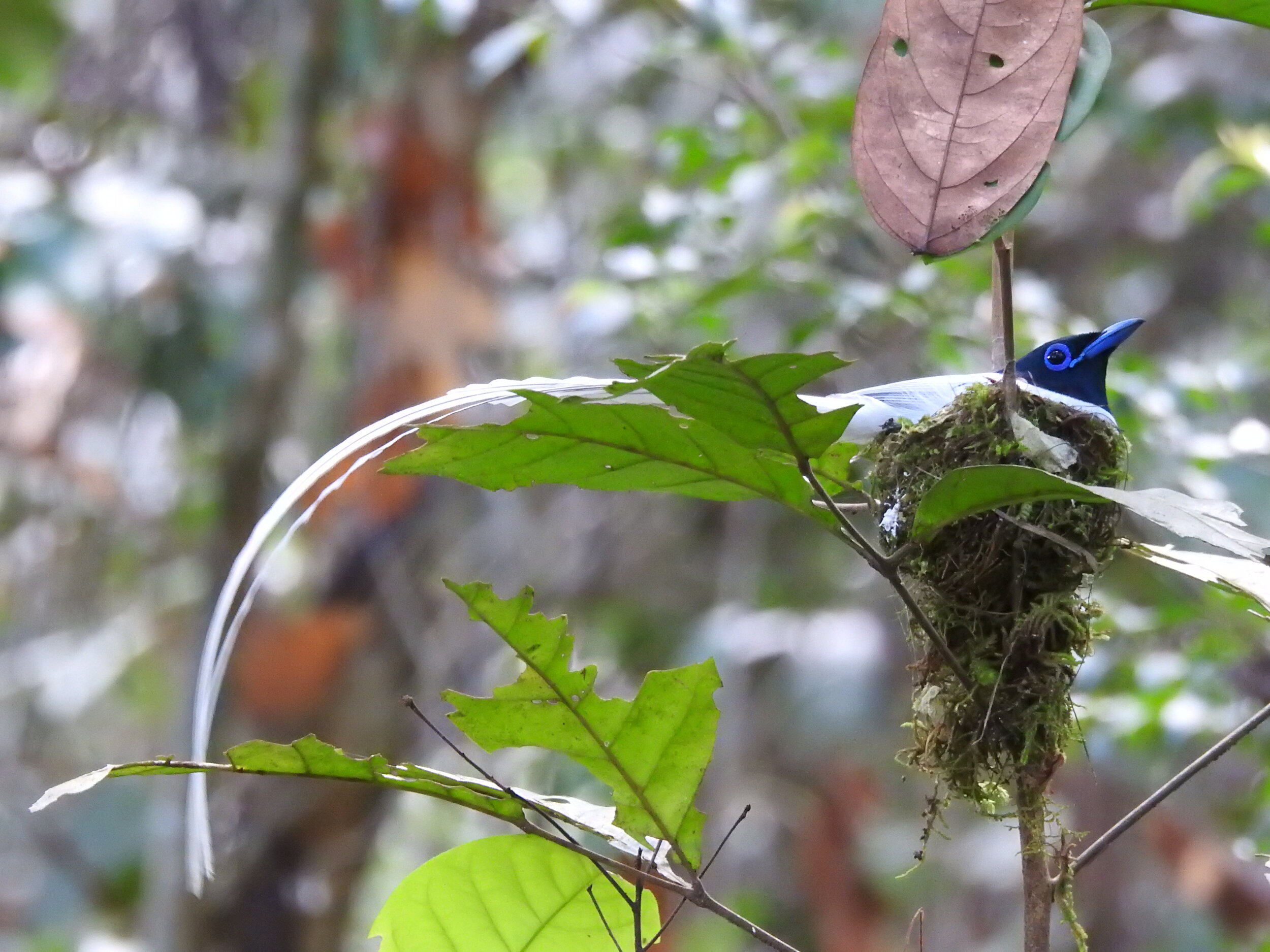
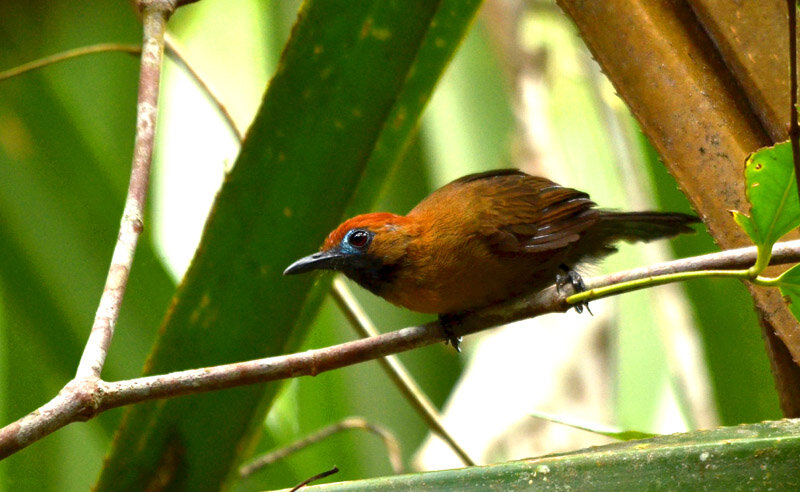
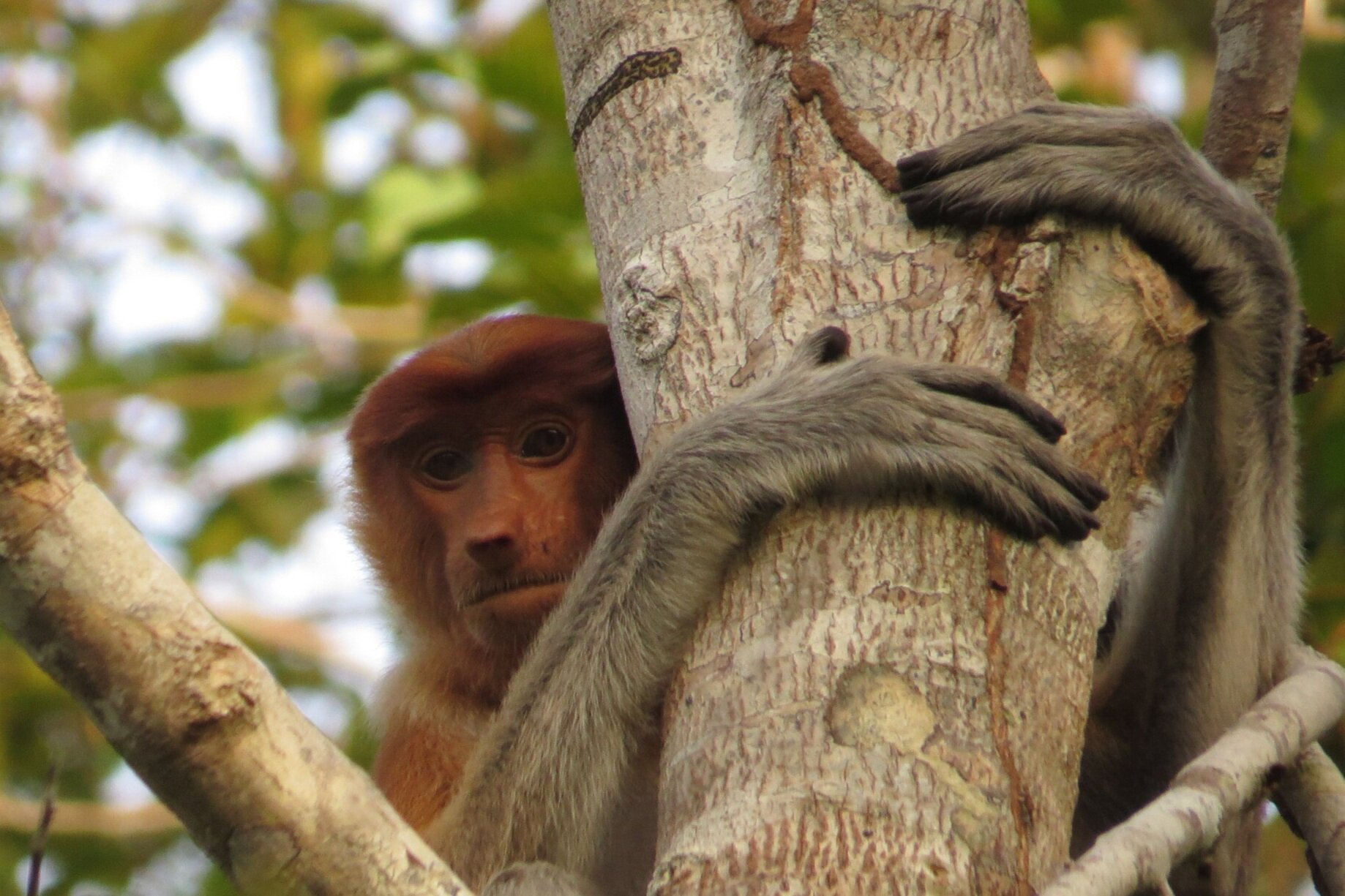
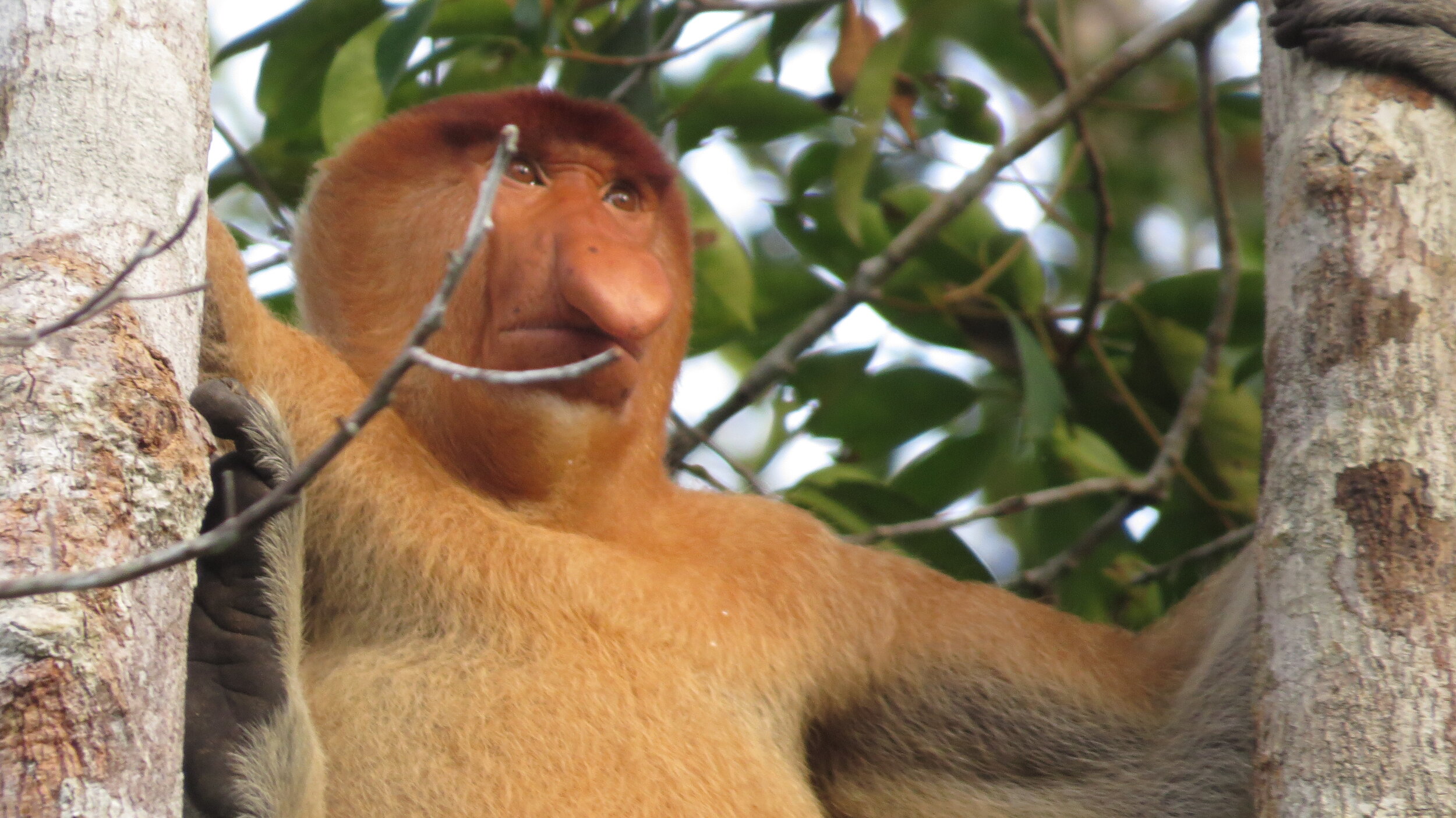
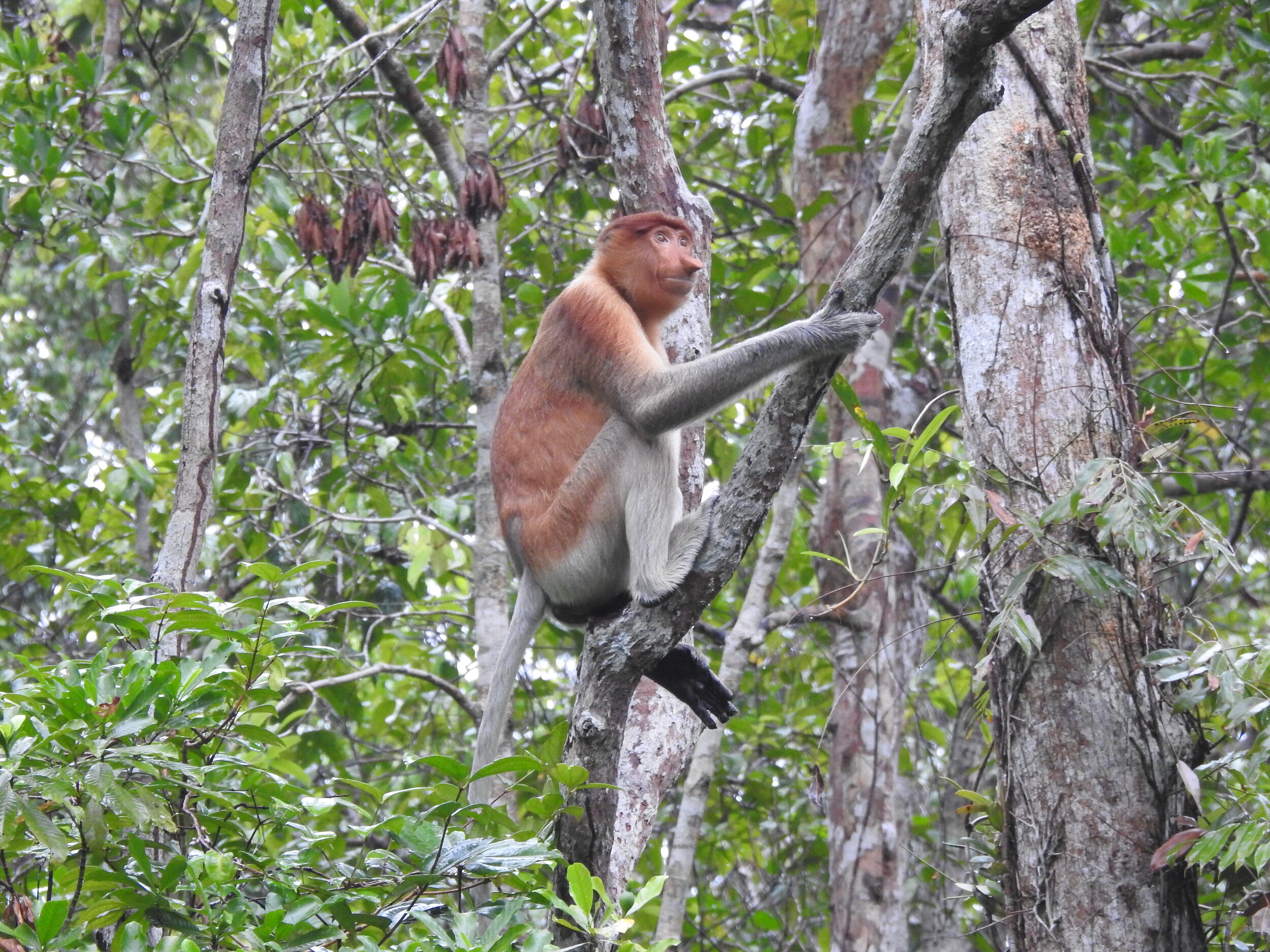
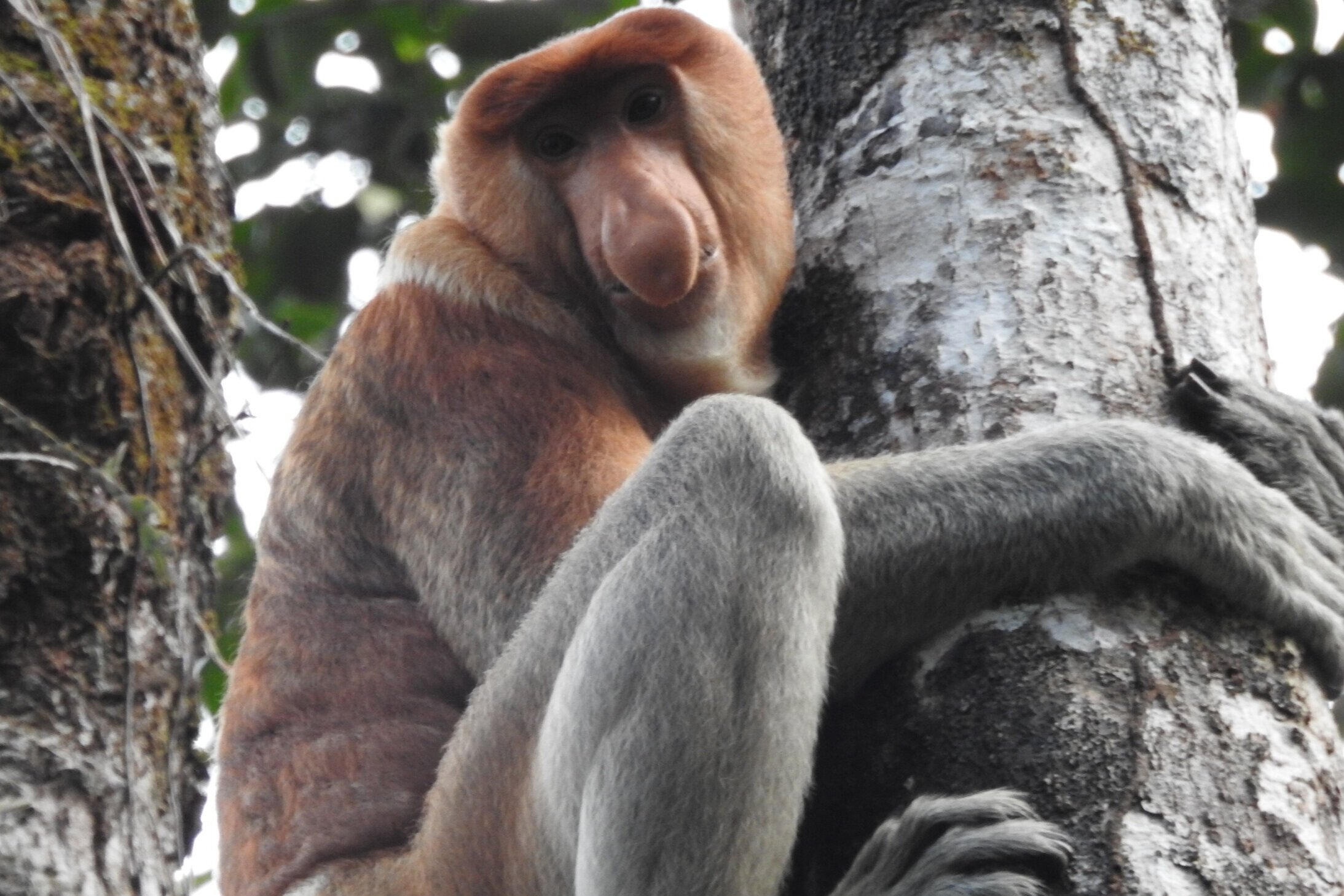
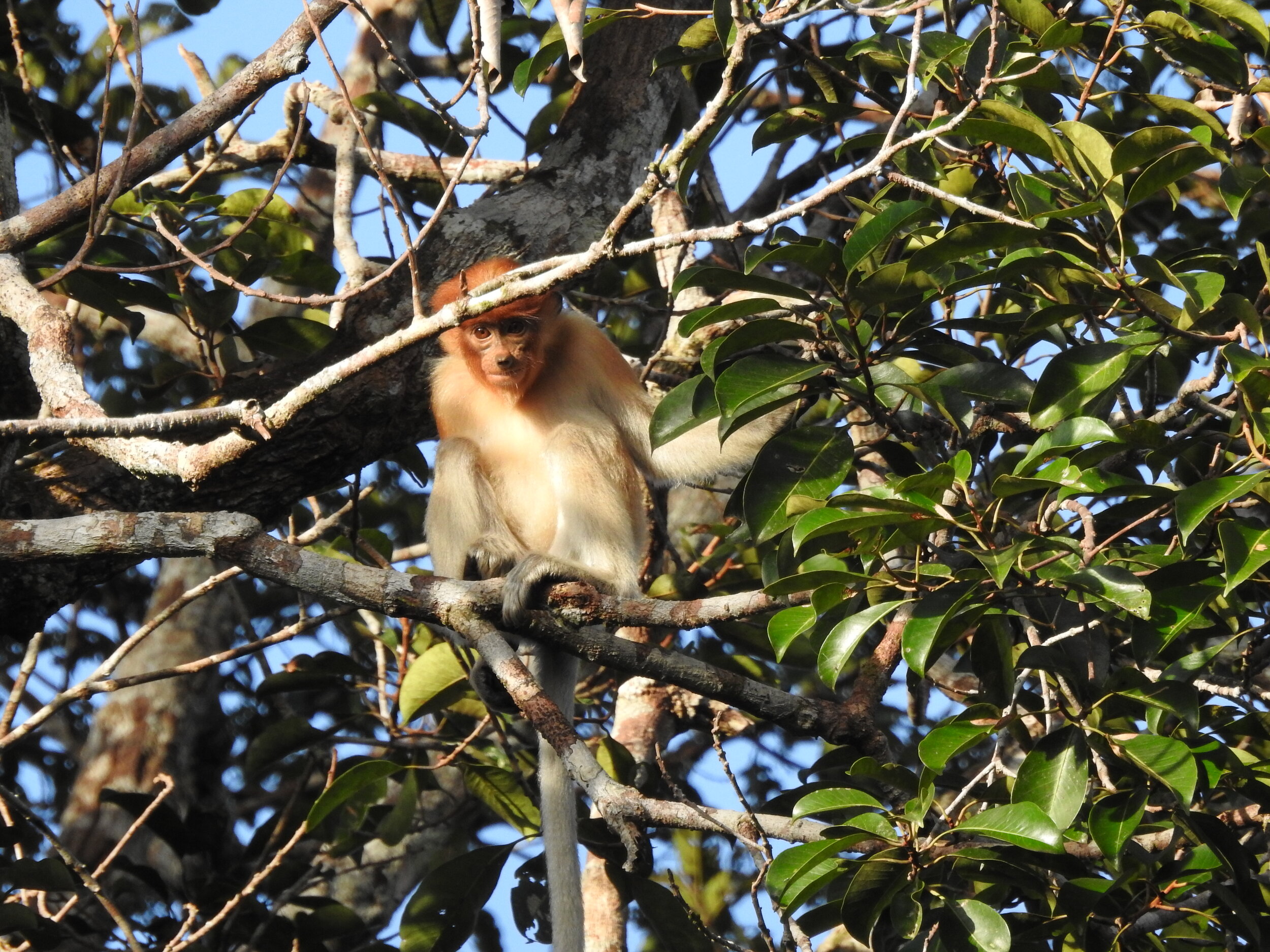
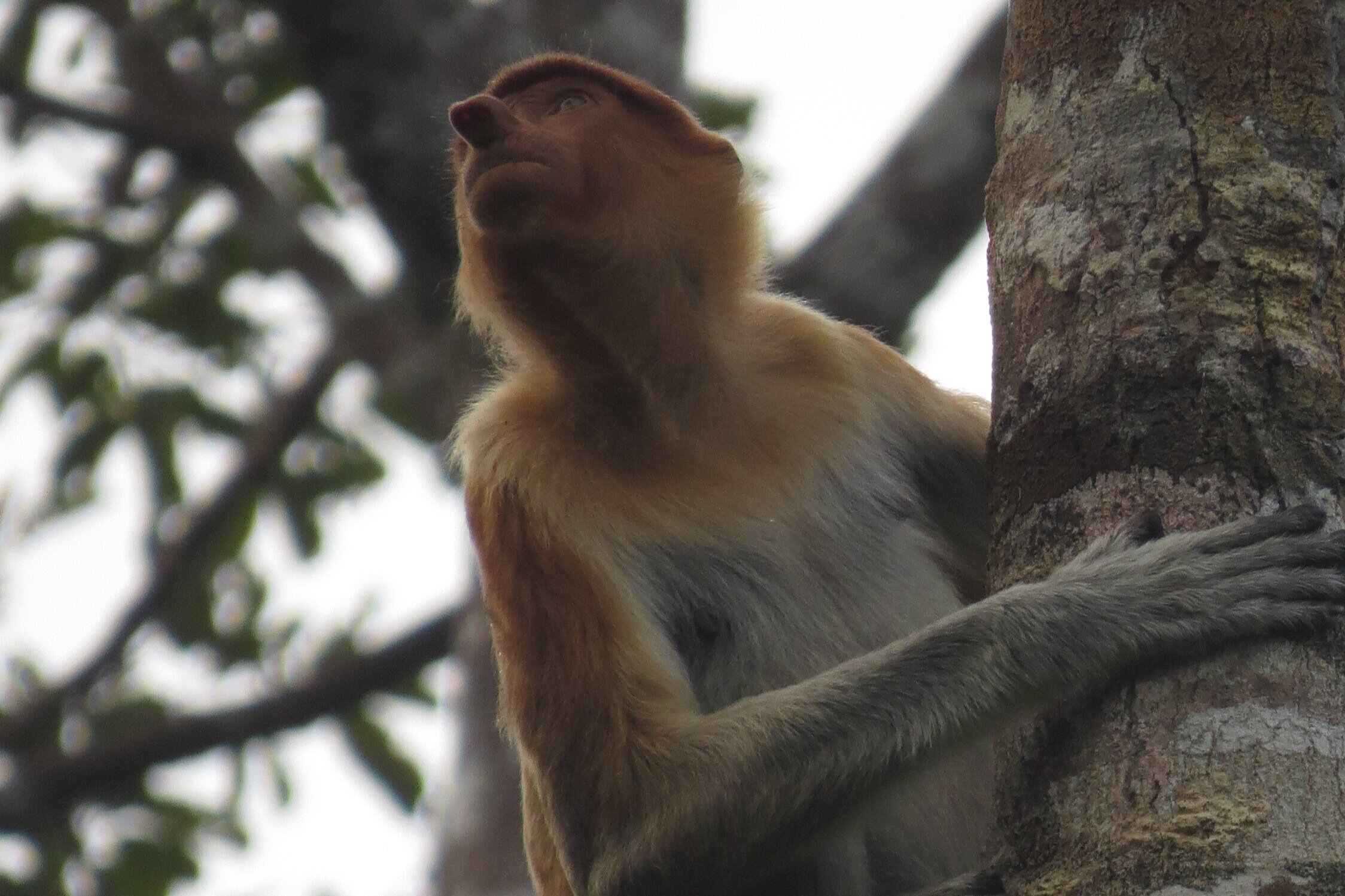
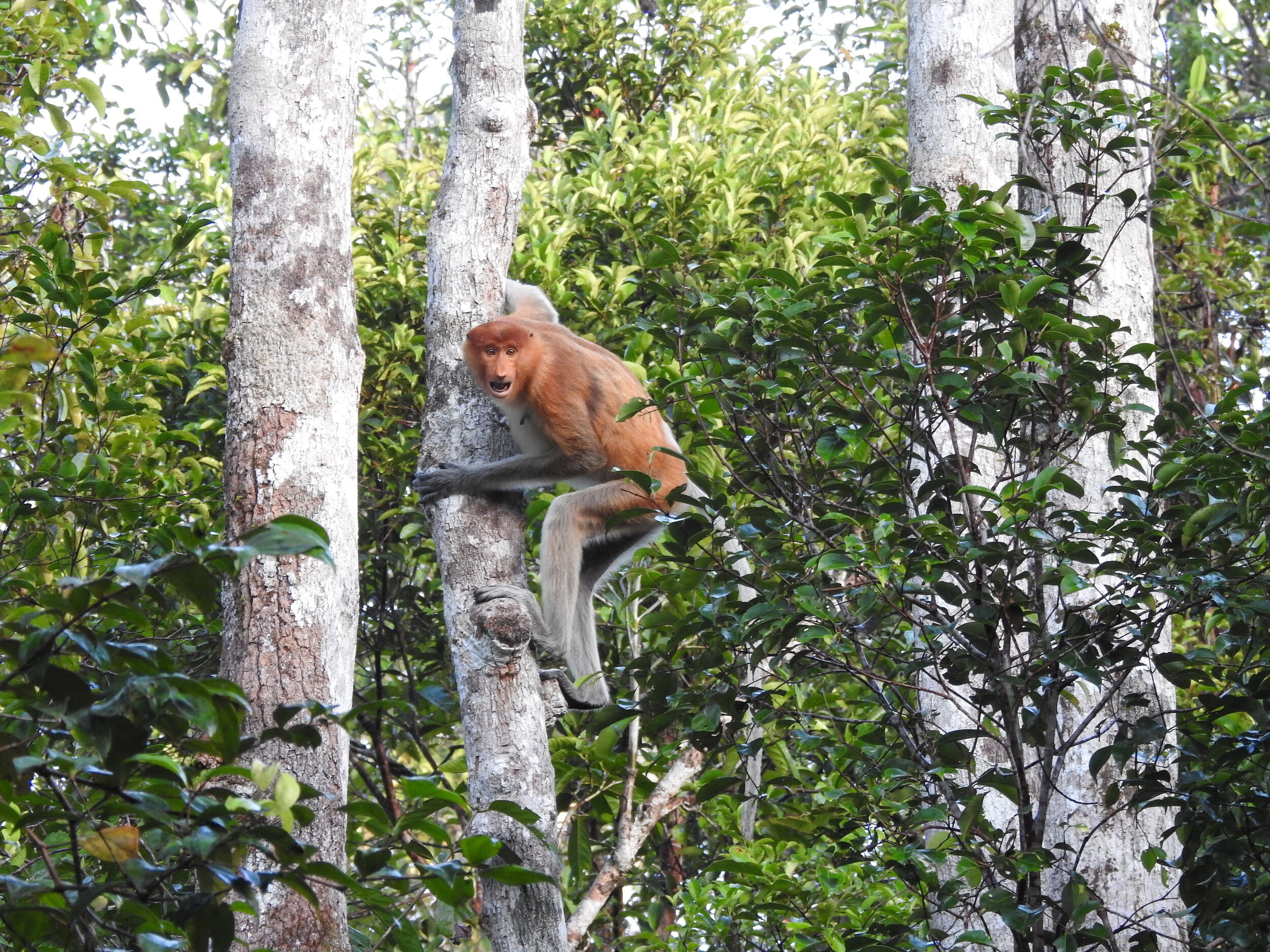
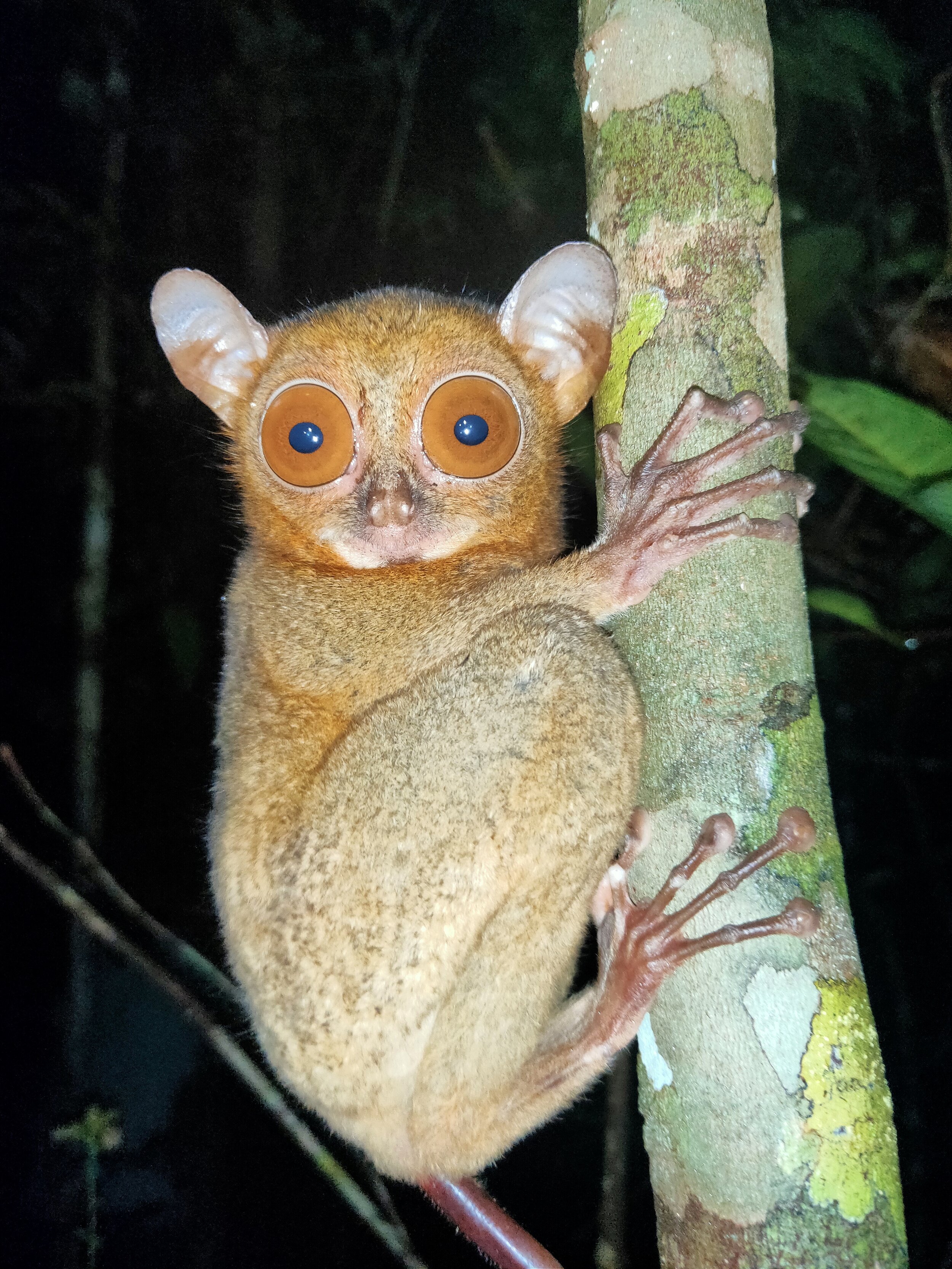
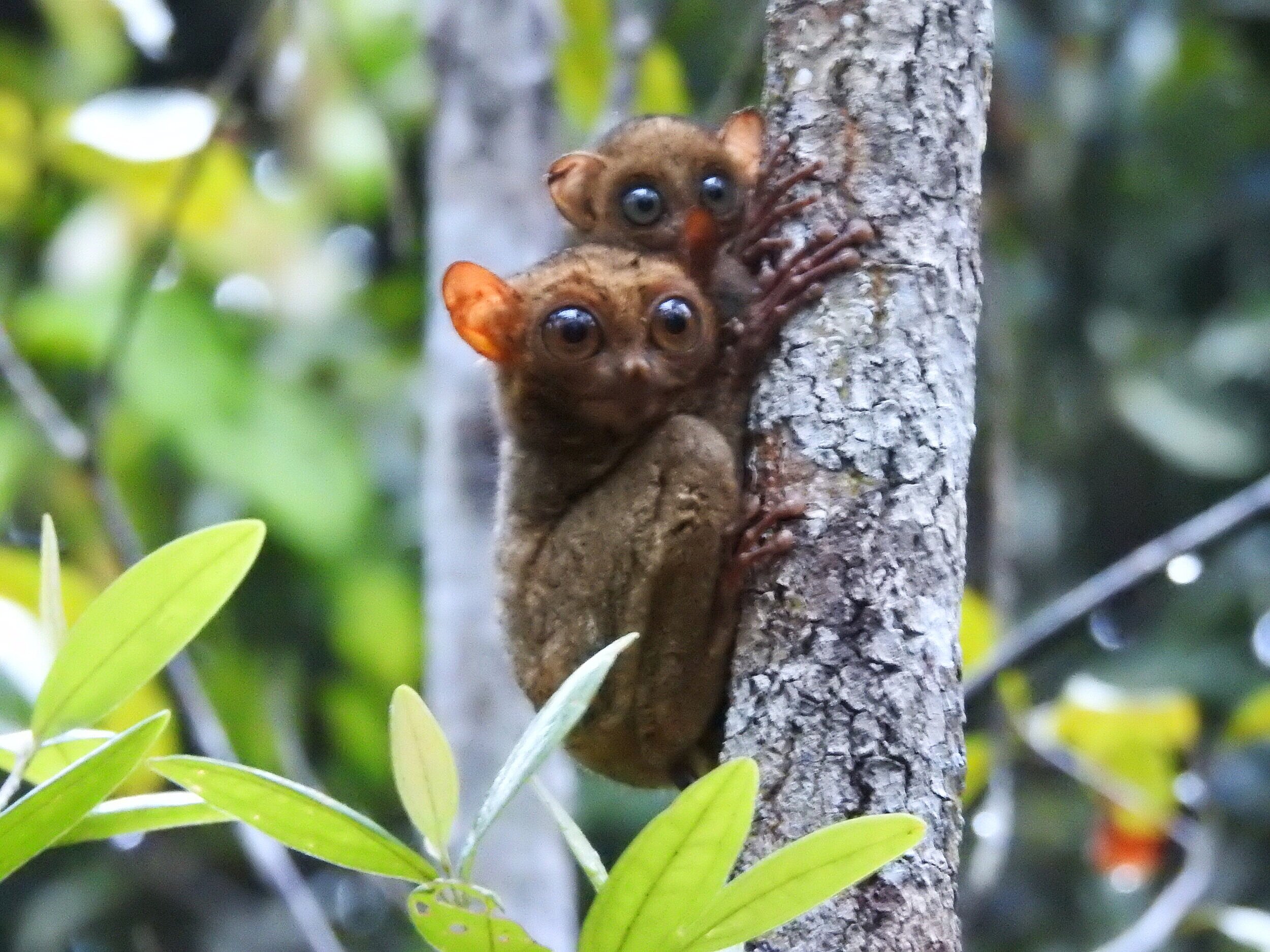
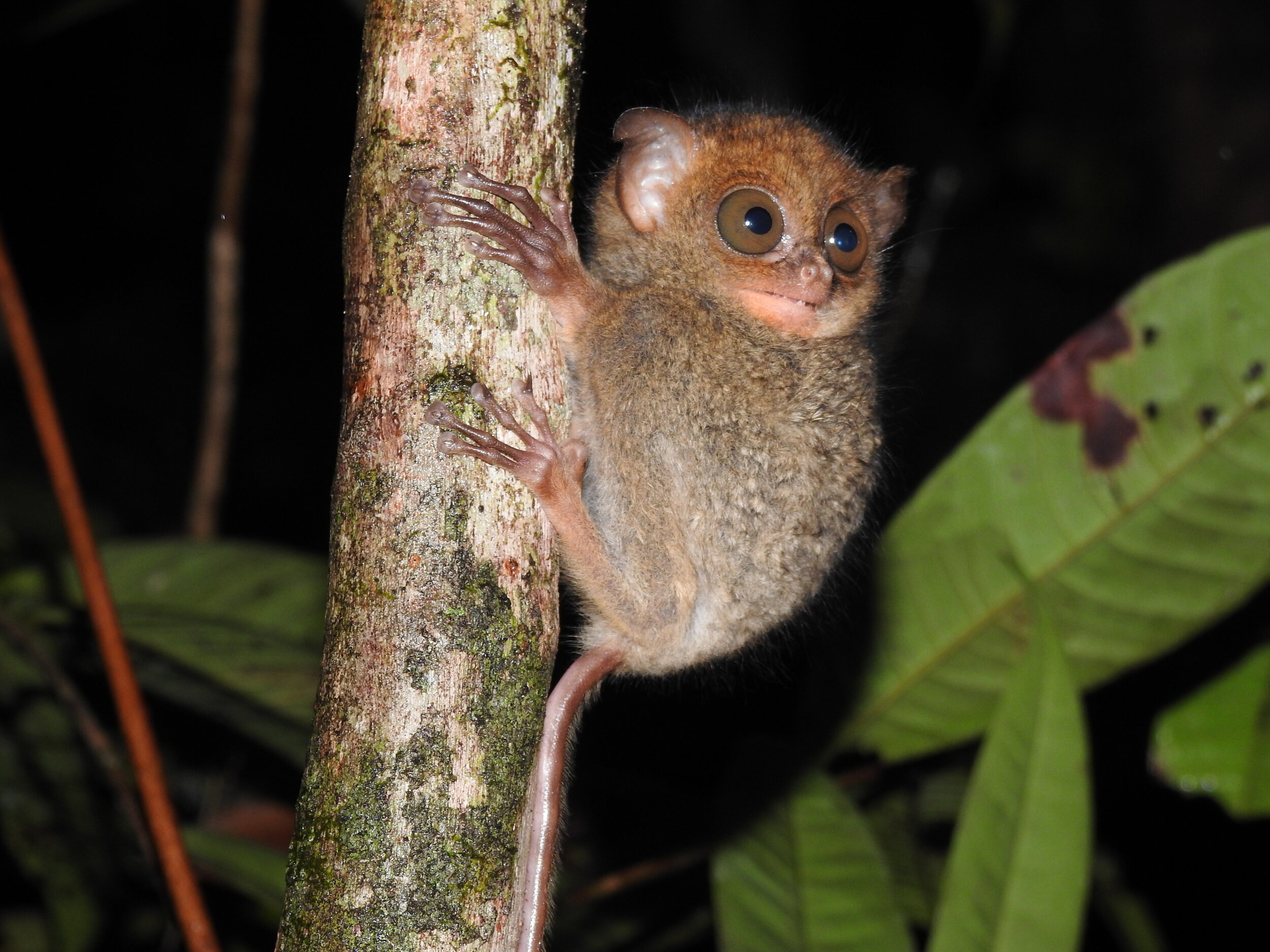
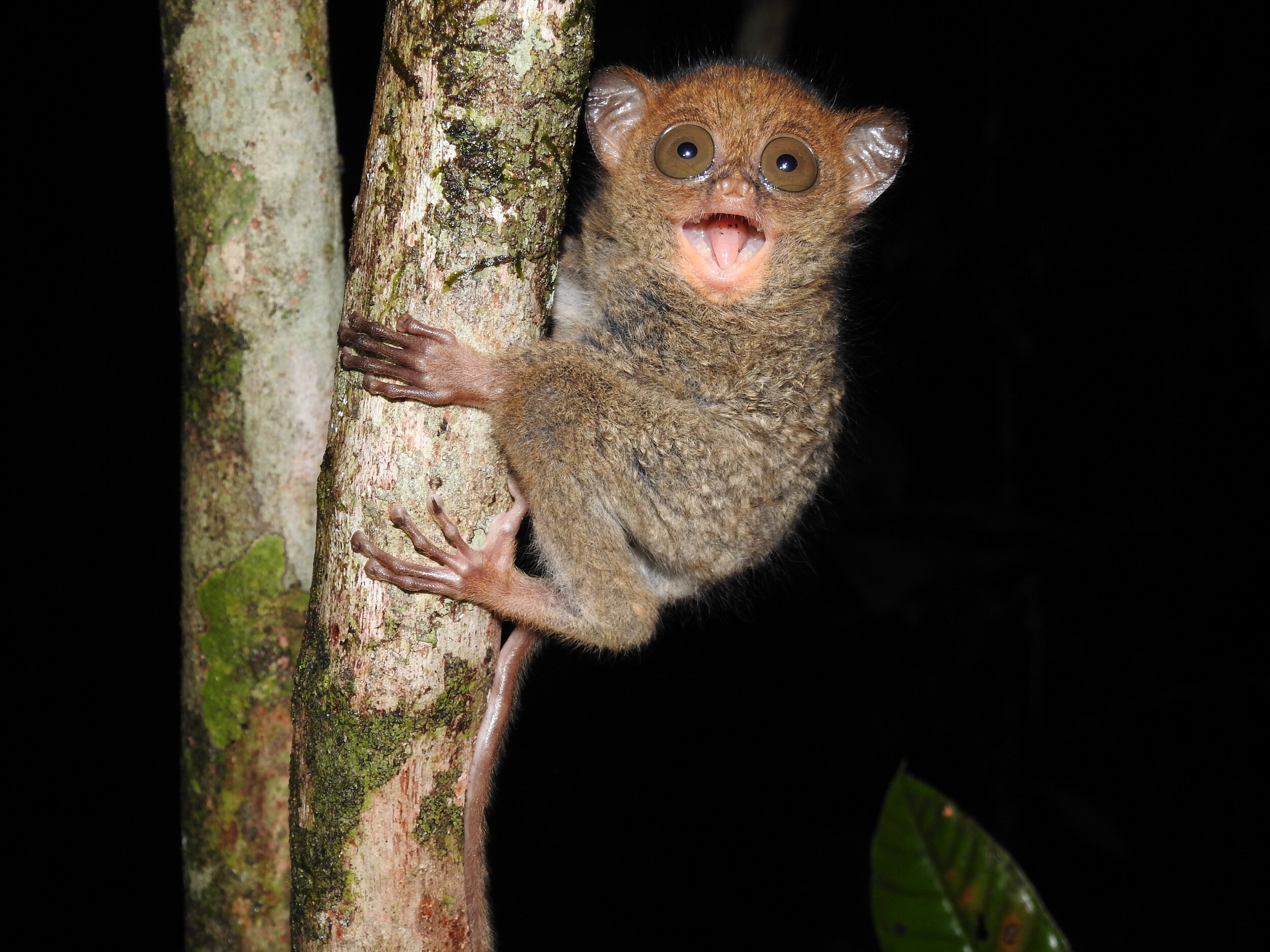
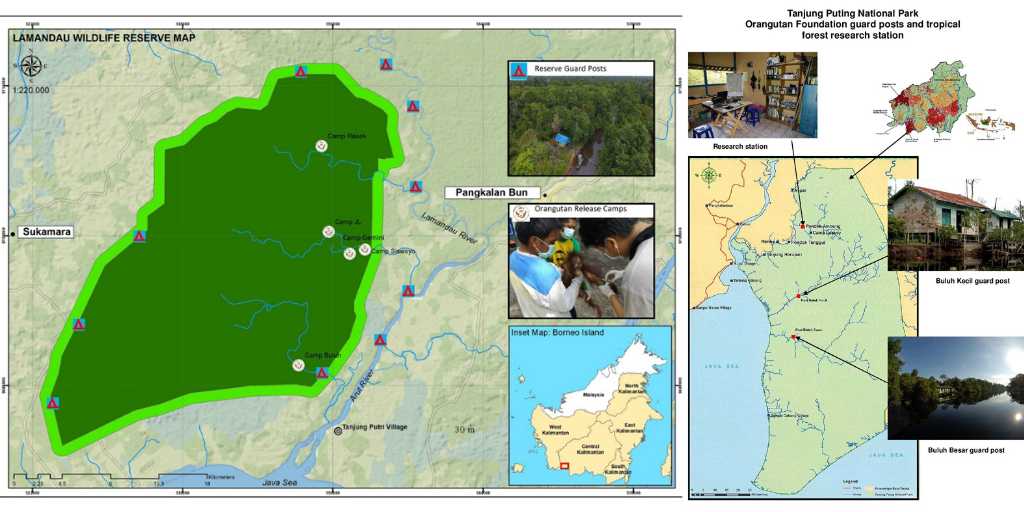
Despite covering around 6% of Earth’s land surface, it’s estimated that tropical rainforests are home to 80% of our planet’s terrestrial biodiversity. These diverse forests are truly bursting with life, and within Tanjung Puting National Park and the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve in Indonesian Borneo, there are prime examples of this rich habitat.
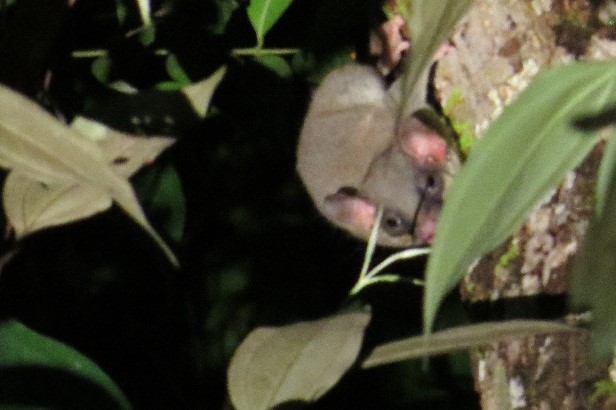
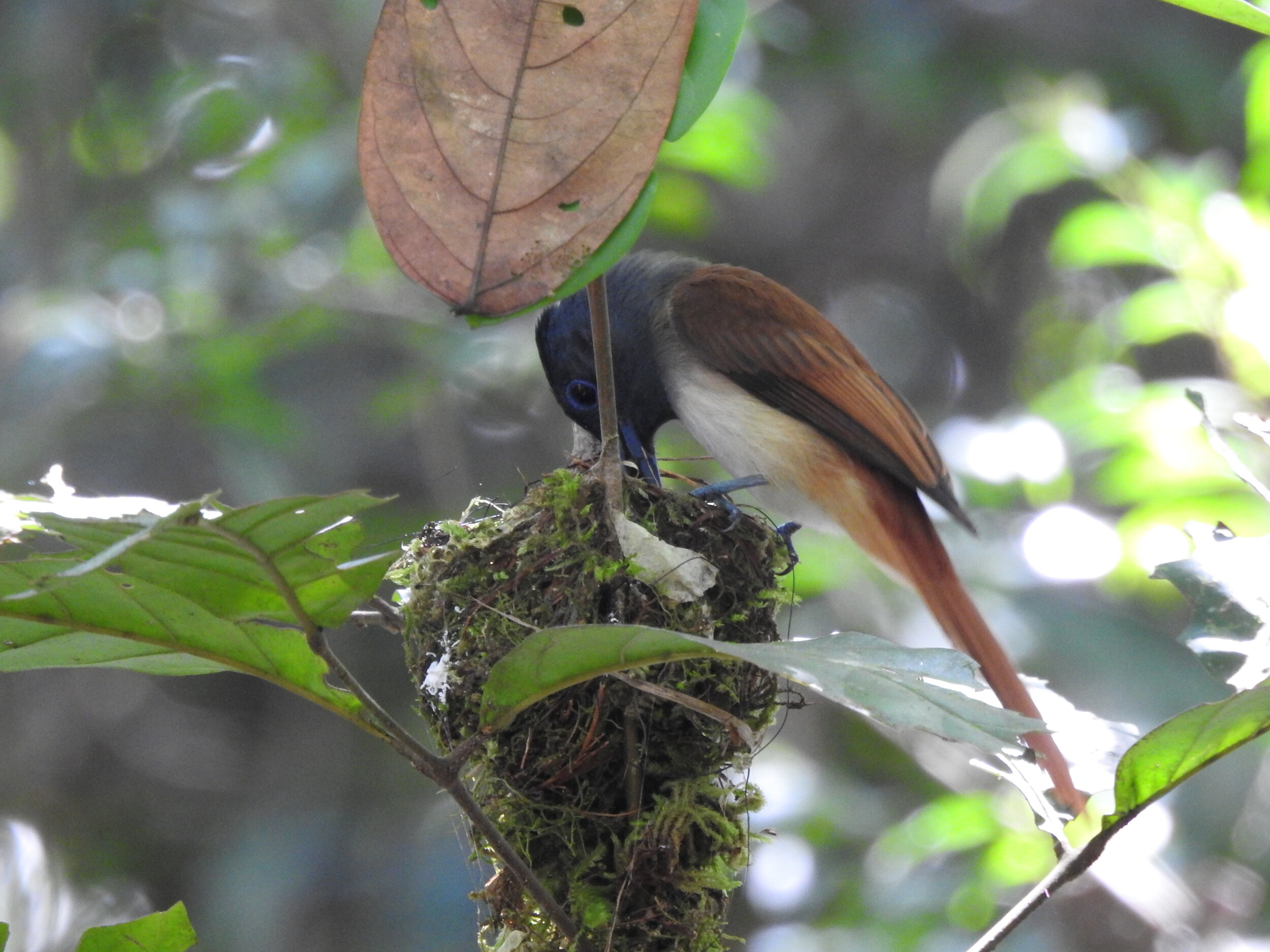
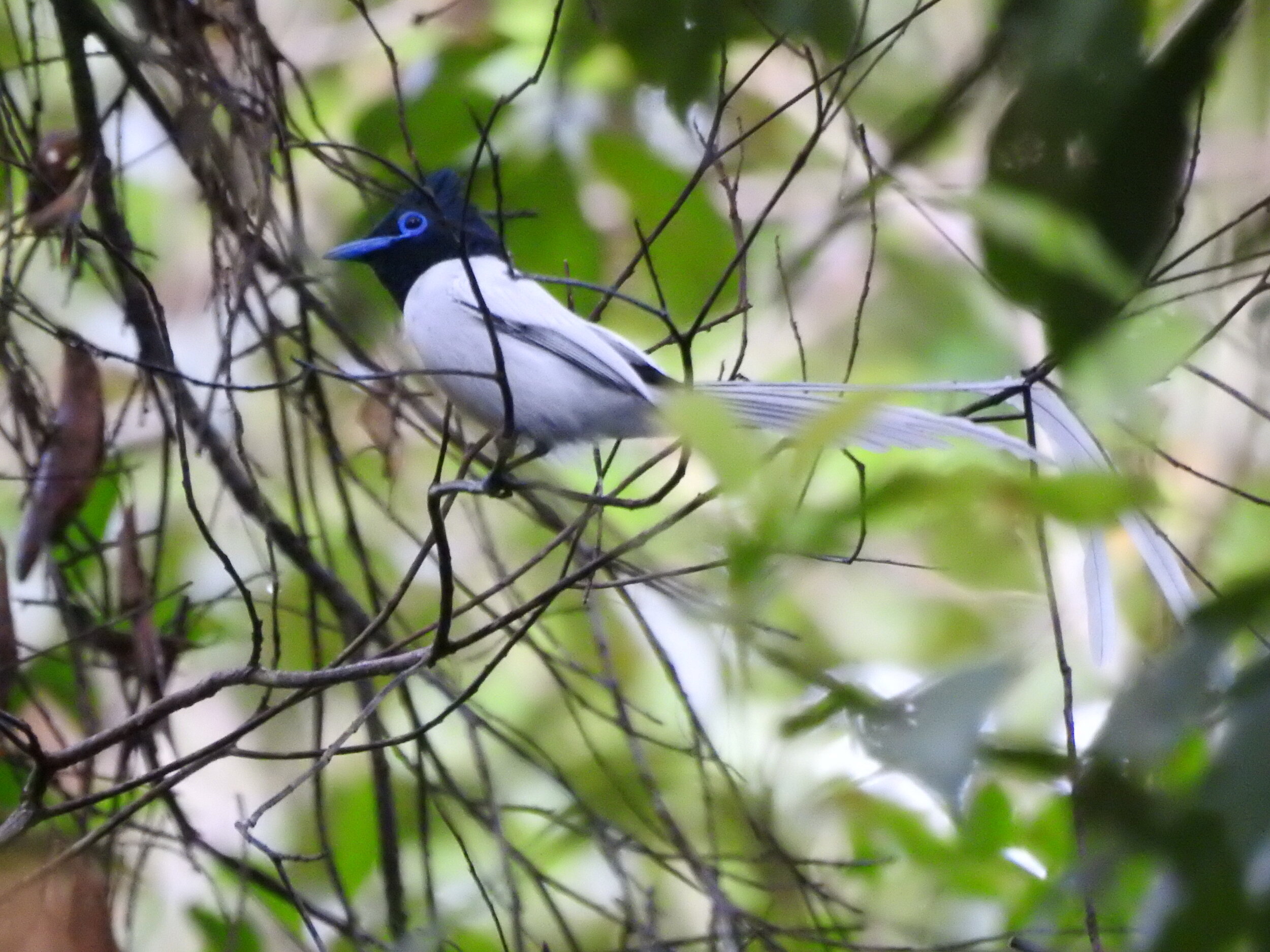
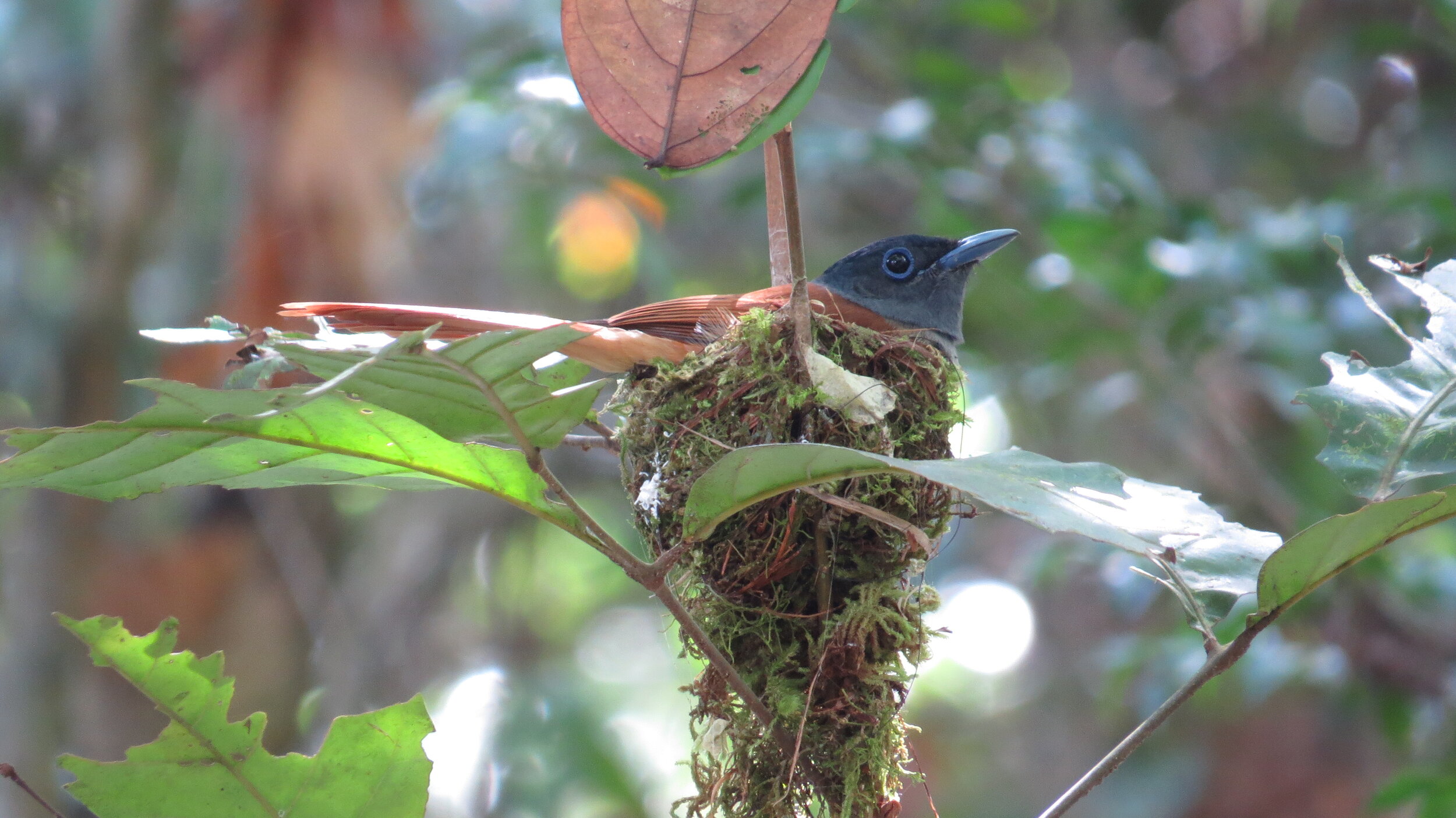
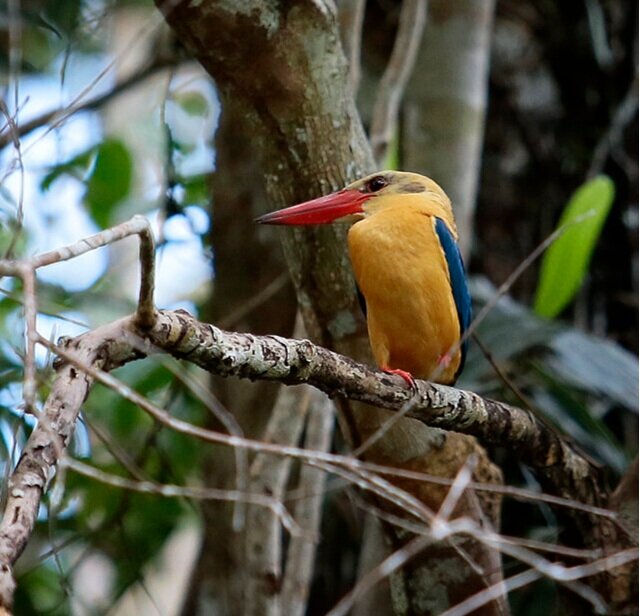
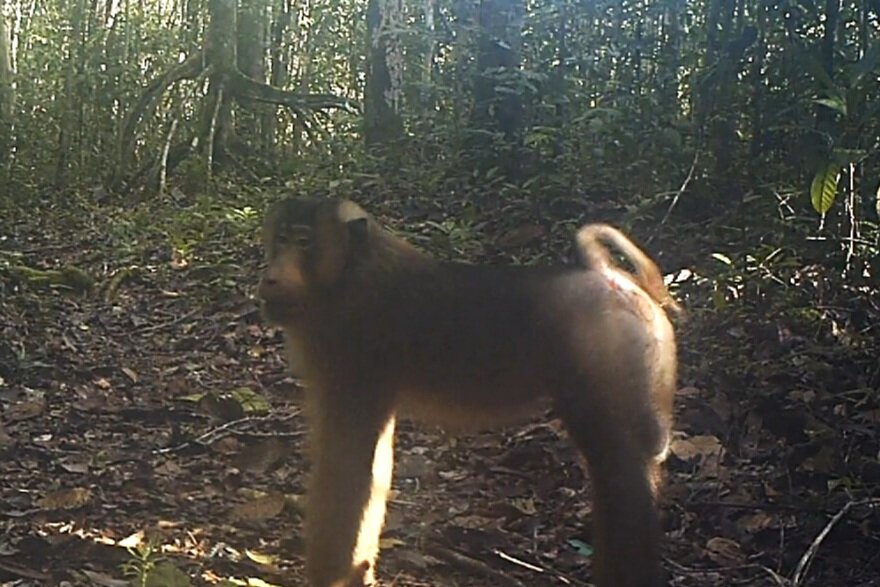
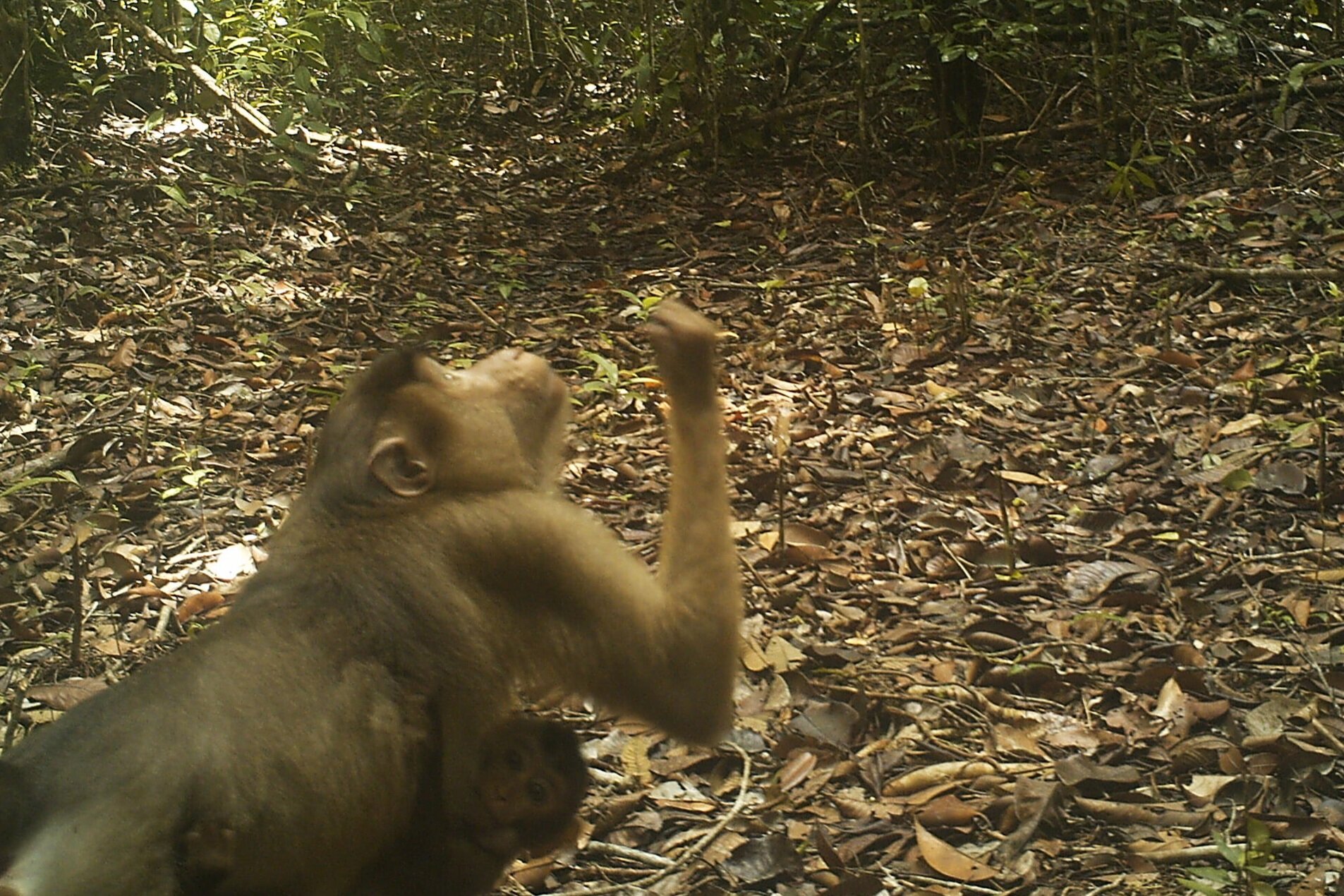
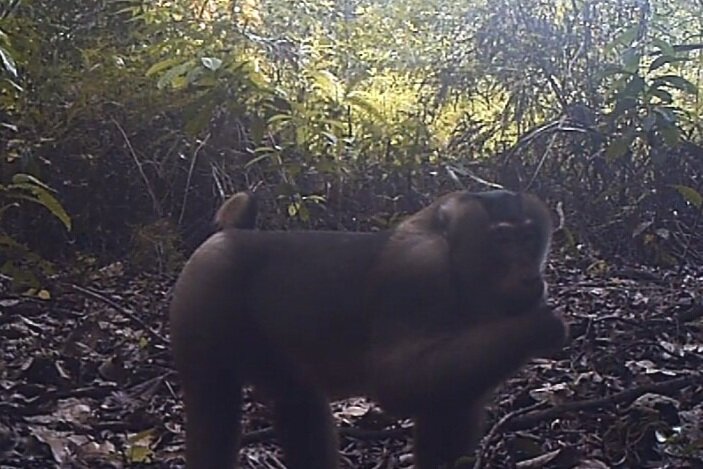
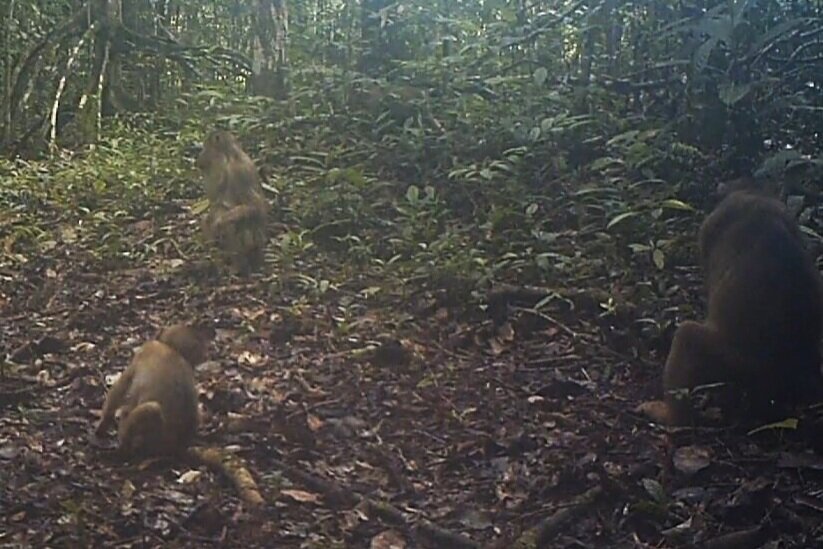
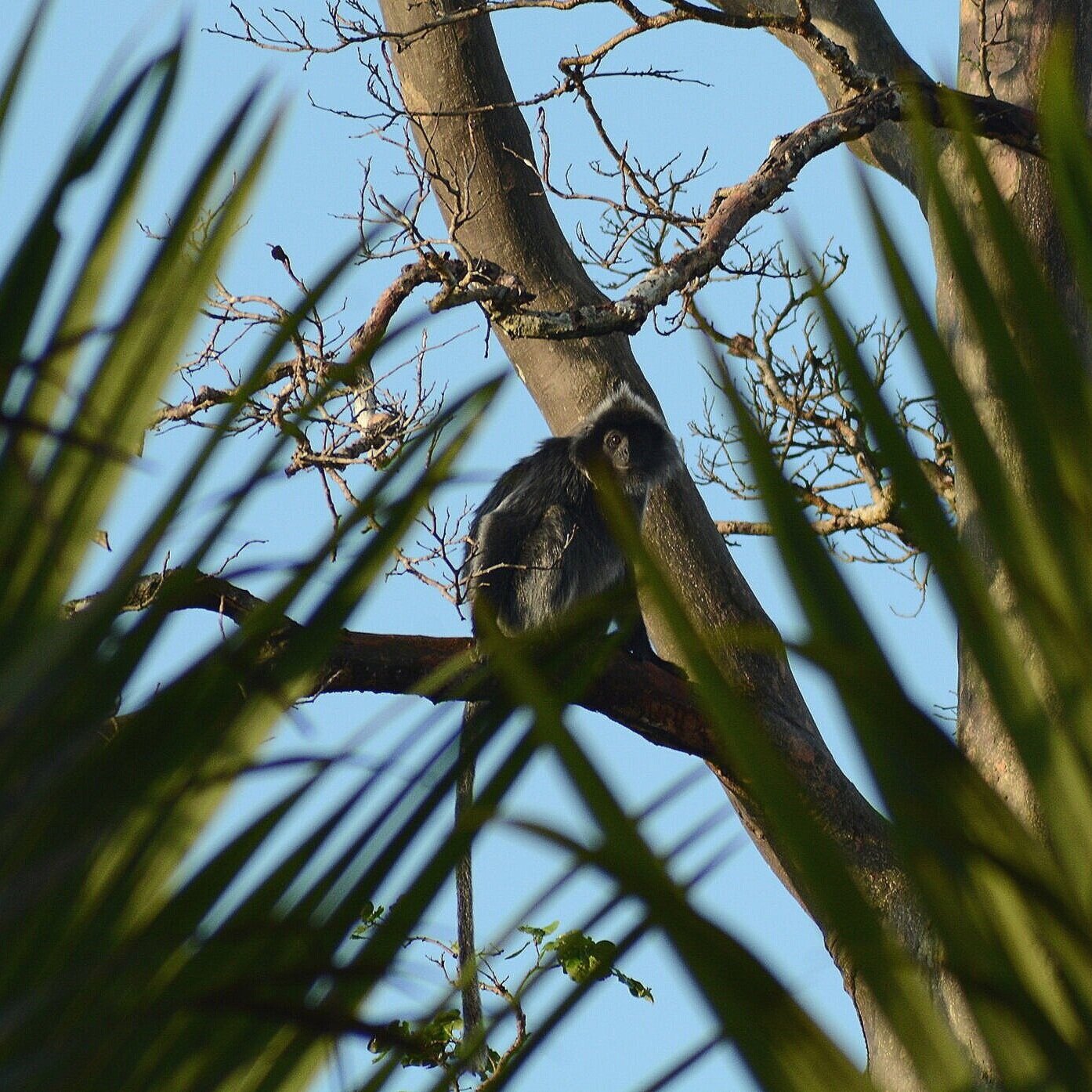
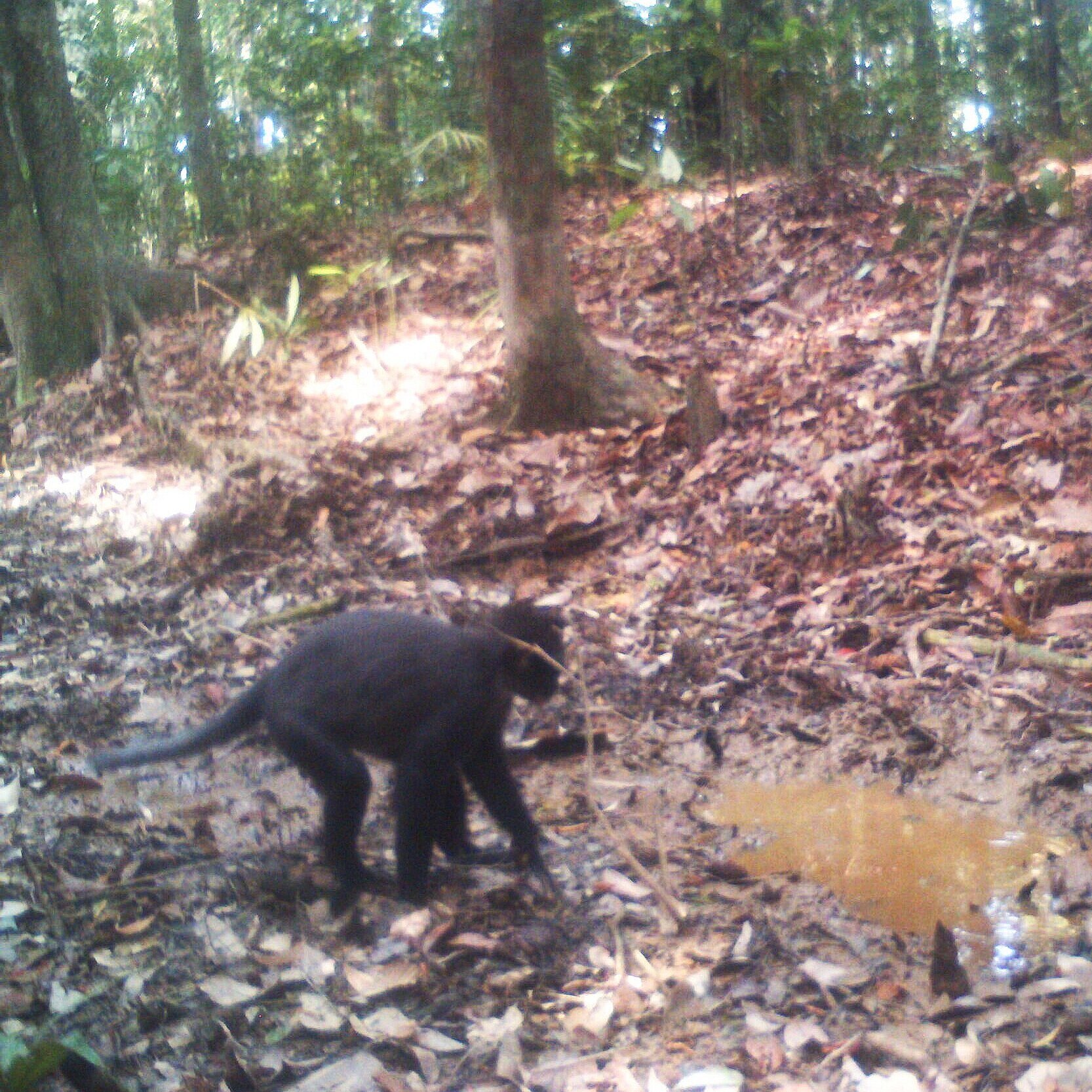
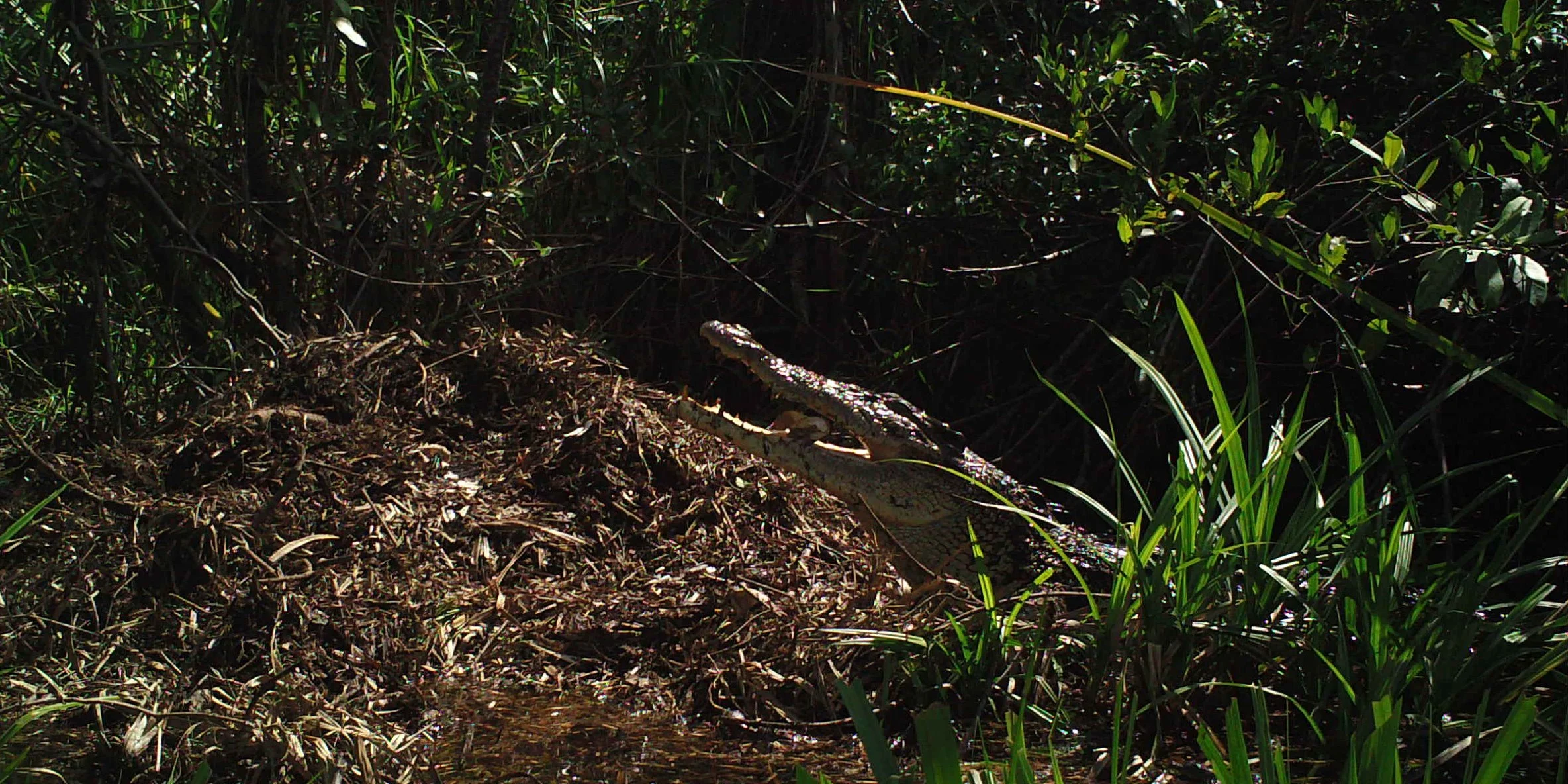
During their work in the forest, our field teams spot orangutans and other primates in the trees, and yet they rarely see other Mammals as many tend to venture out at night. The elusiveness of many mammalian species in the forest means that the only time our team observe them is on remote camera traps or during wildlife rescues. Some of these fascinating species include:
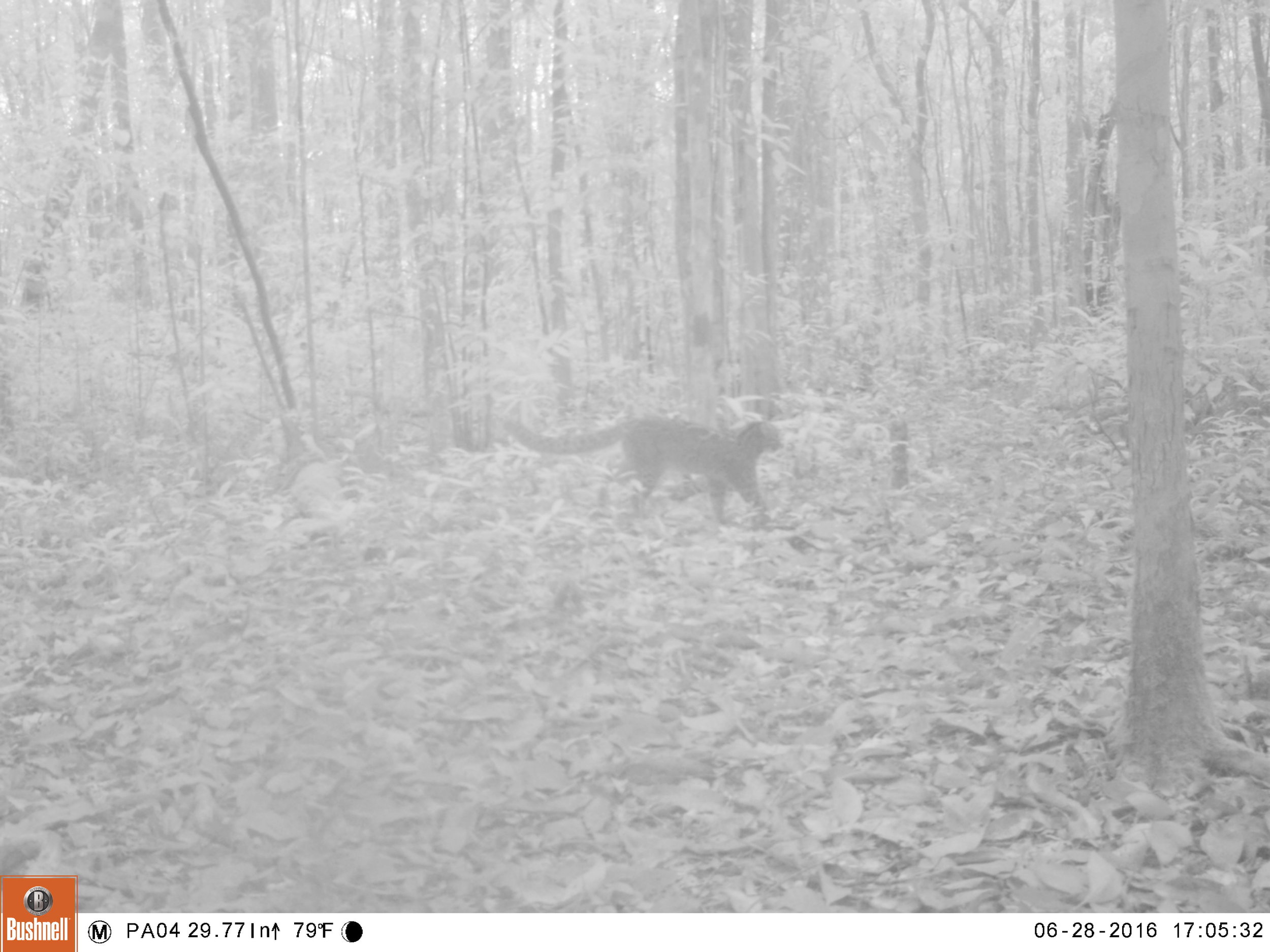
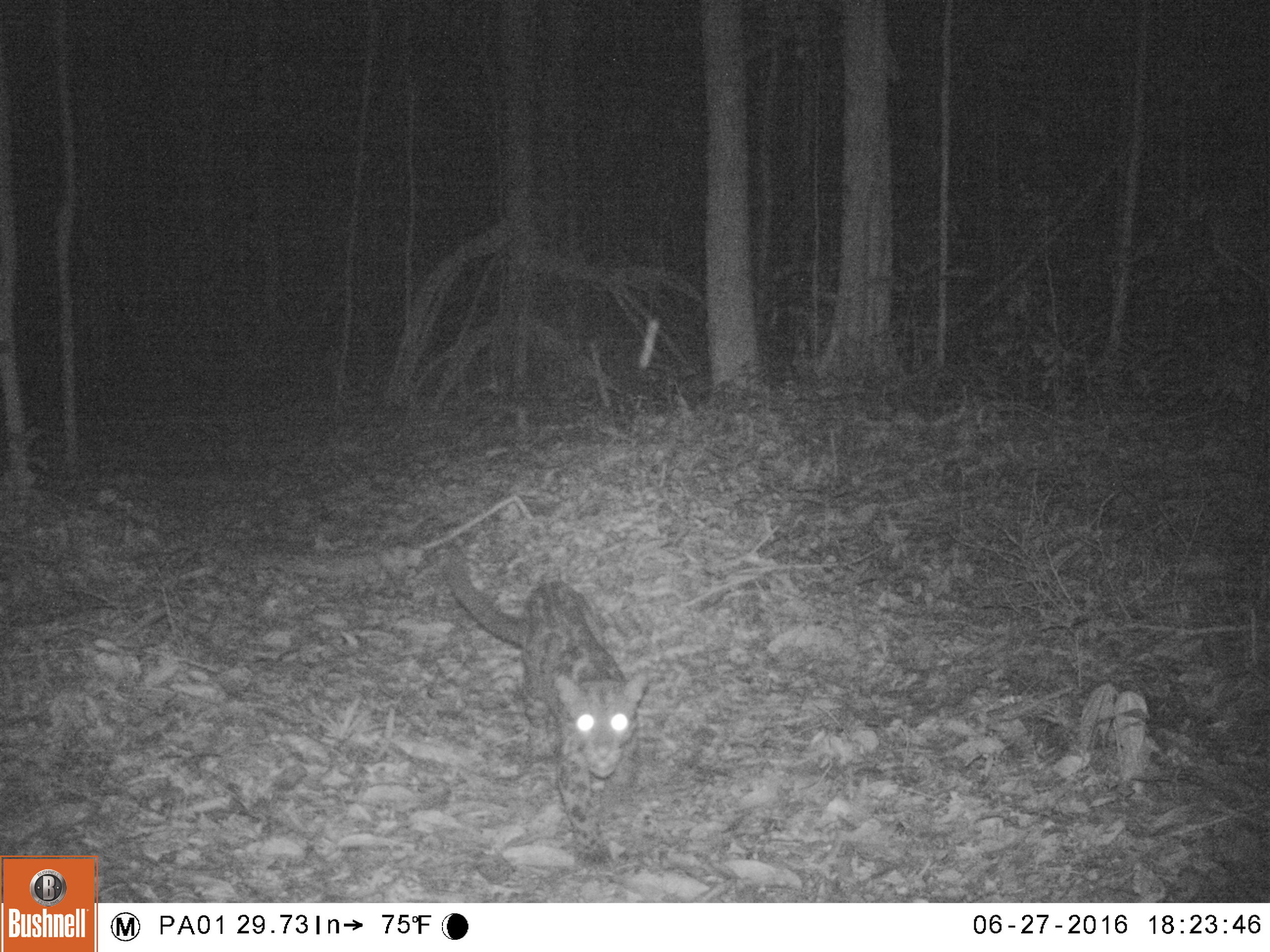
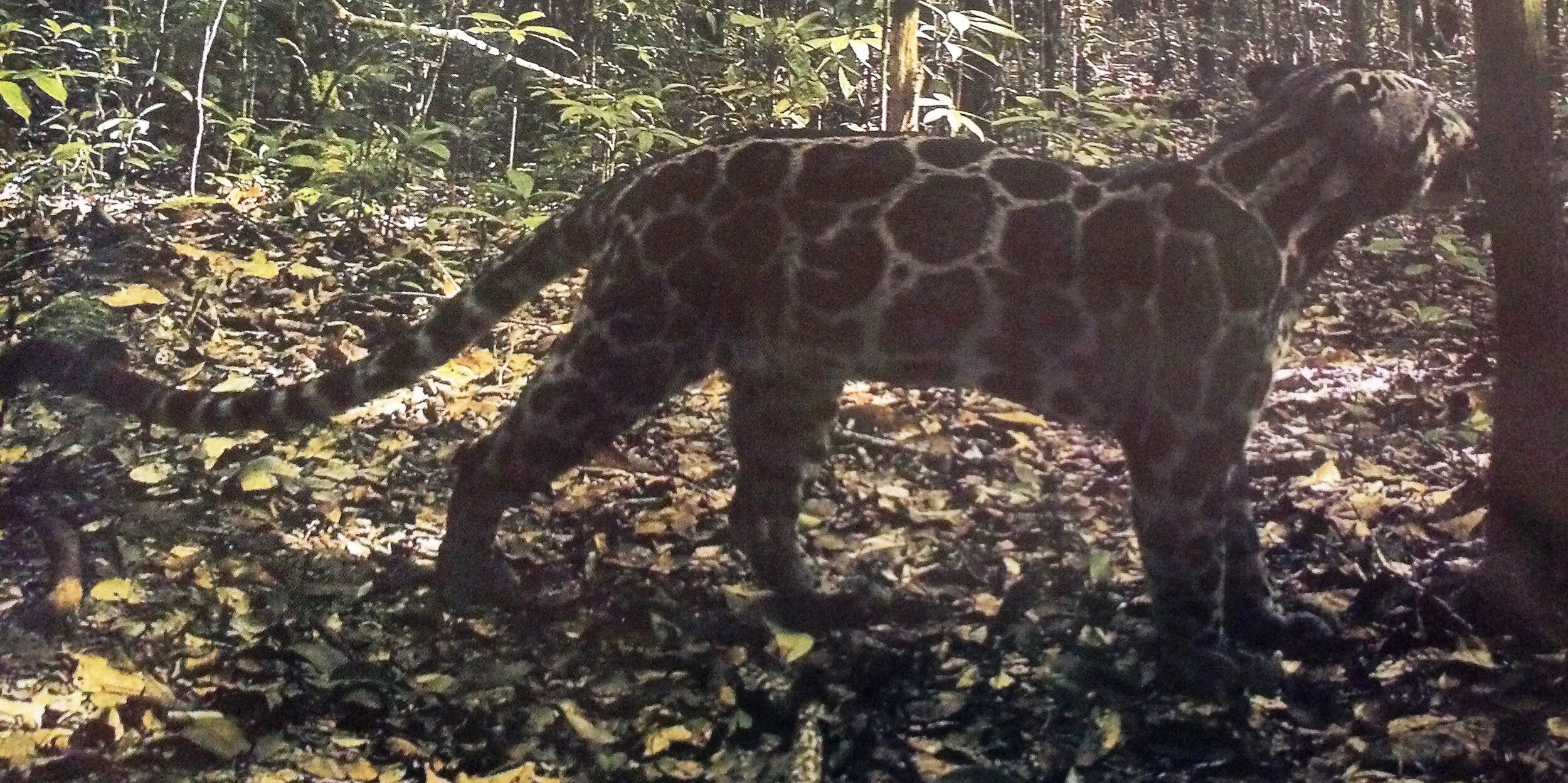
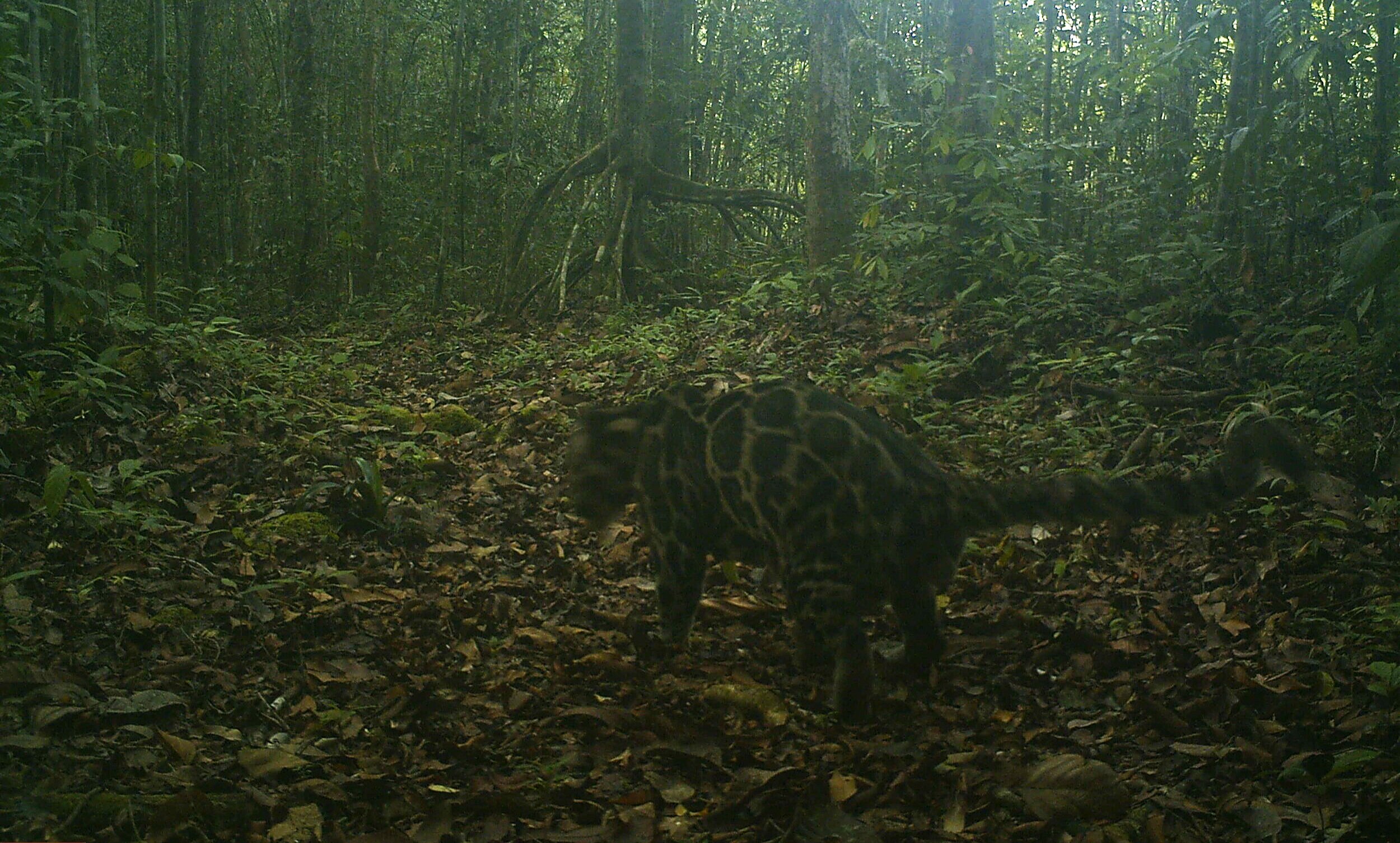
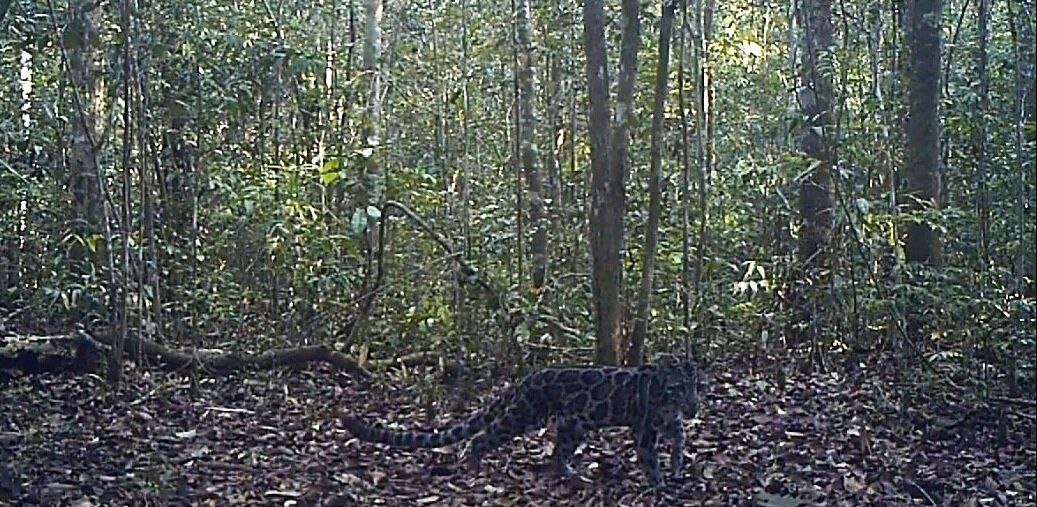
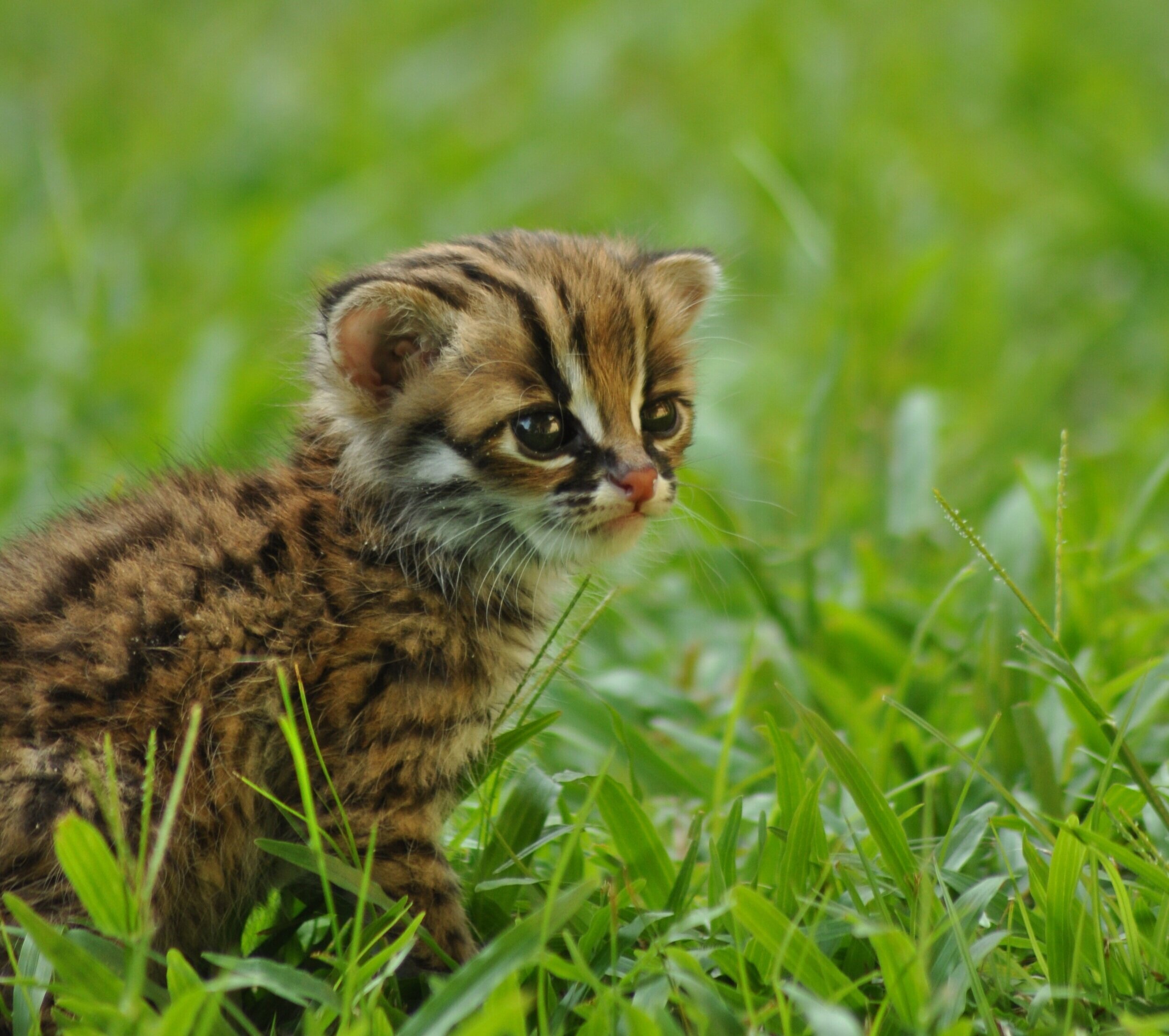
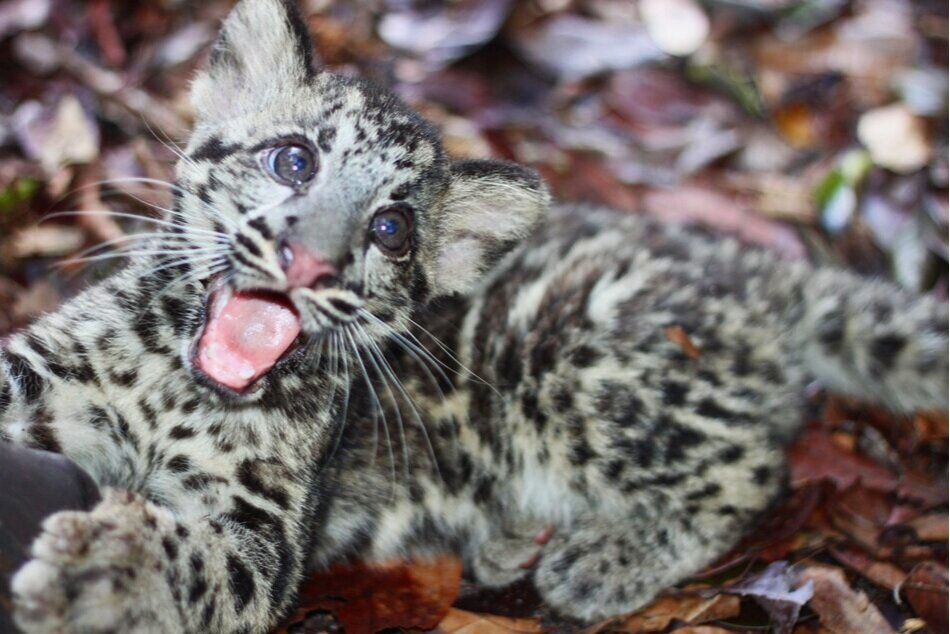
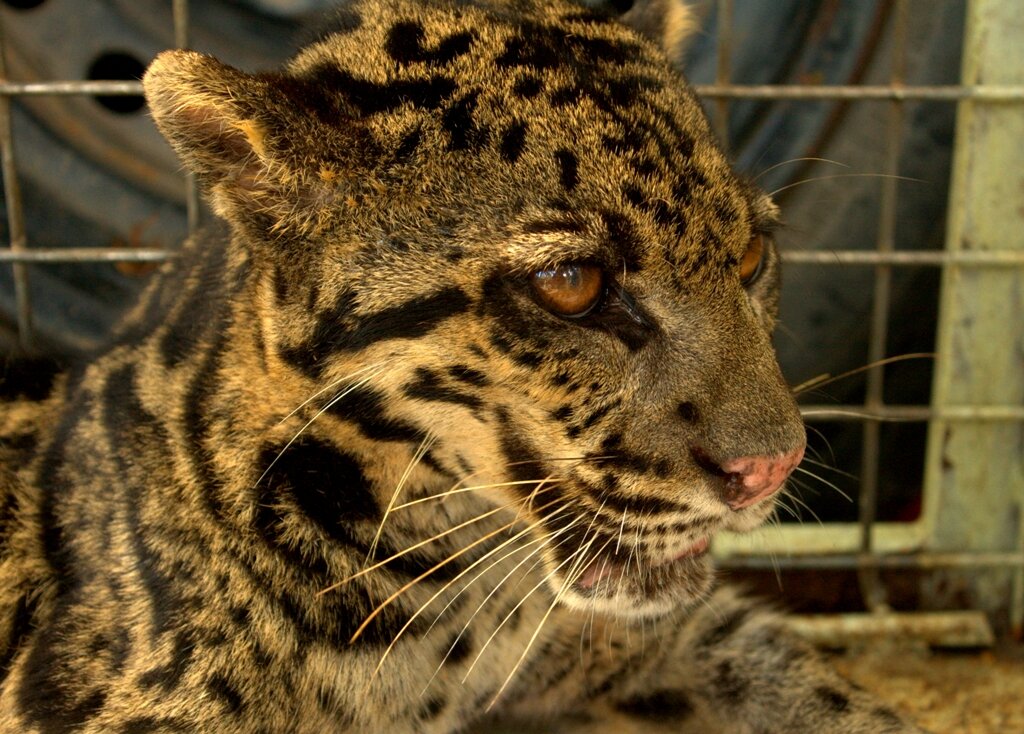
Sunda Clouded Leopard - Neofelis diardi - Like orangutans, this species of leopard is native to the tropical forests of Borneo and Sumatra. Very little is known about the behaviour of these nocturnal and predatory cats due to their elusive nature, however we do know that their canine teeth are longer than any other cat species in relation to their body size, and their long tail helps with balance as they navigate through the tree tops and forest floor.
The main threat to these iconic forest cats is habitat loss; another trait shared with orangutans. Listed as 'Vulnerable' on the IUCN Red List, there are only an estimated 4,500 individuals remaining in the wild.
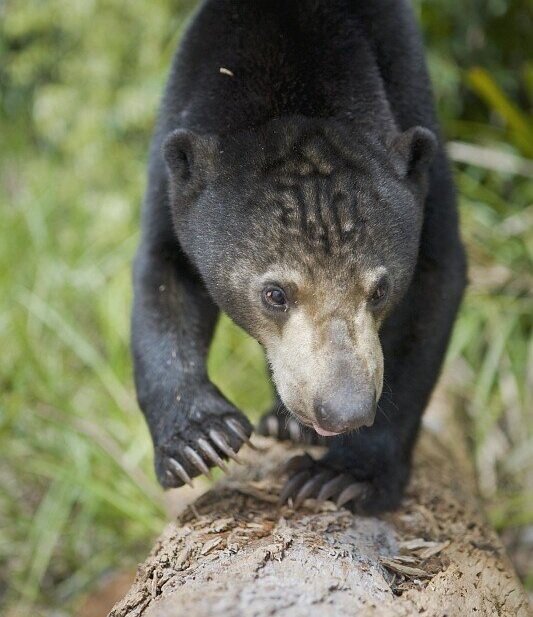
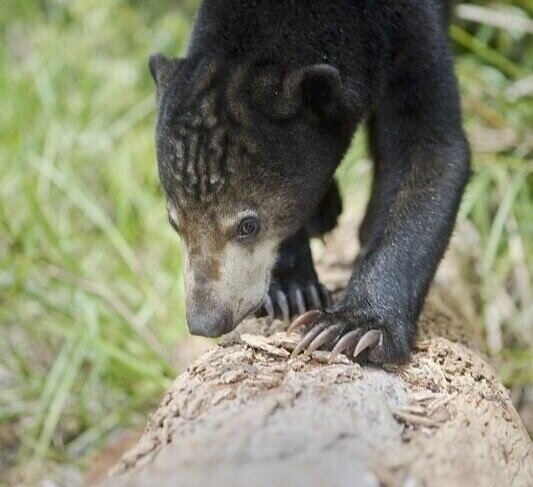
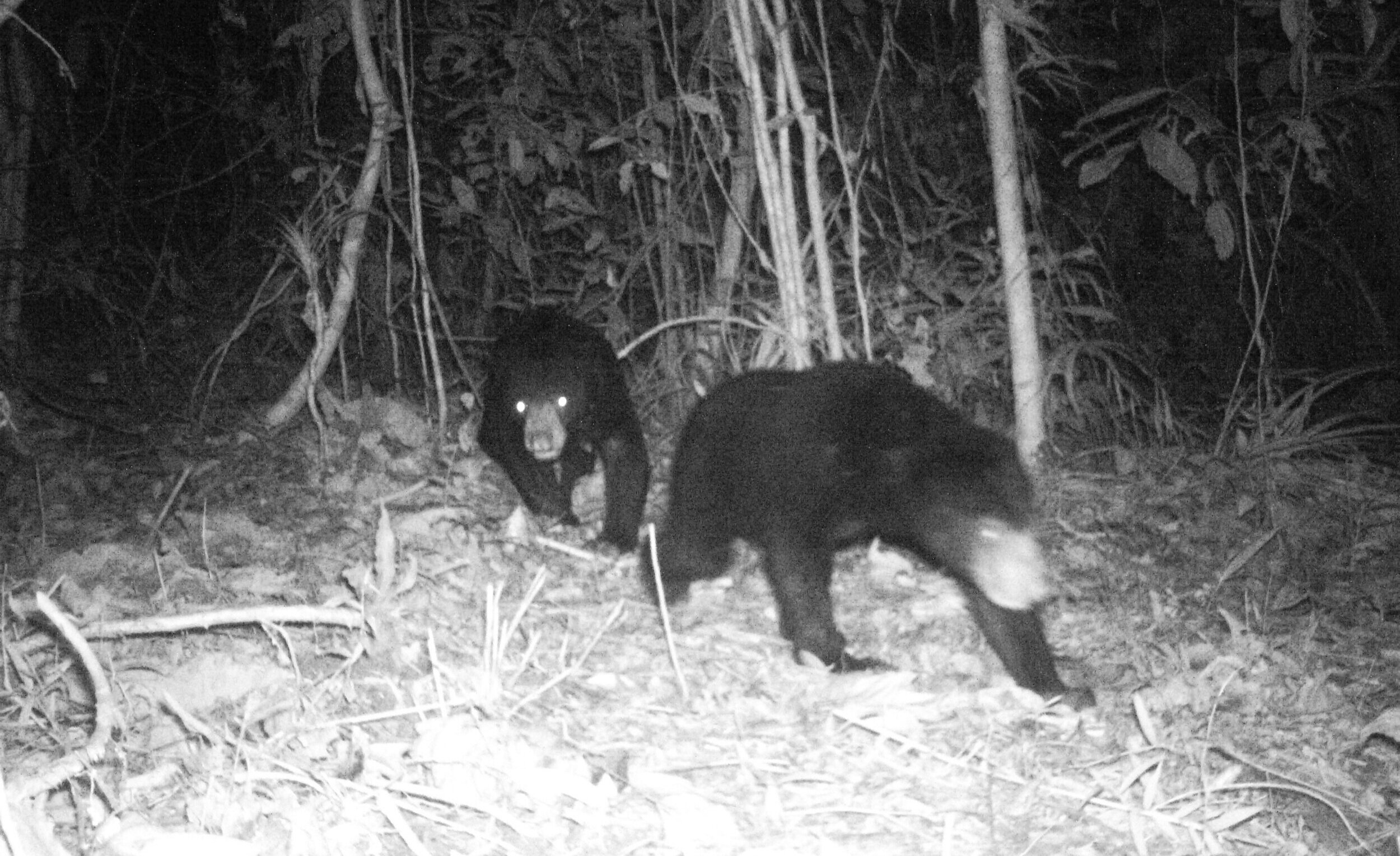
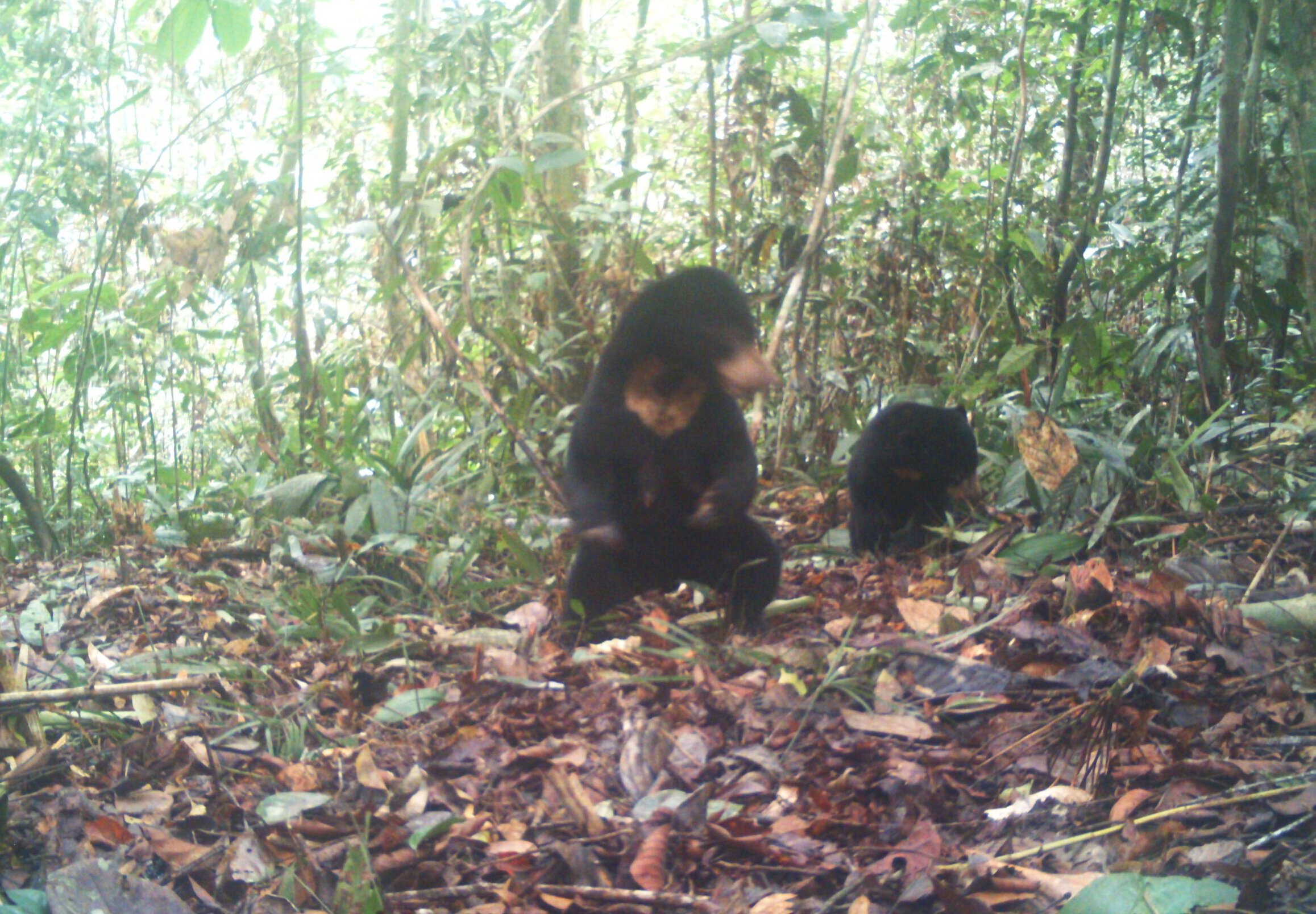
Sun Bear - Helarctos malayanus - This is the only bear found in South East Asia and the smallest of all the 8 bear species. Their smaller size means that they are perfectly suited to an arboreal life and their long claws and tongue are ideal for feeding on insects and honey in the trees.
The name ‘Sun Bear’ comes from the pale patch of fur on their chests which is said to resemble a rising or setting sun. Each pattern is unique like a human fingerprint, helping to distinguish one individual from another.
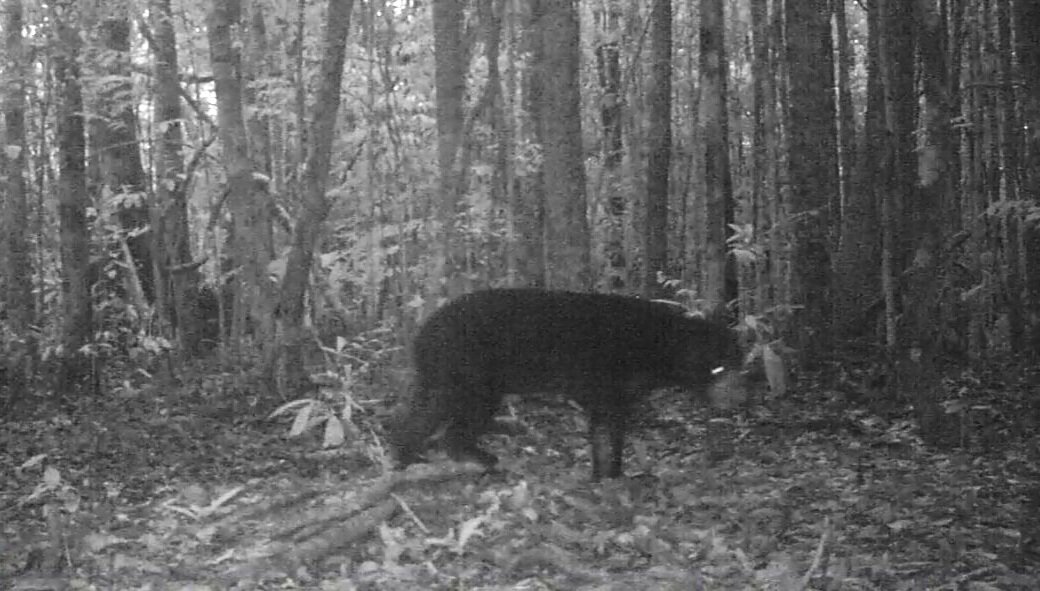
Malayan Civet - Viverra tangalunga - These small omnivorous mammals roam its forest habitat at night in the search for fruit, insects, and anything else it can find to eat. Although largely solitary, it's thought that civets use scent as a way of remotely communicating with one another amongst the dense vegetation by rubbing themselves on trees and the leaves on the forest floor.
Asian Small-clawed Otter - Aonyx cinereus - Rarely observed in the forest’s network of rivers as they tend to search for their food at night, these otters have extremely dexterous hands which are ideal at finding shellfish and crustaceans underwater. Through their high-pitched squeaks the otters can accurately locate one another, and it’s suggested that they can communicate using 12 or more different social calls. These are the smallest of all 13 otter species, but habitat loss and water pollution has impacted their numbers to the extent that they are classified as a species that is ‘Vulnerable’.
Yellow-throated Marten - Martes flavigula - Martens are members of the Mustelidae family (like weasels, ferrets, and badgers), and feast on a variety of food from lizards and bird eggs to fruit and nectar- thought to make them important seed dispersers in the forest. The yellow-throated marten is found throughout wooded areas of South East Asia, and their muscly build and long tail help make them as agile in the canopy as they are on the forest floor.
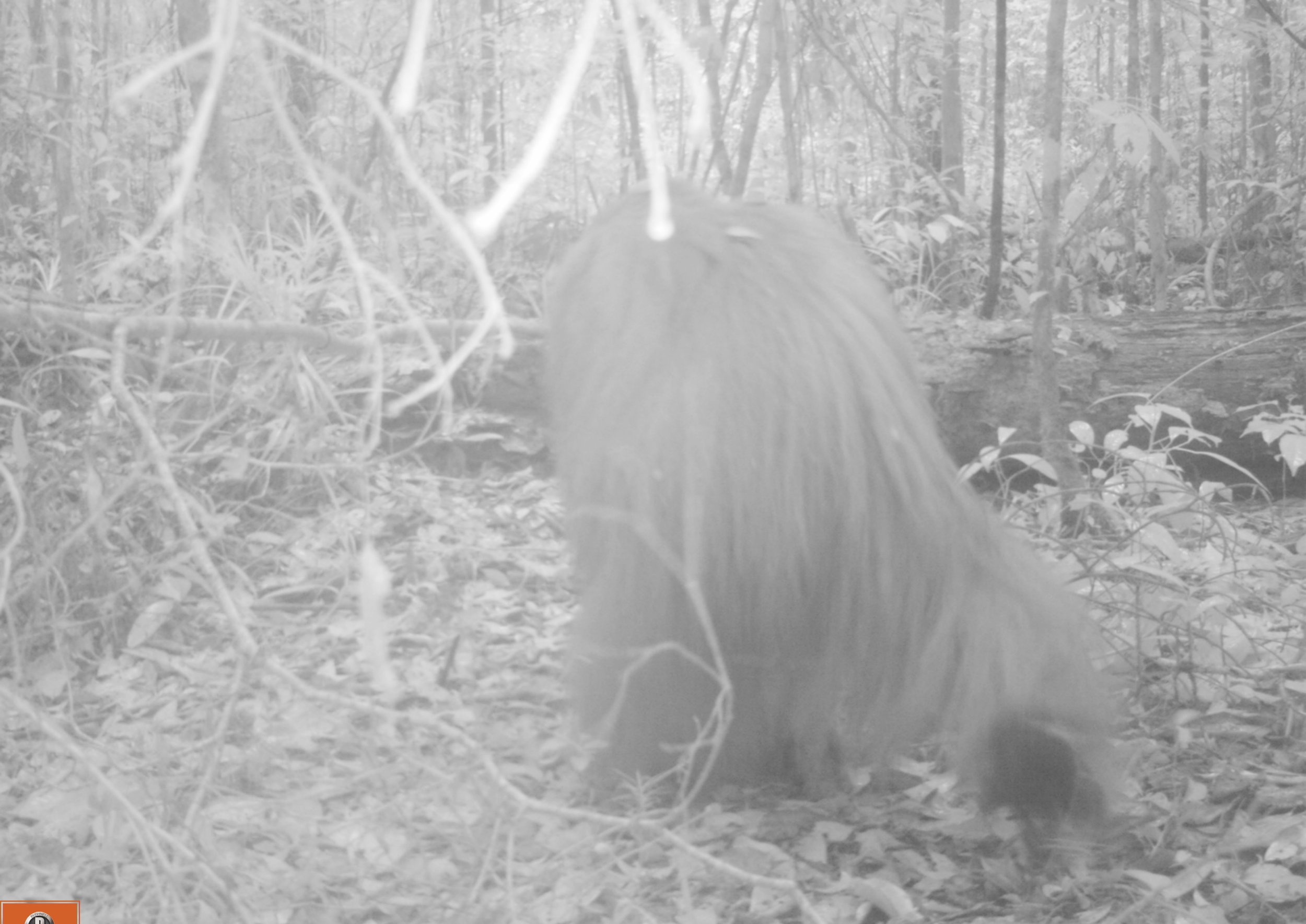
Malayan Porcupine - Hystrix brachyura - This is the largest of the seven porcupine species found in Asia. This species rely on their burrows to stay in during the day, and come out at night to forage for roots, seeds, nuts, and fallen fruit. Malayan porcupines appear to have strong family ties and will often travel in small groups searching for food. They may have few predators in this habitat, but when threatened, porcupines will often charge backwards in the hope that their sharp quills will deter any aggressor.
Bornean Bearded Pig - Sus barbatus - Like other pig species, the Bornean Bearded Pig is omnivorous and will feed on a variety of forest foods. Their long snouts are perfectly evolved to search for worms and tree roots under the soil, and they will also forage for seeds and fruit dropped by animals high up in the canopy. These pigs reach sexual maturity at around 18 months old and usually give birth to between two and four offspring at a time. Piglets have stripy coats to help them camouflage into their surroundings which fade in later life.
Deer - There are a variety of deer found in Borneo, the most commonly observed by our staff are muntjac or barking deer (below centre). With no wild tigers on this tropical island, and clouded leopards and humans being their only predators, deer can thrive in the forest feeding on vegetation. Lesser Mouse Deer (Tragulus kanchil, below left) and the vulnerable Sambar Deer (Rusa unicolor, below right) can also be found in another environment where the Foundation operates in Central Kalimantan, the Belantikan region.








































































































 Vote for Orangutan Foundation -
Vote for Orangutan Foundation -